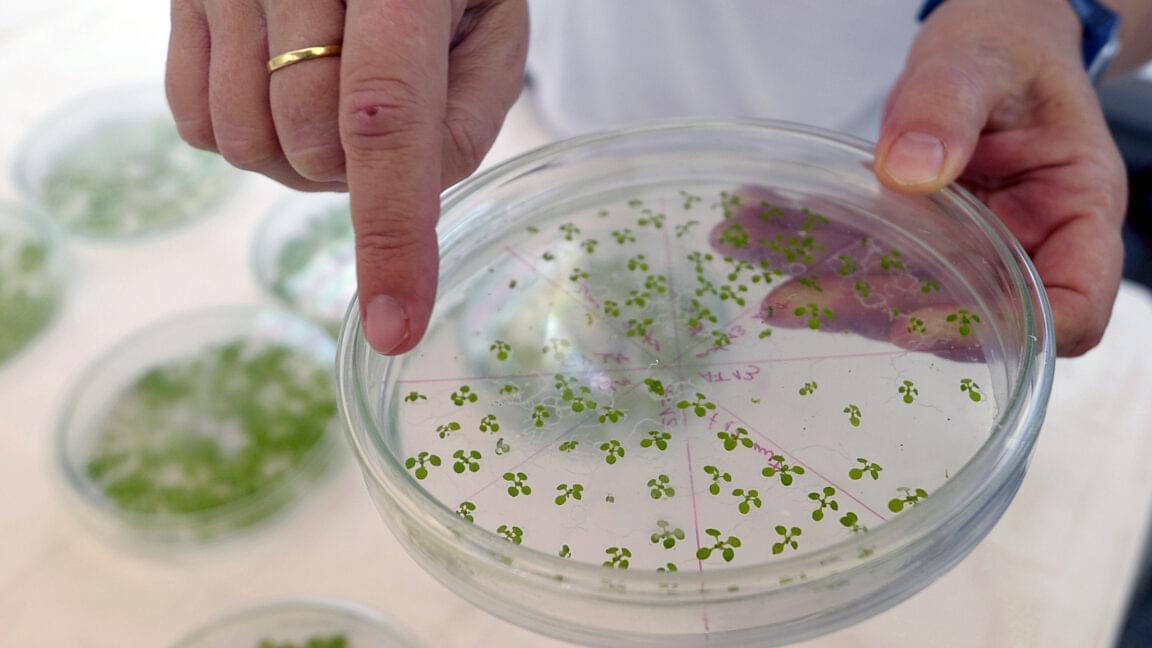
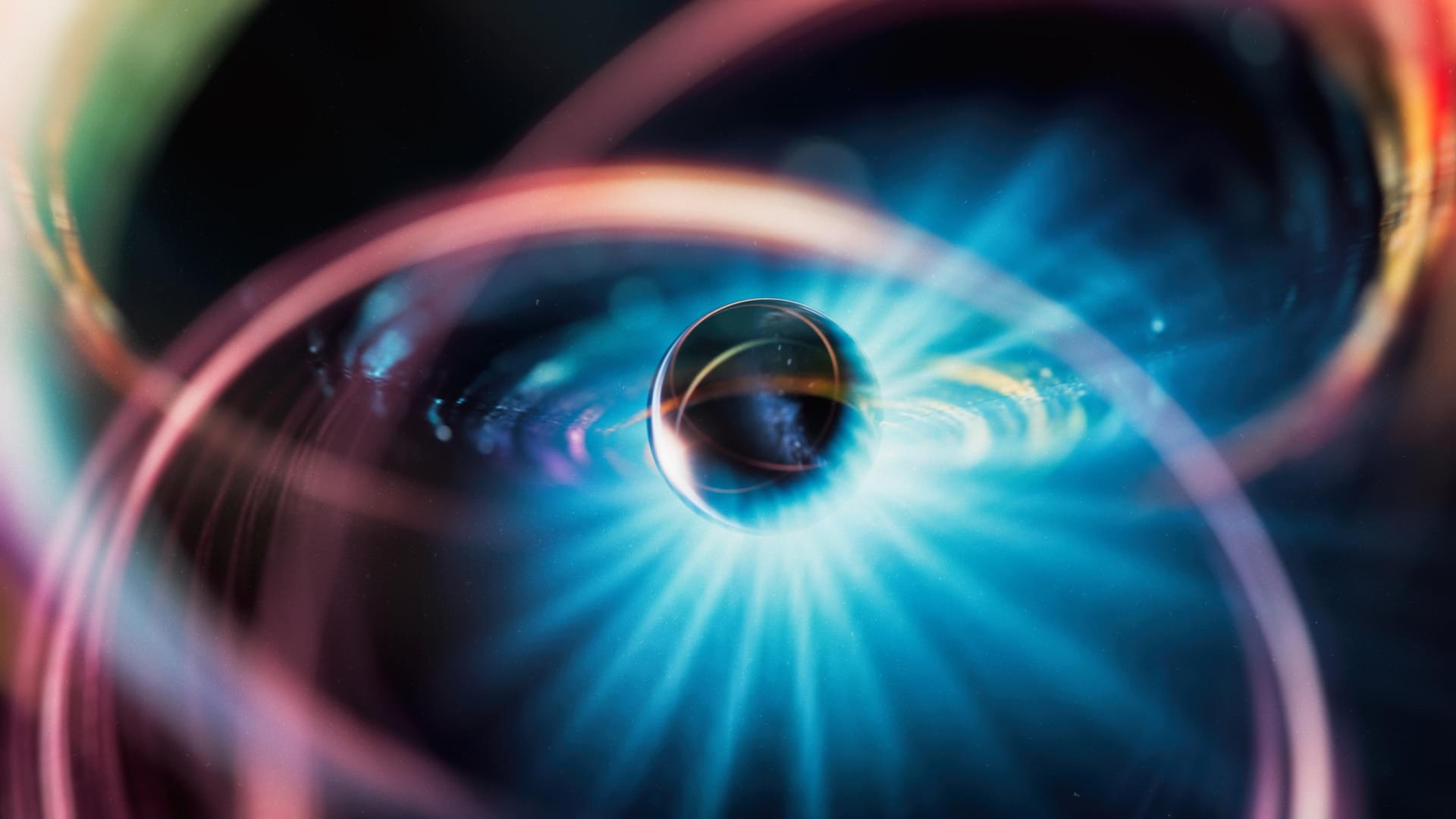
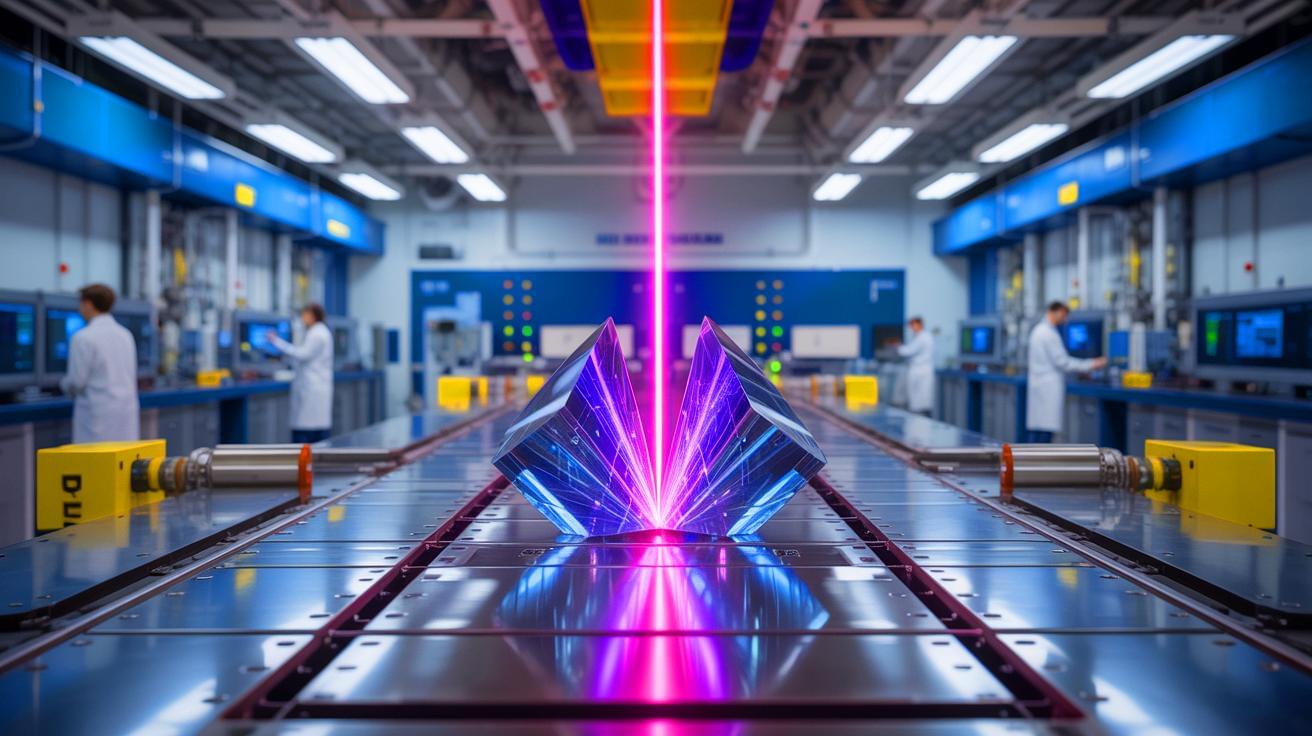
In a remarkable leap for high-power laser technology, the University of Michigan’s ZEUS facility has achieved a significant milestone. Funded by the National


Sorry to interrupt, but our fundraiser won’t last long.
This Tuesday, we ask you to join the 2% of readers who give. If everyone reading this right now gave just $2.75, we’d hit our goal quickly. $2.75 is all we ask.


In an era of heightened geopolitical uncertainty, shifting supply chains, and growing decarbonisation challenges, the Council’s role in fostering transparency, cooperation, and pragmatic transition pathways has never been more vital.
About Crescent Petroleum
Crescent Petroleum is the first and largest private exploration and production company in the Middle East, with over 53 years of experience as an international operator in numerous countries including Egypt, Yemen, Canada, Tunisia, and Argentina, in addition to its continuing operations in the United Arab Emirates and Iraq.
Maglev momentum: Why Asia speeds ahead while Western high-speed projects derail.
Smooth, fast, and futuristic. Maglev trains are transforming Asia’s mobility while the West struggling to keep up. Find out why.
How technological.
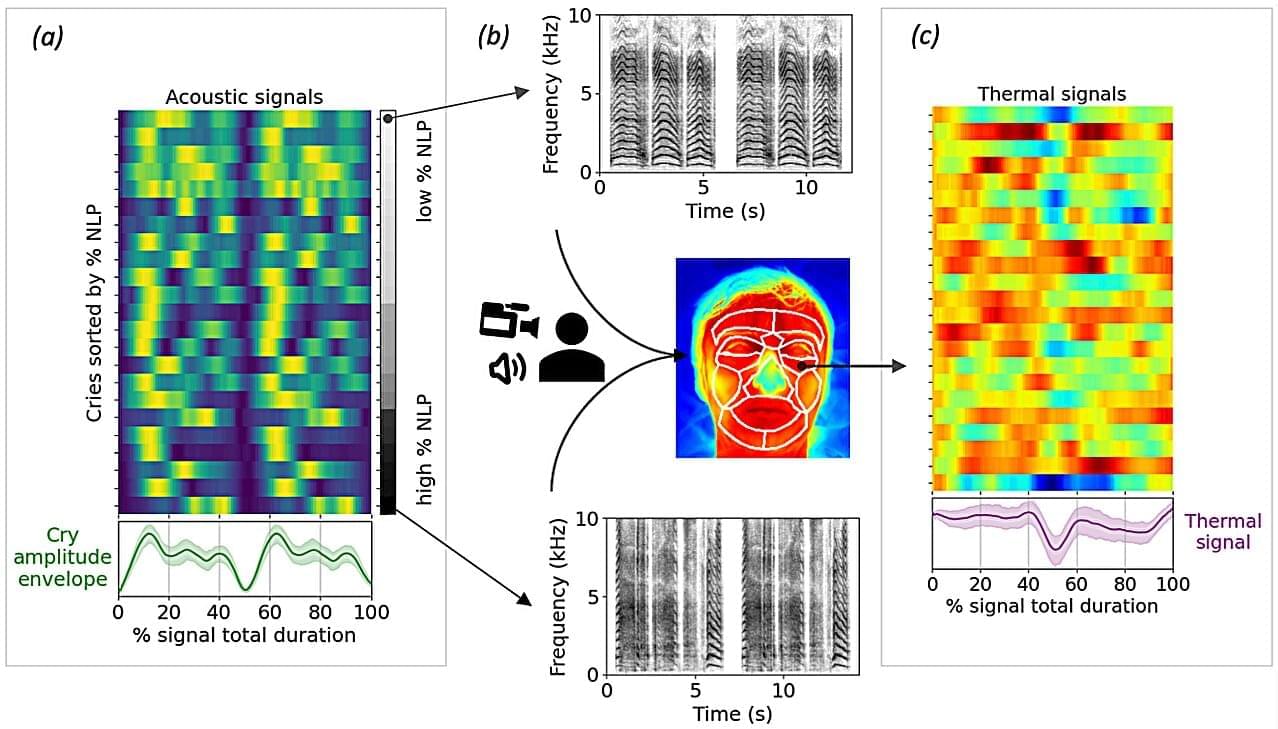
Hearing a baby cry can trigger a range of responses in adults, such as sympathy, anxiety and a strong urge to help. However, new research suggests that a deeper physical reaction is also occurring. A baby’s cry, particularly if it is in pain or distress, makes our faces physically warmer.
Since they can’t speak yet, babies cry to communicate their needs, whether they’re in pain or want some attention. When a baby is in distress, they forcefully contract their ribcage, which produces high-pressure air that causes their vocal cords to vibrate chaotically. This produces complex disharmonious sounds known as nonlinear phenomena (NLP).
To study how adults respond to crying babies, scientists played 23 different recordings to 41 men and women with little to no experience with young infants. At the same time, a thermal infrared imaging camera measured subtle changes to their facial temperatures. A rise in temperature in this part of the body is governed by the autonomic nervous system, a network of nerves that controls unconscious processes such as breathing and digestion. After each cry, the participants rated whether the baby was in discomfort or in pain.


