Category: engineering – Page 93
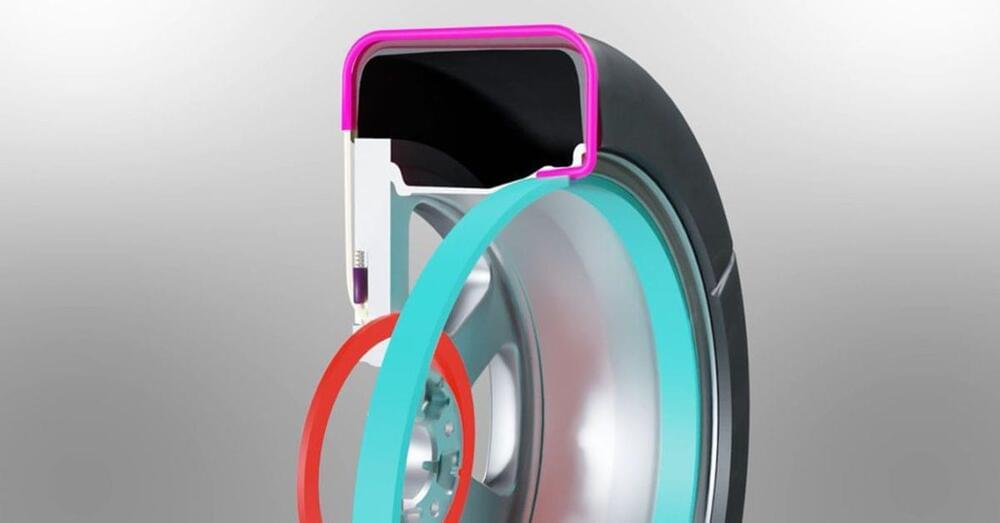

Hyundai and Kia boast another breakthrough, unveiling new tire with retractable ‘snow chains’
Weeks after introducing a potentially game-changing “Uni-wheel” drive system for EVs, Hyundai and Kia are showing off another next-generation technology to keep EV drivers safer during inclement weather. Today, Kia and Hyundai introduced a new snow chain-integrated tire that utilizes shape memory alloy modules inside the wheel. See how this incredible new tech works in the video below.
As EVs continue to saturate the global automotive market, their respective technologies are evolving to benefit consumers. Now more than ever, these electric vehicles drive farther, charge faster, and come equipped with exciting new technologies like vehicle-to-load (V2L) capabilities and Plug & Charge.
Hyundai Motor Group has been one of the early proponents of such technologies, featuring them in EVs atop its E-GMP platform. In fact, Hyundai and Kia especially have rolled out some exciting technologies throughout the electric mobility segment and allocated considerable funds to R&D to explore new engineering breakthroughs.
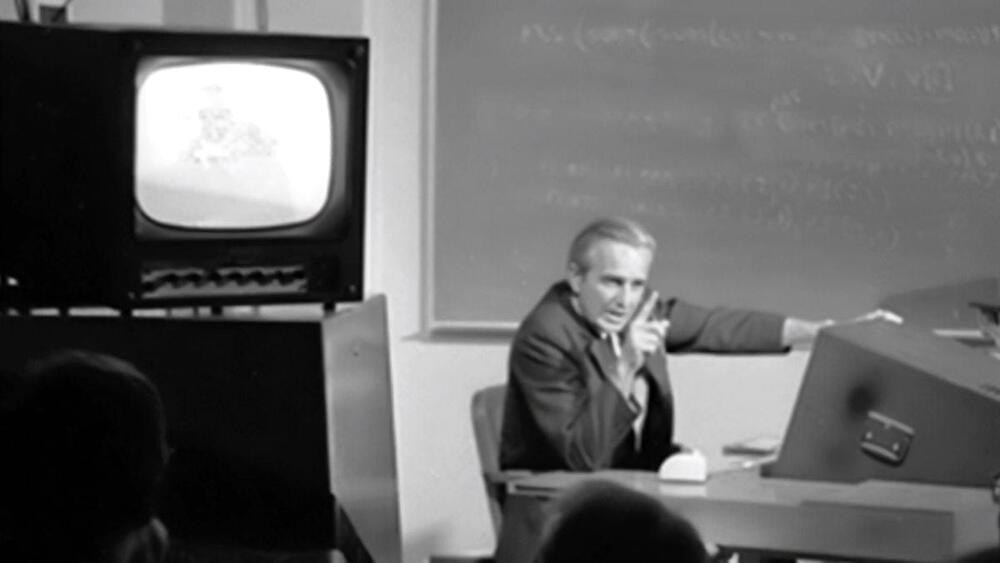

55 years ago, the ‘Mother of All Demos’ foresaw modern computing
Engelbart grew up on a small farm in Southeast Portland where his father operated a radio store.
He graduated from Franklin High School in 1942 and enrolled at Oregon State College, now called Oregon State University, to study electrical engineering.
When World War II interrupted his studies, he spent two years working as a Navy radio and radar technician in the Philippines.

Miles Beneath Our Feet: The Superhot Energy Source That Could Change Everything
In an indication of growing interest in the holy grail of geothermal energy—tapping into the superhot rock miles below our feet—18 papers on the topic were presented over multiple sessions at a recent major conference on the overall geothermal industry.
“By driving down costs and making large-scale geothermal power available nearly anywhere, Superhot Rock energy has the potential to disrupt and revolutionize the energy system.” That’s according to a description of the sessions on Technological, Engineering, and Geological Advances in Superhot Geothermal presented at the 2023 Geothermal Rising Conference held over four days in October.
“For me, a pretty big highlight of Geothermal Rising 2023 was the increased focus on superhot rock geothermal through multiple presentations from around the world,” says Matt Houde, co-founder and project manager at Quaise Energy.
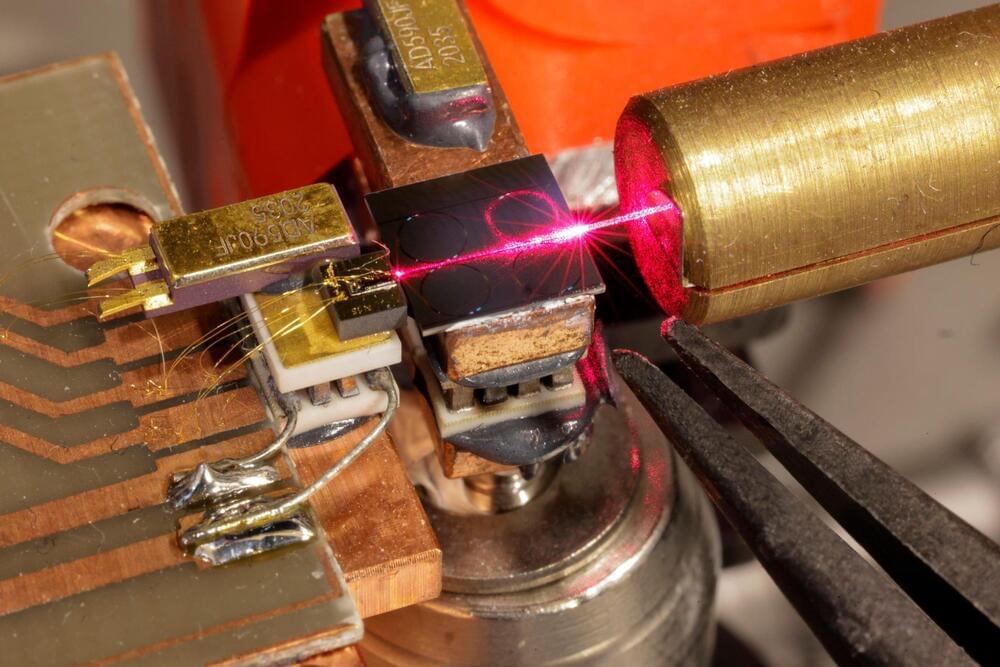
Micro-Ring Resonators: Unlocking New Dimensions in Laser Technology
EPFL researchers have developed a hybrid device that significantly improves existing, ubiquitous laser technology.
The team at EPFL’s Photonic Systems Laboratory (PHOSL) has developed a chip-scale laser source that enhances the performance of semiconductor lasers while enabling the generation of shorter wavelengths. This pioneering work, led by Professor Camille Brès and postdoctoral researcher Marco Clementi from EPFL’s School of Engineering represents a significant advance in the field of photonics, with implications for telecommunications, metrology, and other high-precision applications.
Innovative integration for improved coherence and visibility.

Spinning up control: Propeller shape helps direct nanoparticles (w/video)
Self-propelled nanoparticles could potentially advance drug delivery and lab-on-a-chip systems — but they are prone to go rogue with random, directionless movements. Now, an international team of researchers has developed an approach to rein in the synthetic particles.
Led by Igor Aronson, the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Chair Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Chemistry and Mathematics at Penn State, the team redesigned the nanoparticles into a propeller shape to better control their movements and increase their functionality. They published their results in the journal Small (“Multifunctional Chiral Chemically-Powered Micropropellers for Cargo Transport and Manipulation”).
A propeller-shaped nanoparticle spins counterclockwise, triggered by a chemical reaction with hydrogen peroxide, followed by an upward movement, triggered by a magnetic field. The optimized shape of these particles allows researchers to better control the nanoparticles’ movements and to pick up and move cargo particles. (Video: Active Biomaterials Lab)

Tesla Cybertruck Production Expands, Engineering Details Revealed
Tesla is making progress with Cybertruck production, expanding orders and discussing engineering details and battery options, while also facing production challenges and changes in market demand.
Questions to inspire discussion.
What is Tesla doing with Cybertruck production?
—Tesla is expanding Cybertruck orders and discussing engineering details and battery options, while also facing production challenges and changes in market demand.
Unveiling the Tesla Cybertruck: A Revolutionary Vehicle from Tesla Executives
Sandy talks Cybertruck with 5 Tesla Execs! Lars Moravy: Head of Vehicle Engineering Franz von Holzhausen: Head of Design Drew Baglino: Head of Powertrain (battery + motors) and Energy Pete Bannon: Head of Low Voltage David Lau: Head of Software Munro Live is a YouTube channel that features Sandy Munro and other engineers from Munro & Associates.
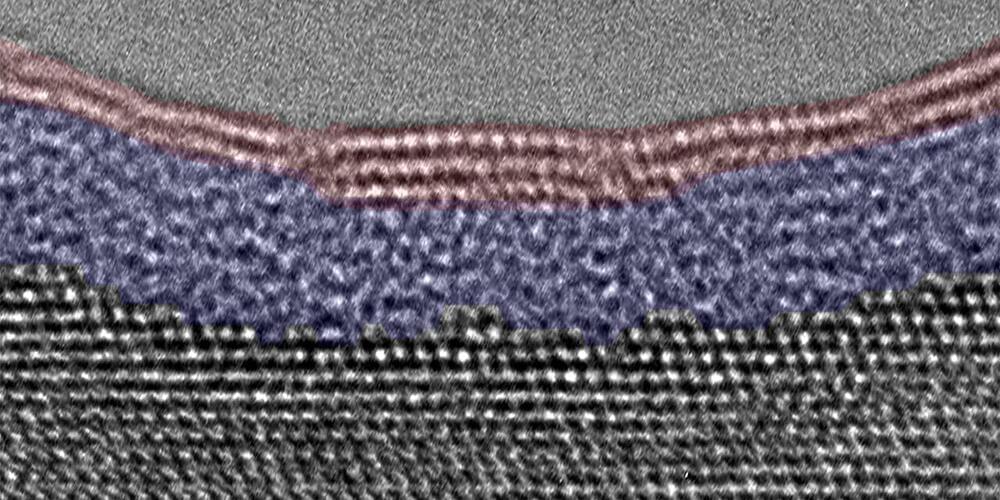
New research examines corrosion on atomic level
When water vapor meets metal, the resulting corrosion can lead to mechanical problems that harm a machine’s performance. Through a process called passivation, it also can form a thin inert layer that acts as a barrier against further deterioration.
Either way, the exact chemical reaction is not well understood on an atomic level, but that is changing thanks to a technique called environmental transmission electron microscopy (TEM), which allows researchers to directly view molecules interacting on the tiniest possible scale.
Professor Guangwen Zhou—a faculty member at Binghamton University’s Thomas J. Watson College of Engineering and Applied Science—has been probing the secrets of atomic reactions since joining the Department of Mechanical Engineering in 2007. Along with collaborators from the University of Pittsburgh and the Brookhaven National Laboratory, he has studied the structural and functional properties of metals and the process of making “green” steel.