Malicious PyPI package rerouted MEXC crypto orders and exposed API keys, downloaded 1,065 times.


*This video was recorded at Foresight’s Vision Weekend 2025 in Puerto Rico*https://foresight.org/vw2025pr/Our Vision Weekends are the annual festivals of For…

🧬 What keeps your cells from dividing at the wrong time? In this video, we dive into the world of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs) — the master regulators of the cell cycle.
📌 Here’s what you’ll learn:
What CDKs are and how they function.
The role of cyclins in activating CDKs.
Key cell cycle checkpoints (G1, G2, M)
How CDK-cyclin complexes regulate progression through each phase.
They just want to save science! But not from the people actually defunding it.
Go to https://ground.news/skeptic to get all sides of every story. Subscribe through my link to save 40% off unlimited access.
Here I annoy you by telling you about the threats to science and the people who have made a career of ignoring them. “The War On Science” will be out soon, and Sabine Hossenfelder, Lawrence Krauss, Richard Dawkins, Gad Saad, and many others are excited. I, an intellectual, will perhaps k_m_s.
This video was researched and co-written by Hemant Mehta.
Follow and support Hemant:
friendlyatheist.com.
Hemant’s channel:

GPT‑4.1, GPT‑4.1 mini, and GPT‑4.1 nano are available now to all developers.
Through efficiency improvements to our inference systems, we’ve been able to offer lower prices on the GPT‑4.1 series. GPT‑4.1 is 26% less expensive than GPT‑4o for median queries, and GPT‑4.1 nano is our cheapest and fastest model ever. For queries that repeatedly pass the same context, we are increasing the prompt caching discount to 75% (up from 50% previously) for these new models. Finally, we offer long context requests at no additional cost beyond the standard per-token costs.

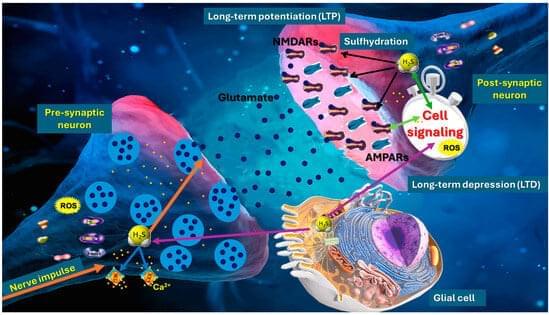
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has emerged as a pivotal gaseous transmitter in the central nervous system, influencing synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory by modulating various molecular pathways. This review examines recent evidence regarding how H2S regulates NMDA receptor function and neurotransmitter release in neuronal circuits. By synthesizing findings from animal and cellular models, we investigate the impacts of enzymatic H2S production and exogenous H2S on excitatory synaptic currents, long-term potentiation, and intracellular calcium signaling. Data suggest that H2S interacts directly with NMDA receptor subunits, altering receptor function and modulating neuronal excitability. Simultaneously, H2S promotes the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA, shaping synaptic dynamics and plasticity.