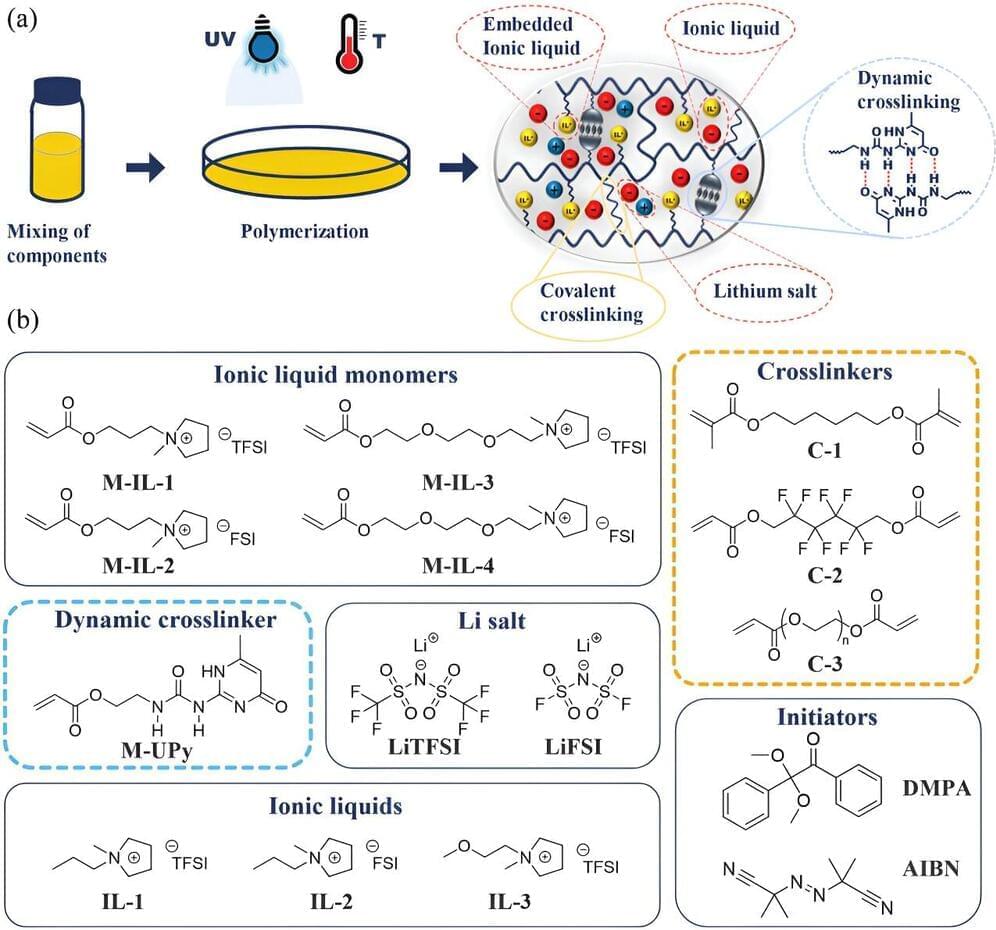
In the digital realm, secrets (API keys, private keys, username and password combos, etc.) are the keys to the kingdom. But what if those keys were accidentally left out in the open in the very tools we use to collaborate every day?
A Single Secret Can Wreak Havoc
Imagine this: It’s a typical Tuesday in June 2024. Your dev team is knee-deep in sprints, Jira tickets are flying, and Slack is buzzing with the usual mix of cat memes and code snippets. Little do you know, buried in this digital chatter is a ticking time bomb – a plaintext credential that gives unfettered access to your company’s crown jewels.