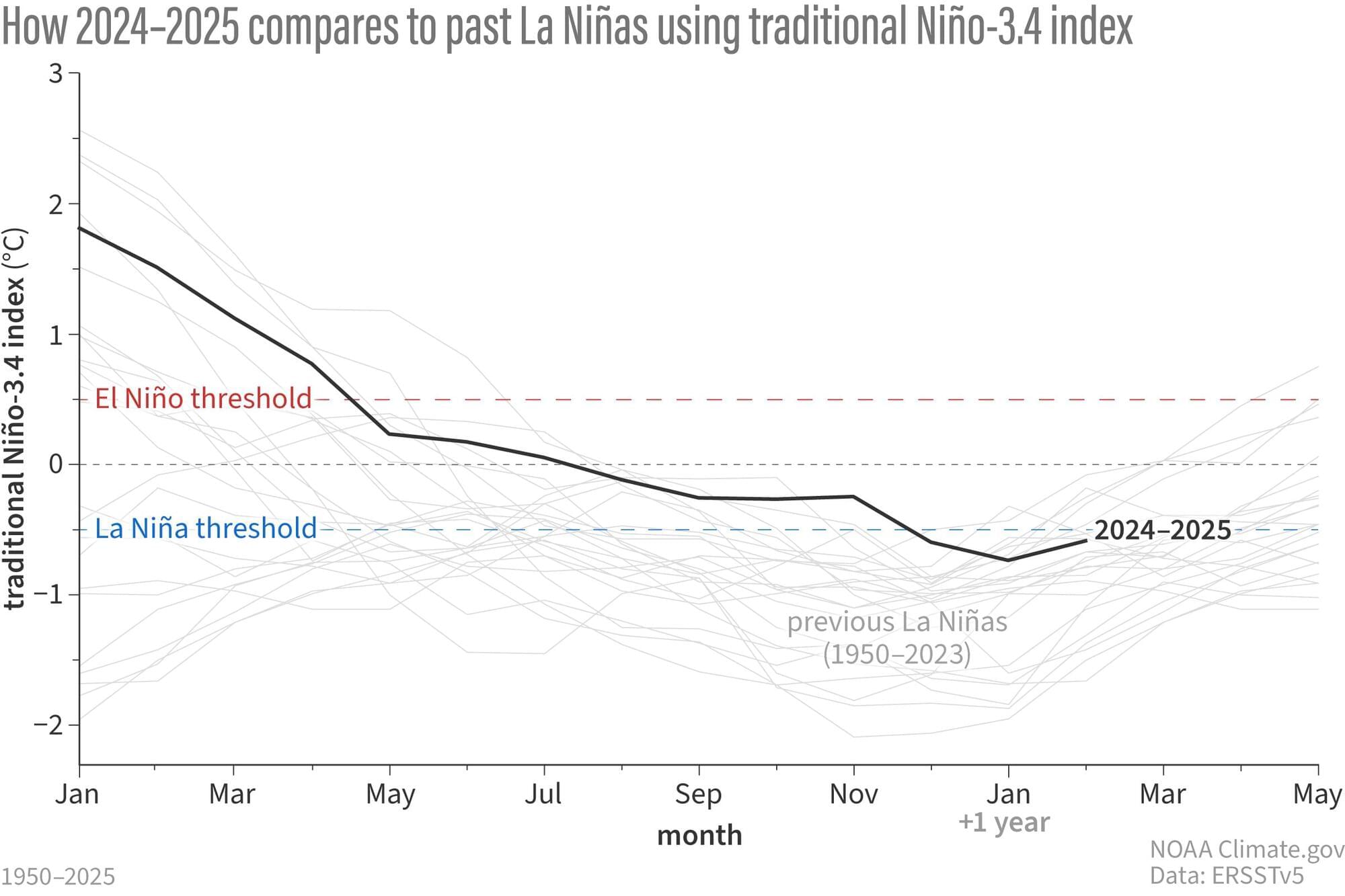
La Niña conditions are waning, and a transition to ENSO-neutral is favored in the next month.



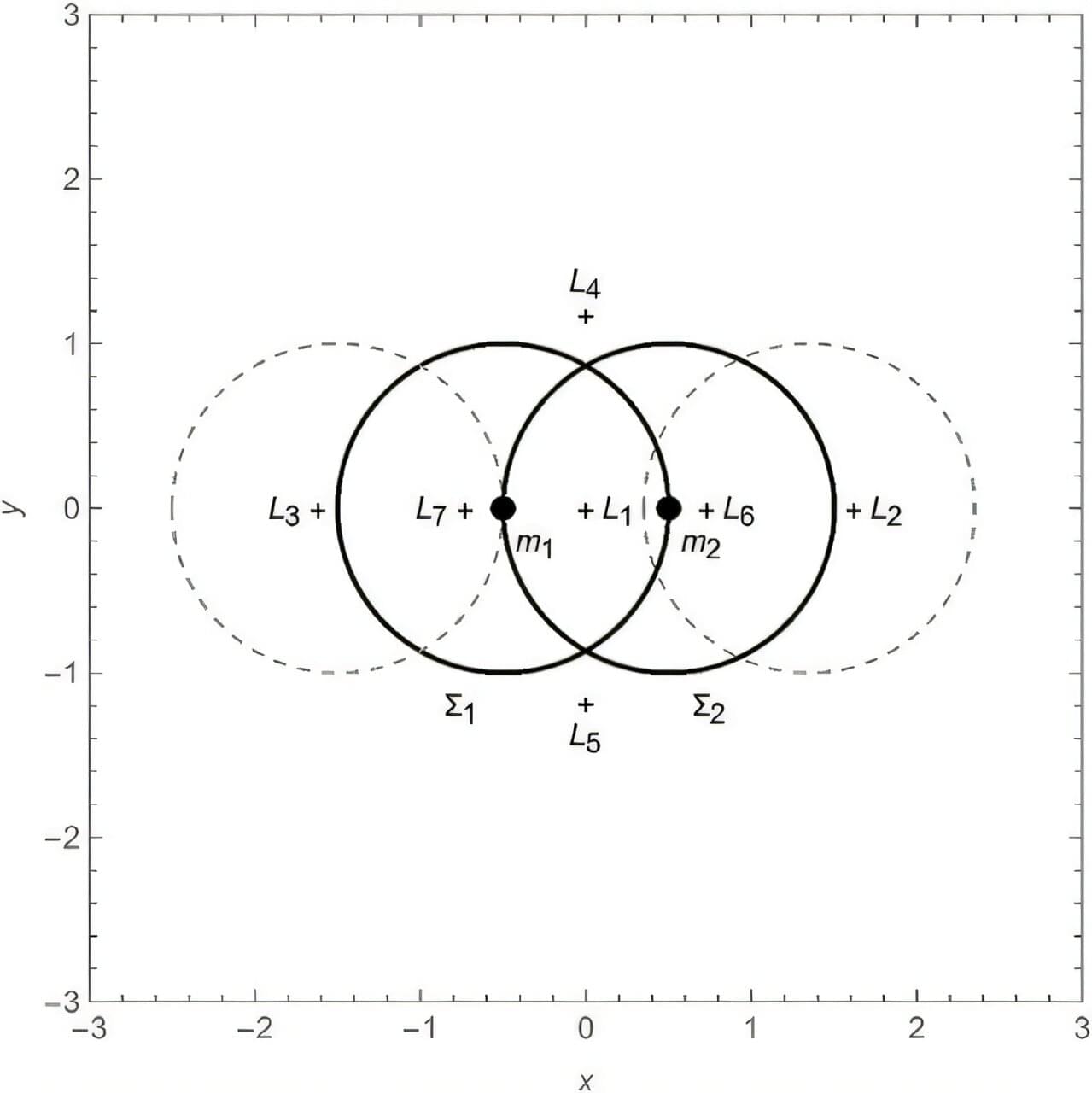
In the realm of science fiction, Dyson spheres and ringworlds have been staples for decades. But it is well known that the simplest designs are unstable against gravitational forces and would thus be torn apart. Now a scientist from Scotland, UK has shown that certain configurations of these objects near a two-mass system can be stable against such fractures. The work is published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.

University allocates funding and contact point for U.S. scholars looking to relocate to Brussels