Spinal cord injury (SCI) imposes a significant physical, social, and economic burden on millions of patients and their families worldwide. Although medical and surgical care improvements have decreased mortality rates, sustained recovery remains constrained. Cell-based therapies offer a promising strategy for neuroprotection and neuro-regeneration post-SCI. This article reviews the most promising preclinical approaches, encompassing the transplantation of embryonic stem cells (ESCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), neural stem cells (NSCs), oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs), Schwann cells (SCs), and olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs), along with the activation of endogenous pluripotency cell banking strategies. We also outline key ancillary strategies to enhance graft cell viability and differentiation, such as trophic factor assistance, engineered biomaterials for supportive scaffolds, and innovative methods for a synergistic effect in treatment, including promoting neuronal regeneration and reducing glial scars. We highlight the key aspects of SCI pathophysiology, the fundamental biology of cell treatments, and the advantages and limitations of each approach.
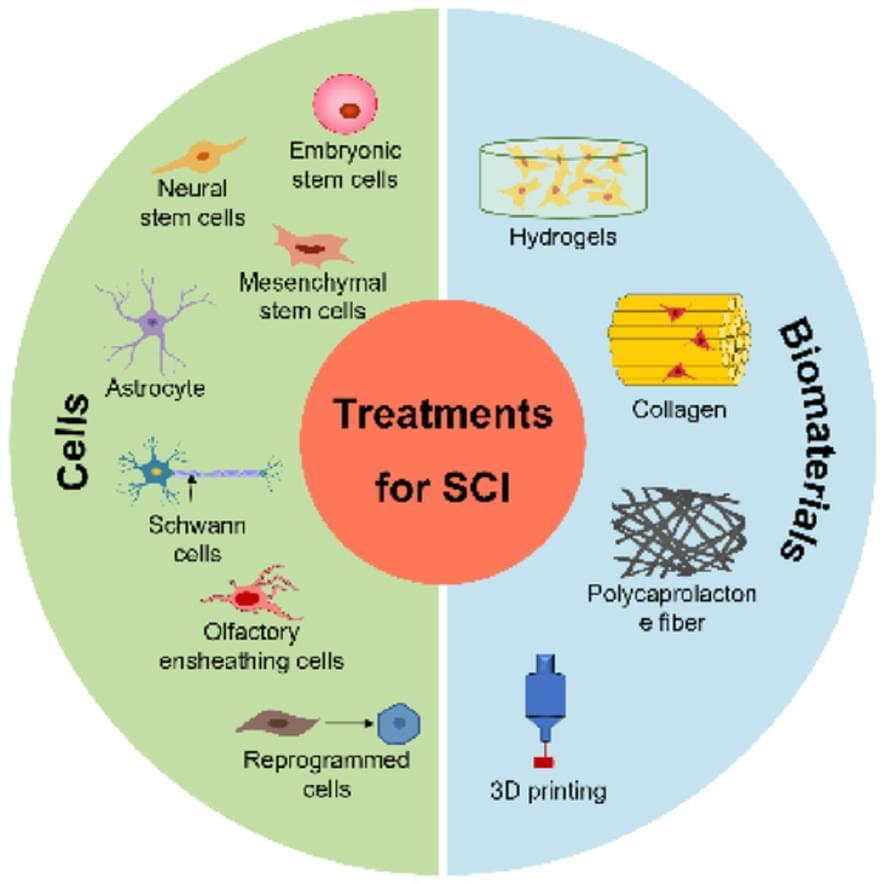
There are several approaches to treating spinal cord injuries that show great promise: Cellular therapies, which utilize a range of cells such as embryonic, neural, and mesenchymal stem cells, along with astrocytes, Schwann cells, olfactory ensheathing cells, and reprogrammed cells; The use of innovative biomaterials, including hydrogels, collagen, polycaprolactone fibers, and advanced 3D-printing technologies, provides valuable support for tissue repair.