Category: futurism – Page 761

Our Anxiety Level Should Decrease As The Day Goes On. For Some People, It Doesn’t
“At healthy levels, worry can help us anticipate threats and prepare for the future,” says Rebecca C. Cox, the lead author of the research from the Department of Integrative Psychology, University of Colorado, Boulder. “Worry can become a cause for concern if the frequency or intensity of the worry is disproportionate to the source of the worry. If I’m so worried about an upcoming test that I can’t focus on studying, or I’m so frequently worried about storms that I don’t leave my house, then worry has crossed into a problematic range.”
According to previous research, in those with generalized anxiety disorder, worry may function to keep anxiety at a high but predictable level to avoid experiencing an unexpected shift in emotion.
To** **investigate this on a day-to-day level, Cox and her team asked participants to respond to daily survey prompts in the morning, afternoon, and evening to indicate how anxious they felt in that moment. This method, called ecological momentary assessment, is often employed by psychologists to measure emotions in real-time.
Full Story:
New research suggests excessive worrying does more harm than good.
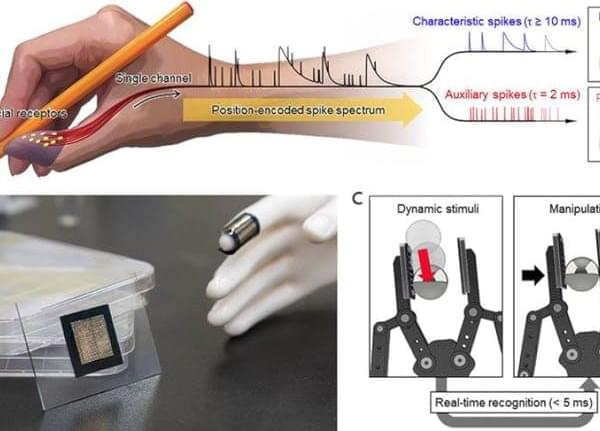
Scientists Have Discovered an Exotic Magnetic State of Matter
Scientists identify a long-sought magnetic state predicted nearly 60 years ago.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered a long-predicted magnetic state of matter called an “antiferromagnetic excitonic insulator.”
“Broadly speaking, this is a novel type of magnet,” said Brookhaven Lab physicist Mark Dean, senior author on a paper describing the research just published in Nature Communications. “Since magnetic materials lie at the heart of much of the technology around us, new types of magnets are both fundamentally fascinating and promising for future applications.”


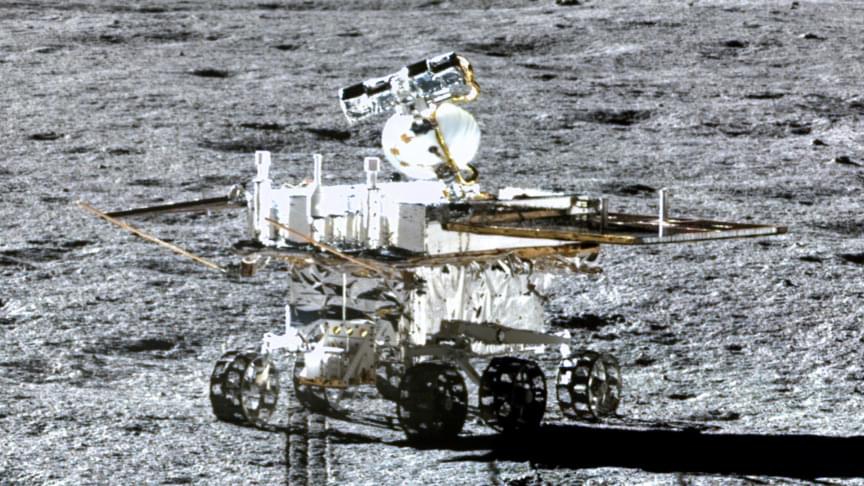
China found mysterious glass spheres on the Moon. Are they a window into its past?
Glass isn’t uncommon on the Moon. But these spheres are.
China’s Yutu-2 lunar rover on a mission to find out more about the far side of the Moon has made a startling new discovery. It has found mysterious glass spheres that may have captured within them important information about the Moon’s composition and history of its impact events, * Science Alert* reported.
Originally scheduled to be operational on the lunar surface for just three months, the Yutu-2 now holds the record of being the longest operational rover on the Moon. When it landed in 2019, it became the first rover to reach the far side of the Moon and has since been providing us insights about the side we cannot see from Earth. Last month, we learned that the soil on the far side is a lot stickier, and now there is the mystery of the glass spheres on the Moon aren’t a new finding. But the nature of these spheres makes them interesting and possibly a gateway for future missions.