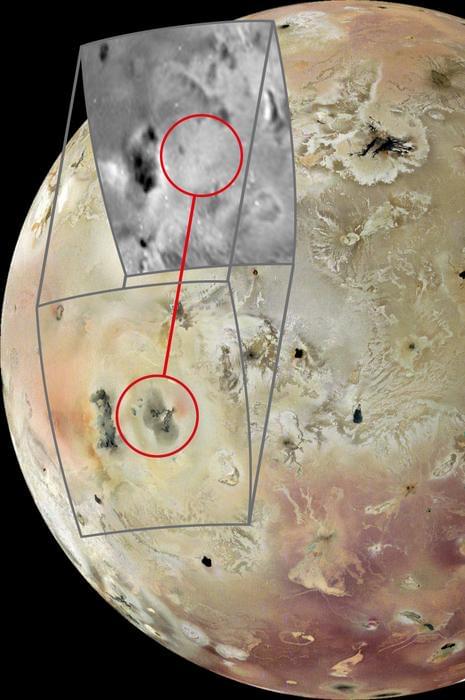
Jupiter’s moon, Io, is the most volcanically active planetary body in the entire solar system as it boasts hundreds of active volcanoes. This number continues to grow as recent study at the Europlanet Science Congress 2024 meeting showed a new active volcano on the small moon taken by NASA’s JunoCam after the spacecraft conducted the first up-close images of Io in more than a quarter of a century.
Not only have Io’s volcanoes been observed to shoot volcanic material hundreds of miles into space, but its lava fields also spread almost as far across its surface due to the much smaller gravity. For example, the volcanic deposits from this new image were observed to encompass an area spanning 180 kilometers by 180 kilometers (112 miles by 112 miles).
“Our recent JunoCam images show many changes on Io, including this large, complicated volcanic feature that appears to have formed from nothing since 1997,” said Dr. Michael Ravine, who is an Advanced Projects Manager at Malin Space Science Systems, Inc, which designed, developed and operates JunoCam for the NASA Juno Project, and is lead author of the study.