We spoke to Sara Ord, director of species restoration at Colossal, the world’s first “de-extinction” company, about its big ambitions.



WASHINGTON, Nov 8 (Reuters) — The United States and Russia are expected to meet soon and discuss resuming inspections under the New START nuclear arms reduction treaty that have been paused since before Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, U.S. State Department spokesperson Ned Price said on Tuesday.
Speaking at a daily press briefing, Price said the bilateral consultative commission (BCC), the mechanism for implementation of the last remaining arms control agreement between the world’s two largest nuclear powers, will meet “in the near future.”
Russia in August suspended cooperation with inspections under the treaty, blaming travel restrictions imposed by Washington and its allies over Moscow’s February invasion of Ukraine, but said it was still committed to complying with the provisions of the treaty.

Nuclear arsenals remain large enough to fundamentally shift the Earth system in the blink of an eye.
The U.S. and Russia have recently agreed to hold talks on the New START Treaty, and the only accord left regulating the two largest nuclear arsenals in the world. While this is undoubtedly good news, we must not allow it to lull us into complacency. Global events this year, most notably in Ukraine, have raised fears of a nuclear conflict to levels not seen since the cold war. More than 10,000 nuclear warheads remain in the world, and the Kremlin’s language regarding weapons of mass destruction has become increasingly threatening in 2022.
Global famine and climate breakdown
In 1982, a group of scientists, including Carl Sagan, began to raise the alarm about a climate apocalypse that could follow a nuclear war. Using simple computer simulations and historic volcanic eruptions as natural analogs, they showed how smoke that lofted into the stratosphere from urban firestorms could block the sun for years.
They found that this “nuclear winter,” as it came to be called, could trigger catastrophic famine far from the location of the war. Ronald Reagan and Mikhail Gorbachev, leaders of the United States and Soviet Union in the 1980s, both cited this work when they declared that a nuclear war could not be won.
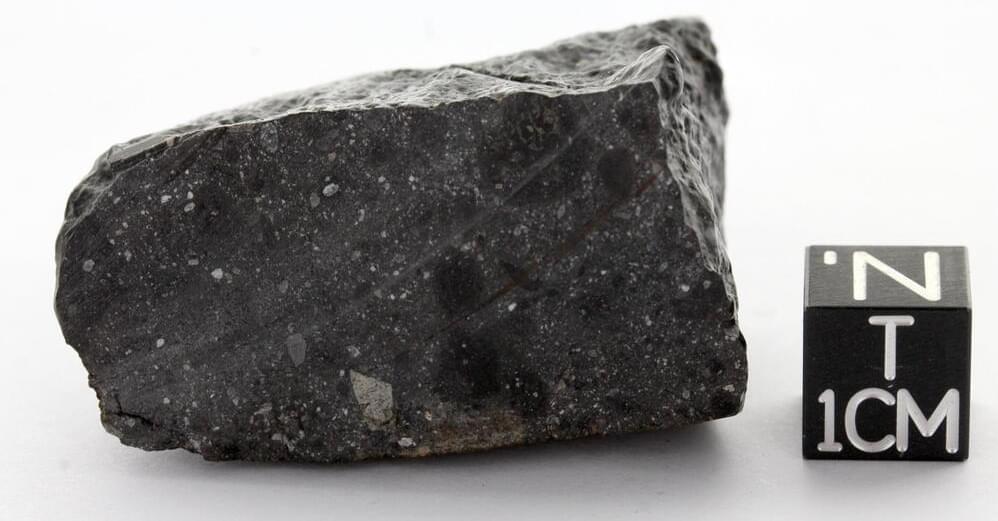

A team of researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Center for Star and Planet Formation, working with colleagues from Université de Paris, ETH Zürich and the University of Bern, has found evidence suggesting that most of the water that made up an ancient global ocean on Mars came from carbon-rich chondrite meteorites from the outer solar system. The study is published in Science Advances.
Prior research has suggested that at one time, Mars was either mostly or entirely covered by a watery ocean, and that the water came from gases seeping from below the surface and liquifying as they cooled. In this new effort, the researchers suggest the water more likely came from another source—meteorites traveling from the outer solar system.
The researchers came to this conclusion after studying fragments flung from the surface of Mars after asteroid strikes, which made their way to Earth as meteorites. The researchers studied 31 of them, looking most specifically for chromium isotopic fingerprints. Chromium-54 does not occur naturally on Mars; thus, its presence in crust samples from Mars would indicate that the surface had been struck by material from somewhere else.

Perhaps Arthur C. Clarke was being uncharacteristically unambitious. He once pointed out that any sufficiently advanced technology is going to be indistinguishable from magic. If you dropped in on a bunch of Paleolithic farmers with your iPhone and a pair of sneakers, you’d undoubtedly seem pretty magical. But the contrast is only middling: The farmers would still recognize you as basically like them, and before long they’d be taking selfies. But what if life has moved so far on that it doesn’t just appear magical, but appears like physics?
After all, if the cosmos holds other life, and if some of that life has evolved beyond our own waypoints of complexity and technology, we should be considering some very extreme possibilities. Today’s futurists and believers in a machine “singularity” predict that life and its technological baggage might end up so beyond our ken that we wouldn’t even realize we were staring at it. That’s quite a claim, yet it would neatly explain why we have yet to see advanced intelligence in the cosmos around us, despite the sheer number of planets it could have arisen on—the so-called Fermi Paradox.
For example, if machines continue to grow exponentially in speed and sophistication, they will one day be able to decode the staggering complexity of the living world, from its atoms and molecules all the way up to entire planetary biomes. Presumably life doesn’t have to be made of atoms and molecules, but could be assembled from any set of building blocks with the requisite complexity. If so, a civilization could then transcribe itself and its entire physical realm into new forms. Indeed, perhaps our universe is one of the new forms into which some other civilization transcribed its world.
Today we return to the Fermi Paradox to contemplate the notion of civilizations which neither expand outwards to colonize the galaxy nor go extinct, but exist as long-term, high-tech civilizations just on their own planet or solar system. To discuss the possible motives and reasoning we will look at the many arguments raised for and against space exploration.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join the Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Support the Channel on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Visit the sub-reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/fermi-paradox-…ilizations.
Cover Art by Jakub Grygier: https://www.artstation.com/artist/jakub_grygier

Microbial life may have resided within the first four kilometers of Mars’s porous crust.
Four billion years ago, the solar system was still young. Almost fully formed, its planets were starting to experience asteroid strikes a little less frequently. Our own planet could have become habitable as long as 3.9 billion years ago, but its primitive biosphere was much different than it is today. Life had not yet invented photosynthesis, which some 500 million years later would become its main source of energy. The primordial microbes — the common ancestors to all current life forms on Earth — in our planet’s oceans, therefore, had to survive on another source of energy.
Some of the oldest life forms in our biosphere were microorganisms known as “hydrogenotrophic methanogens” that particularly benefited from the atmospheric composition of the time. Feeding on the CO2 (carbon dioxide) and H2 (dihydrogen) that abounded in the atmosphere (with H2 representing between 0.01 and 0.1% of the atmospheric composition, compared to the current approximate of 0.00005%), they harnessed enough energy to colonize the surface of our planet’s oceans.
In return, they released into the atmosphere large amounts of CH4 (a.k.a., methane, from which they get their name), a potent greenhouse gas that accumulated and heated up the climate. Since our sun at the time was not as bright as it is today, it may not have been able to maintain temperate conditions on the planet’s surface without the intervention of other aspects. As such, thanks to these methanogens, the very emergence of life on Earth may itself have helped ensure our planet’s habitability, setting the right conditions for the evolution and complexification of the terrestrial biosphere for the billions of years that followed.
While this is the likeliest explanation for the early development of habitability on Earth, what was it like for the other planets of the solar system, such as our neighbor, the red planet? As we continue to explore Mars, it is becoming ever clearer that similar environmental conditions were developing on its surface at the same time as those that enabled methanogens to flourish in the oceans back on Earth.
As in physics, paradoxes in biology really are just unsolved puzzles. Enter Peto’s paradox. Biologist Richard Peto noticed in the 1970s that mice had a much higher rate of cancer than humans do, which doesn’t make any sense. Humans have over 1,000 times as many cells as mice, and cancer is simply a rogue cell that goes on multiplying out of control. One would expect humans to be more likely to get cancer than smaller creatures such as mice. This paradox occurs across all species, too: blue whales are much less likely to get cancer than humans, even though they have many more cells in their bodies.
Fermi paradox
Named after physicist superstar Enrico Fermi, the Fermi paradox is the contradiction between how likely alien life is in the universe and its apparent absence. Considering the billions of stars in the galaxy like the sun, the many Earth-like planets that must be orbiting some of those stars, the likelihood that some of those planets developed life, the likelihood that some of that life is as intelligent or more intelligent than humanity, the galaxy should be teeming with alien civilizations. This absence led Fermi to pose the question, “Where is everybody?” Some answers to that question are unfortunately a little disturbing.