Time depends on speed and mass, which means it’s not as consistent as we think.


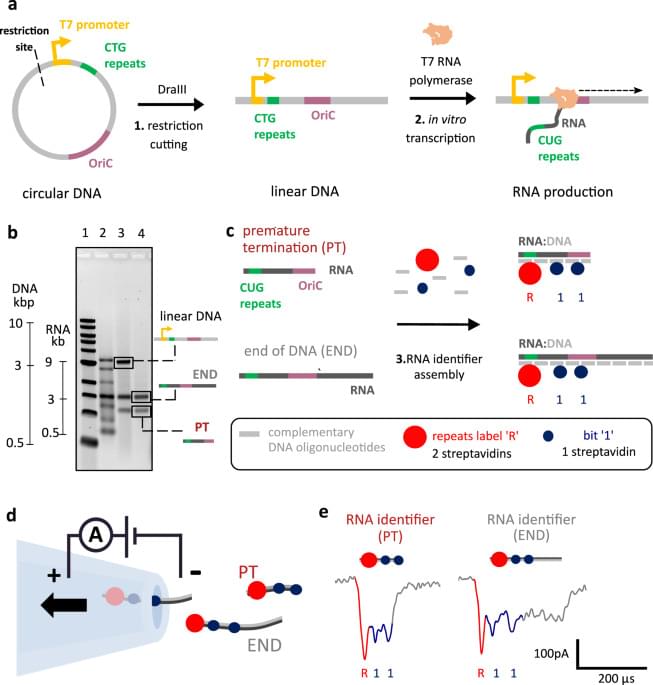
The development of RNA technologies demands accurate assessment of transcript size and heterogeneity. Here, authors report a nanopore-based approach to study full-length RNA transcripts at the single-molecule level, identify premature transcription termination and study rolling-circle transcription.






In a vacuum like space, the speed of light is just over 186,280 miles per second. Scientists have now shown it’s possible to slow it down to zero miles per second without sacrificing its brightness, regardless of its frequency or bandwidth.