When targeted by a high-energy laser that generates pressures over one million atmospheres, carbon samples melt at around 6700K.


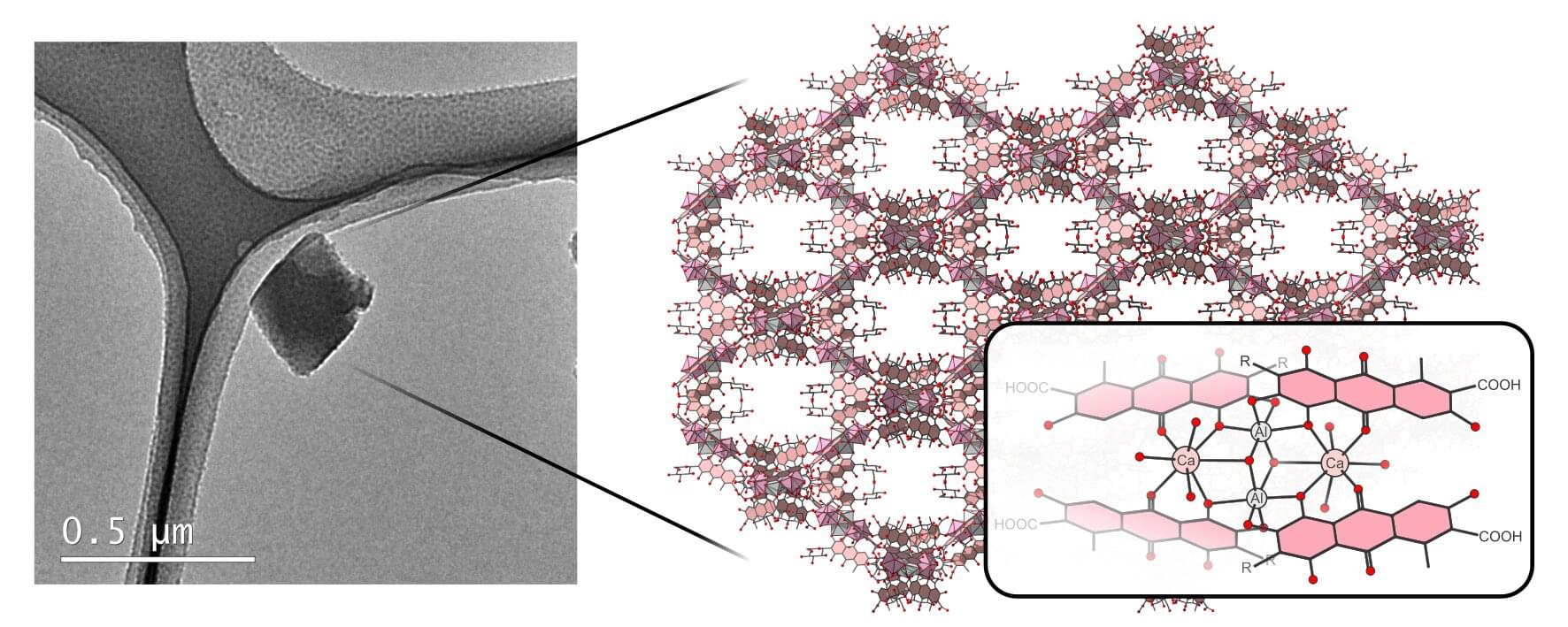
Using advanced electron crystallography techniques, researchers at Stockholm University have succeeded in determining the structure of the historically significant red pigment carmine. It turns out that the substance, used today in products such as candy and paint, has a complex porous structure.
The study is published in the journal Crystal Growth & Design.
Carmine is a natural red coloring agent produced from cochineal extract. The extract from these insects is rich in carminic acid, which is combined with aluminum (Al) and calcium (Ca) to produce carmine. Analysis using advanced electron microscopy techniques has now revealed that this pigment has an unexpected structure. It is a so-called metal complex, built from two calcium ions, two aluminum ions, and four organic ligand molecules of carminic acid.
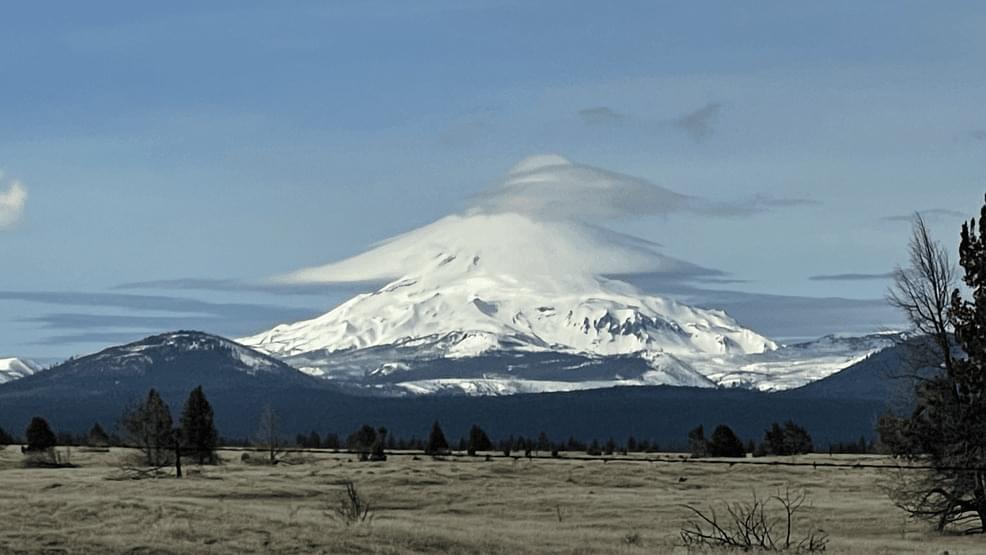




The 1980 eruption cycle made Mount St. Helens one of the most famous and now best-monitored volcanoes in the Cascades. But it is far from the only volcano in the range.
From southern British Columbia to Northern California, the Cascade Range comprises an 800-mile chain of volcanoes.
So, how did this volcanic landscape come to be?

The global EUV Photoresists market is projected to grow from US$176.19 million in 2024 to US$646.71 million by 2030, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 24.20% during the forecast period.
In terms of production side, this report researches the EUV Photoresists production, growth rate, market share by manufacturers and by region (region level and country level), from 2022 to 2024, and forecast to 2030.
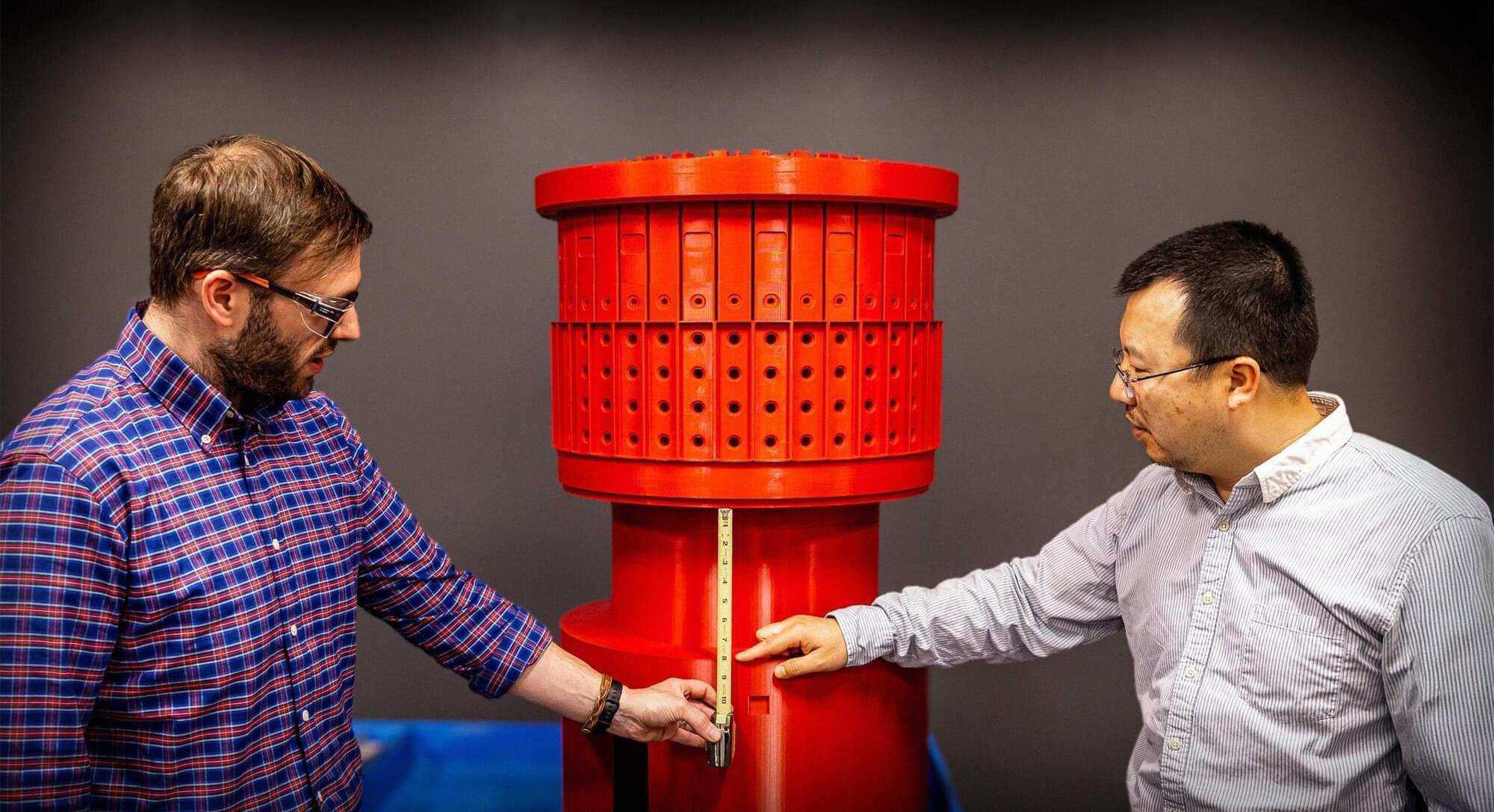

The bundle of magnets at the heart of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory’s (PPPL) National Spherical Torus Experiment-Upgrade (NSTX-U) is the star of the show.
Its magnets will produce the highest magnetic field of any large spherical torus, allowing for near steady-state conditions. They are critical to the design of NSTX-U. When it begins operating, it will be essential in determining whether spherical tokamaks, which are smaller and more compact than traditional doughnut-shaped tokamaks, could provide a more efficient and cost-effective model for a fusion pilot plant.
The 19-foot toroidal field (TF) magnet carries up to 4 million amps of electric current to stabilize and confine the superhot plasma in fusion experiments. It will eventually connect to 12 TF coils on the outside of the vacuum vessel. Wrapped around it like a slinky is the ohmic heating (OH) coil, a 4-kilovolt magnet that induces an electric field, which drives an electric current into the vessel and helps to heat the plasma.
