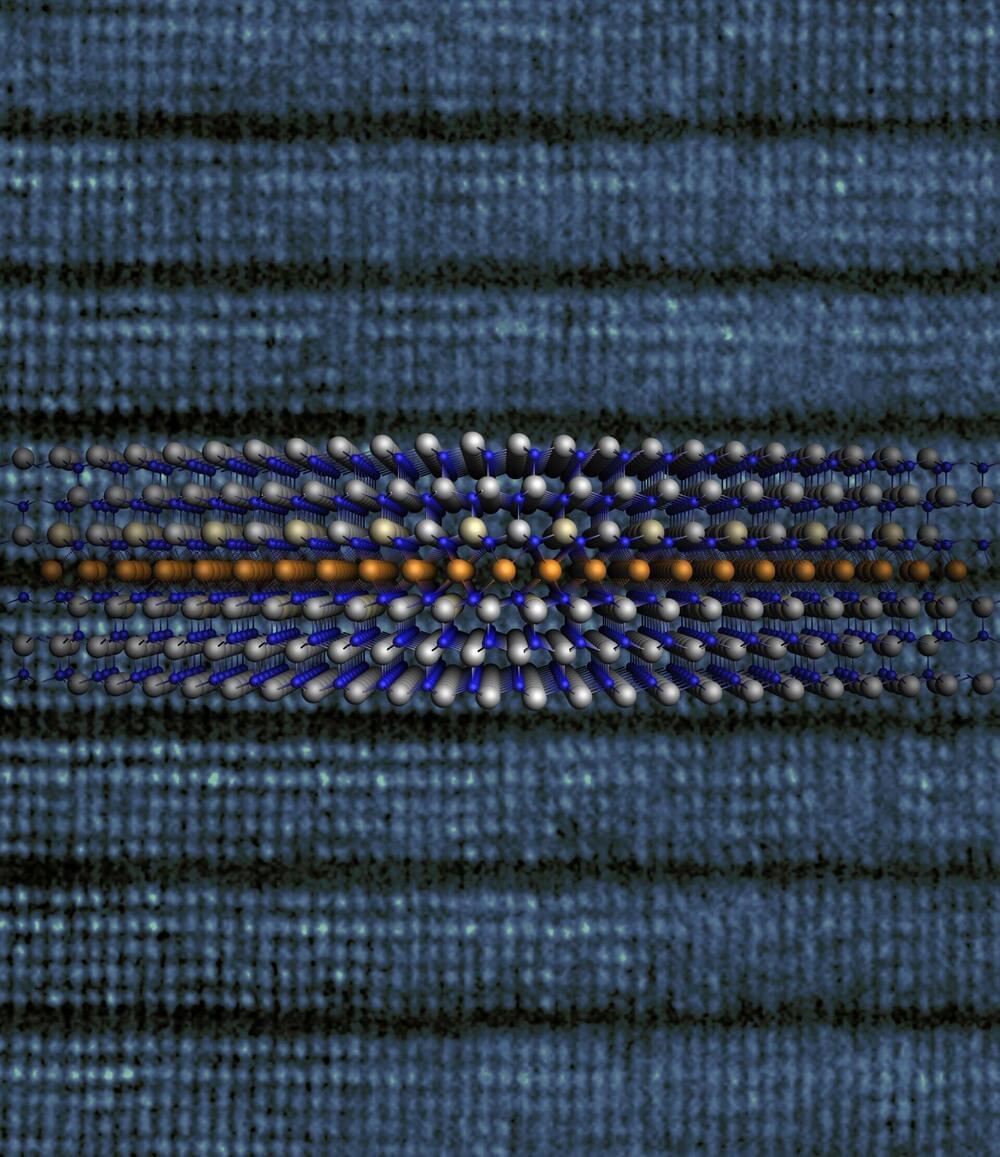
A new study reveals that oxide membranes can confine infrared light to a greater extent than traditional methods, promising advancements in imaging resolution and applications in photonics and thermal management.
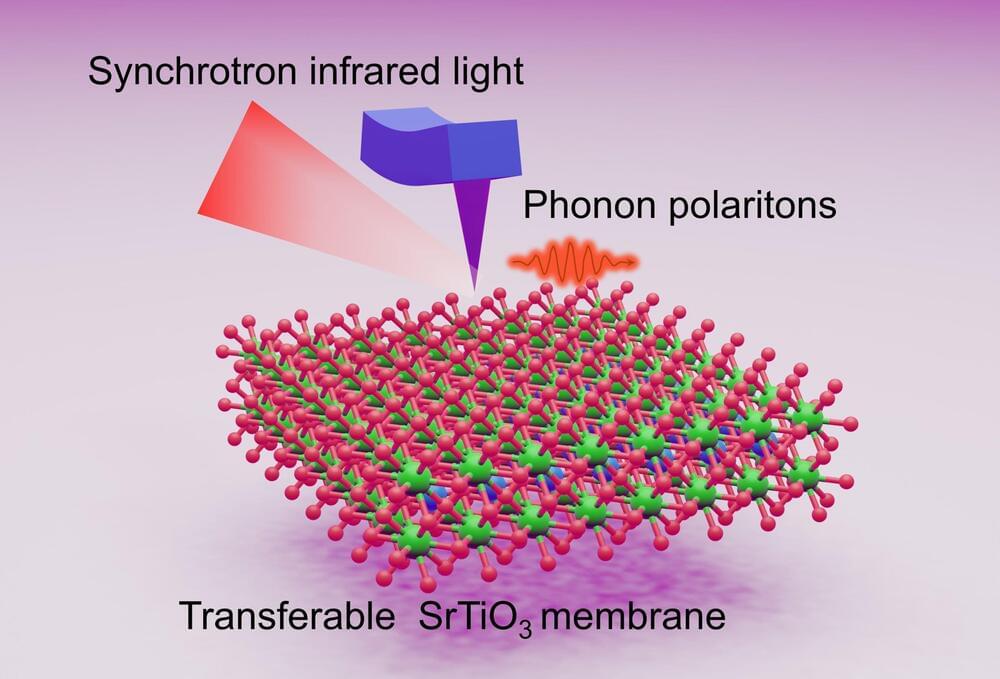
Researchers have successfully shown that a particular type of oxide membranes can effectively confine, or “squeeze,” infrared light. This breakthrough could enhance future infrared imaging technologies. These thin-film membranes outperform traditional bulk crystals in confining infrared light.
“The thin-film membranes maintain the desired infrared frequency, but compress the wavelengths, allowing imaging devices to capture images with greater resolution,” says Yin Liu, co-corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at North Carolina State University.