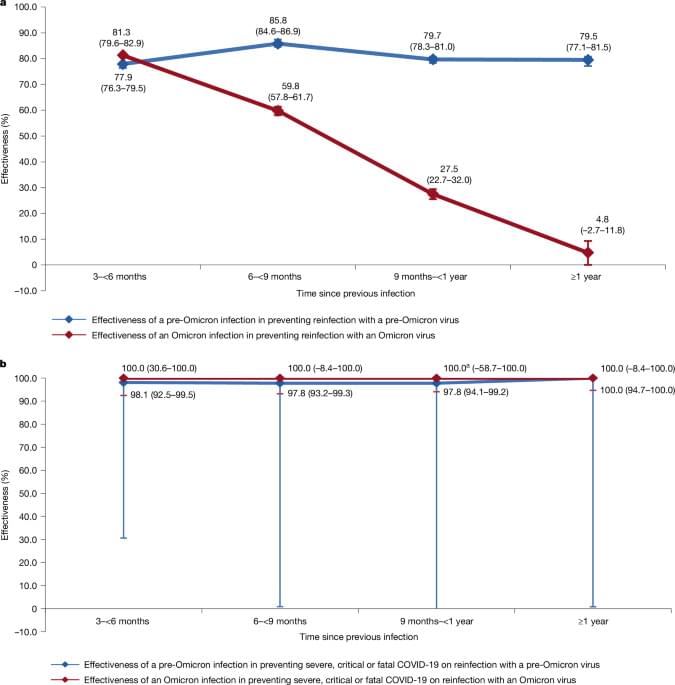
The results show two distinct patterns in the protective effect of natural infection against reinfection in the Omicron era compared to the pre-Omicron era. Before the emergence of Omicron, natural infection offered robust protection against reinfection, with roughly 80% effectiveness and minimal signs of waning over time after the infection. However, during the Omicron era, this protection was strong only for recently infected individuals, rapidly declining over time after the infection and ultimately diminishing within a year. These patterns were consistent regardless of whether any infection or only symptomatic infection was considered as an outcome, and for both vaccinated and unvaccinated populations.
The two distinct patterns observed in the Omicron versus pre-Omicron eras provide population-level results that validate previous experimental molecular evidence1,2,18,19,20, and are probably the result of a complex interplay of several interrelated factors, in addition to waning immunity, immune evasion and the accelerated and convergent evolution of Omicron, such as immune imprinting, varying immunogenicity, global population immunity faced by the strains and population characteristics associated with infections at different stages of the pandemic.
Whereas these factors are interconnected and challenging to disentangle, the observed differences in protection against reinfection may stem from distinct evolutionary pressures acting on SARS-CoV-2 during the pre-Omicron and Omicron eras. In the pre-Omicron era, with a large proportion of individuals remaining immune naive because of non-pharmaceutical interventions and delayed scale-up of vaccination, intrinsic transmissibility may have been the primary driver of viral adaptation. This was evidenced by the emergence of more transmissible variants such as Alpha4,22,23 and Delta24,25. Conversely, following the very large and widespread Omicron wave in early 2022 (Extended Data Fig. 3)26, most individuals possessed some level of immunity, either from infection or vaccination. This may have shifted the dominant evolutionary pressure towards immune escape through not only antigenic drift, but also recombination and convergent evolution as the adaptive mechanisms for the virus2,18,27,28.