The Apple store in Dubai has the coolest windows.


The Apple store in Dubai has the coolest windows.
The future of advertising is here.
Holographic advertisements are here.

Hyper-Reality presents a provocative and kaleidoscopic new vision of the future, where physical and virtual realities have merged, and the city is saturated in media. If you are interested in supporting the project, sponsoring the next work or would like to find out more, please send a hello to [email protected] by Keiichi Matsuda | km.cx
More at hyper-reality.co
Hardly a day has gone by this month without the announcement of a new virtual reality (VR) camera system. Facebook, Google and GoPro all aim to make VR more immersive with new cameras, some of which won’t be commercially released for the foreseeable future. However, researchers at Adobe believe that you may not need new camera hardware at all for a big leap in immersion.
Adobe’s head of research Gavin Miller is going to present new cutting-edge technology at NAB in Las Vegas this Tuesday that could one day be used to turn flat, monoscopic 360-degree videos shot with consumer-grade spherical cameras into fully immersive VR video, complete with the ability to lean into the video — something that’s being called six degrees of freedom (6DoF) among industry insiders.
The difference between monoscopic 360-degree video and VR experiences offering six degrees of freedom is especially important for users of high-end VR headsets like the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive. These headsets offer room-scale tracking, which means that the headset knows where in the room the viewer is, accurately translating a motion like “leaning forward” into corresponding visuals.

This mesh screen blocks pollution from entering your home.

It’s at the opening evening reception. I’m also giving a formal 45-min talk tomorrow at 1:30PM. Join me at the Santa Clara Marriot in San Jose for the convention. https://ca.lp.org/speakers/ www.zoltanistvan.com
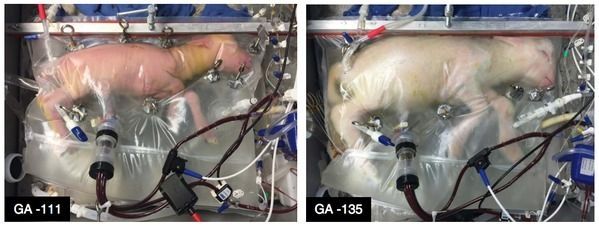
Many people thought I was way too optimistic with my prediction (read the Popular Science article) about artificial wombs in 2004 with my Vice Motherboard story (which went viral). It turns out the tech is coming sooner than many imagined. Enjoy! http://www.popsci.com/artificial-womb-science-fiction #transhumanism
A bag-like device kept lamb fetuses alive longer than anything else has before. What does that mean for human pregnancy? Read on.