Nick Bostrom is a Swedish philosopher at the University of Oxford known for his work on existential risk, the anthropic principle, human enhancement ethics, superintelligence risks, and the reversal test.
Category: existential risks – Page 97
Russian x-risks newsletter, summer 2019
This is the first Russian x-risks newsletter, which will present news about Russia and global catastrophic risks from the last 3 months.
Given the combination of high technological capabilities, poor management, high risk tolerance and attempts to catch up with West and China in the military sphere, Russia is prone to technological catastrophes. It has a 10 times higher level of aviation catastrophes and car accidents than developed countries.
Thus it seems possible that a future global catastrophe may be somehow connected with Russia. However, most of the work in global catastrophic and existential risk (x-risks) prevention and policy efforts are happening in the West, especially in US, UK and Sweden. Even the best policies adopted by the governments of these countries may not help if a catastrophe occurs in another country or countries.


Why superintelligence is a threat that should be taken seriously
Circa 2017
In a recent article for Skeptic, Michael Shermer (the magazine’s founding publisher) put forth an argument for “why AI is not an existential threat,” where “AI” stands for “artificial intelligence” and an “existential threat” is anything that could cause human extinction or the irreversible decline of civilization.
Japan warns North Korea now has miniaturized nukes
North Korea has miniaturised nuclear warheads and made them small enough to fit on ballistic missiles, Japan believes.
Tokyo defence chiefs warn in a new white paper that North Korea’s military activities pose a ‘serious and imminent threat’.
In last year’s report Japan said it was ‘possible’ that North Korea had achieved miniaturisation, but Tokyo now appears to have upgraded its assessment, according to Japanese newspaper Yomiuri.

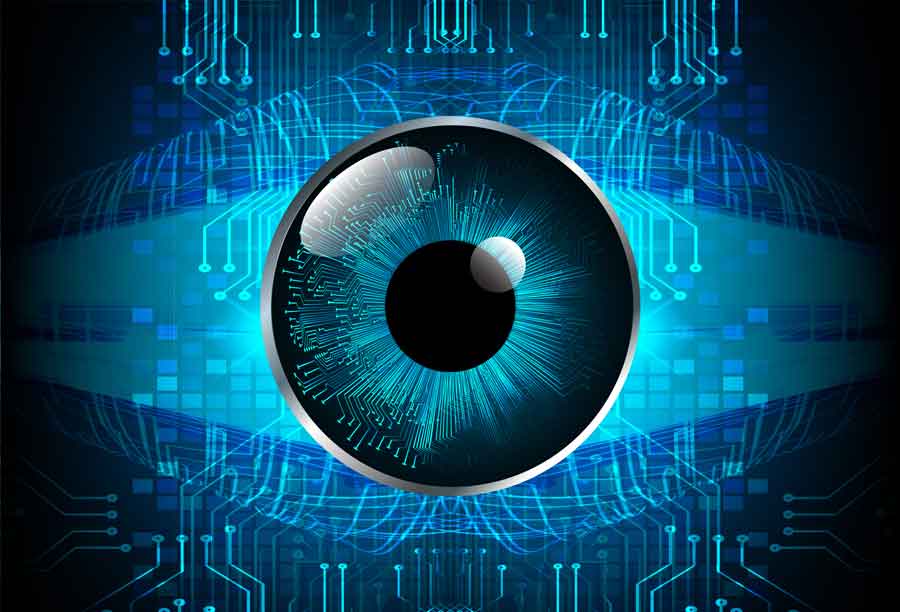
6 Extinct Animals That Could Be Brought Back to Life
There are some extinct species — such as the woolly mammoth, shown above — that may be brought back to life if scientists can overcome some practical hurdles and thorny ethical questions. This gallery shows six of the species that researchers talked about reviving at a March 2013 forum called TEDxDeExtinction in Washington, D.C.
This photo shows a museum worker inspecting a replica of a woolly mammoth.
Thylacines, or Tasmanian tigers, were found throughout most of the Australian island of Tasmania before Europeans settled there in 1803.

Future Bioweapons Could Kill People With Specific DNA
In the future, we may have to deal with biological weapons that target specific groups of people, passing over everyone else.
That’s according to a new report out of Cambridge University’s Centre for the Study of Existential Risk reviewed by The Telegraph. In it, the Cambridge researchers argue that world governments have failed to prepare for futuristic weapons based on advanced technology like artificial intelligence and genetic manipulation — or even a killer pathogen designed to kill only people of a particular race.
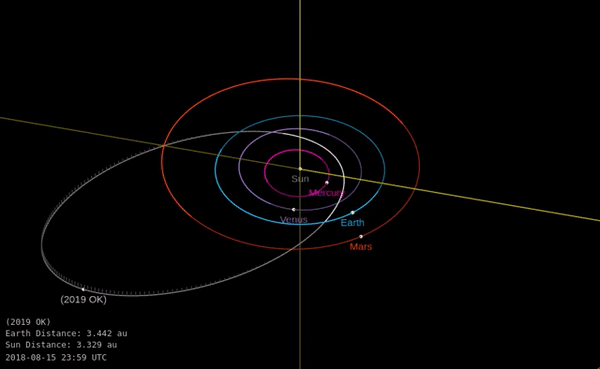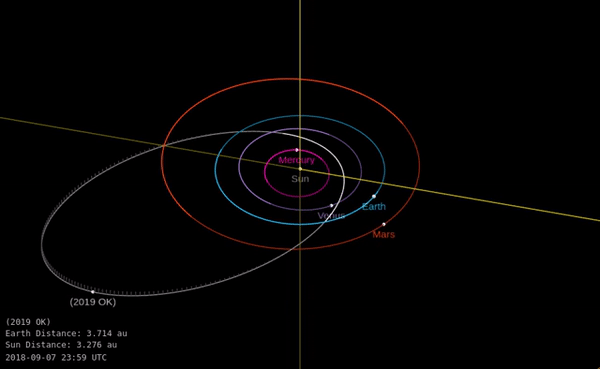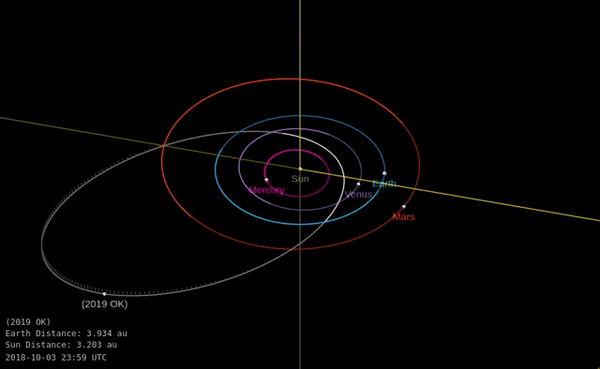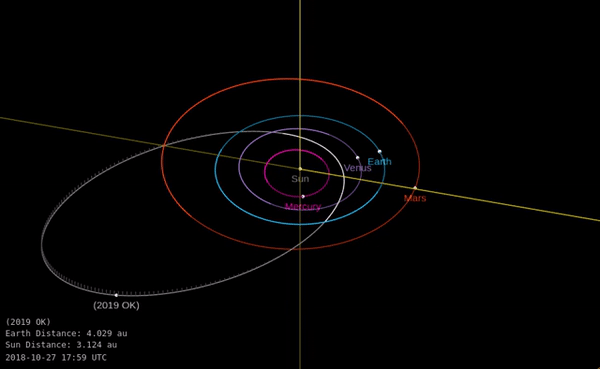
A huge asteroid flew very close to Earth last week. How did we miss it?
The asteroid managed to get within just 73,000 kilometers of our planet without anyone noticing. The miss lends a new sense of urgency to preparations for a potential collision one day.
The news: On Thursday July 25 an asteroid dubbed “Asteroid 2019 OK”, measuring 57 to 130 meters wide (187 to 427 feet), got uncomfortably close to Earth, according to NASA’s near-Earth objects database. It was less than one-fifth of the distance to the moon away, making it a very close call in space terms. If it had landed on a populated area it could have caused major damage, although this outcome is statistically quite unlikely.
Should we worry? It’s hard not to feel concerned that a “city-killer” sized asteroid wasn’t detected further ahead of time. It was announced just hours before it passed by Earth, after being detected just a few days beforehand by teams in the US and Brazil. Its relatively small size, unusual orbit, and fast speed all conspired to make it tough to spot, researchers told the Washington Post.