There are key moments in the history of every disruptive technology that can make or break its public perception and acceptance. For CRISPR-based genome editing, such a moment occurred 1 year ago—an unsettling push into an era that will test how society decides to use this revolutionary technology.
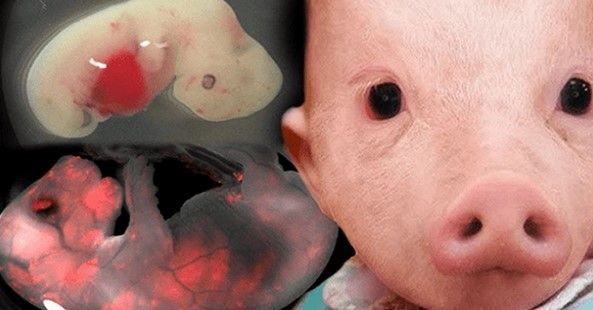
In November 2018, at the Second International Summit on Human Genome Editing in Hong Kong, scientist He Jiankui announced that he had broken the basic medical mantra of “do no harm” by using CRISPR-Cas9 to edit the genomes of two human embryos in the hope of protecting the twin girls from HIV. His risky and medically unnecessary work stunned the world and defied prior calls by my colleagues and me, and by the U.S. National Academies of Sciences and of Medicine, for an effective moratorium on human germline editing. It was a shocking reminder of the scientific and ethical challenges raised by this powerful technology. Once the details of He’s work were revealed, it became clear that although human embryo editing is relatively easy to achieve, it is difficult to do well and with responsibility for lifelong health outcomes.
It is encouraging that scientists around the globe responded by opening a deeper public conversation about how to establish stronger safeguards and build a viable path toward transparency and responsible use of CRISPR technology. In the year since He’s announcement, some scientists have called for a global but temporary moratorium on heritable human genome editing. However, I believe that moratoria are no longer strong enough countermeasures and instead, stakeholders must engage in thoughtfully crafting regulations of the technology without stifling it. In this vein, the World Health Organization (WHO) is pushing government regulators to engage, lead, and act. In July, WHO issued a statement requesting that regulatory agencies in all countries disallow any human germline editing experiments in the clinic and in August, announced the first steps in establishing a registry for future such studies.