A paper from Thales, dstl, and others advocates for quantum systems engineering to combines innovation with interdisciplinary collaboration.



In recent years, biomedical devices have proven to be able to target also different neurological disorders. Given the rapid ageing of the population and the increase of invalidating diseases affecting the central nervous system, there is a growing demand for biomedical devices of immediate clinical use. However, to reach useful therapeutic results, these tools need a multidisciplinary approach and a continuous dialogue between neuroscience and engineering, a field that is named neuroengineering. This is because it is fundamental to understand how to read and perturb the neural code in order to produce a significant clinical outcome.
A new stroke-healing gel created by UCLA researchers helped regrow neurons and blood vessels in mice whose brains had been damaged by strokes. The finding is reported May 21 in Nature Materials.
“We tested this in laboratory mice to determine if it would repair the brain and lead to recovery in a model of stroke,” said Dr. S. Thomas Carmichael, professor of neurology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and co-director of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research. “The study indicated that new brain tissue can be regenerated in what was previously just an inactive brain scar after stroke.”
The results suggest that such an approach could some day be used to treat people who have had a stroke, said Tatiana Segura, a former professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at UCLA who collaborated on the research. Segura is now a professor at Duke University.
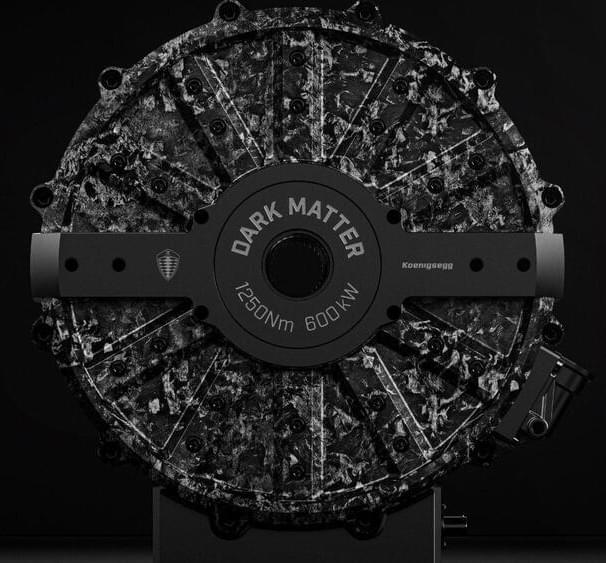


Meet the Dark Matter, the groundbreaking electric motor powering Koenigsegg’s new Gemera hypercar. Officially known as the Dark Matter Raxial Flux 6-phase E-motor, this revolutionary piece of technology debuted at the 2023 Goodwood Festival of Speed. Boasting an impressive 800 horsepower and 922 lb-ft of torque, while weighing just 40kg, the Dark Matter is hailed as the world’s most powerful automotive-grade electric motor. With its unique six-phase technology, it marks a major leap forward in electric vehicle engineering, surpassing the three-phase motors commonly used in most electric vehicles today.
The Dark Matter electric motor is considered the world’s most powerful automotive-grade motor, using a unique six-phase technology. This motor is a significant improvement over the three-phase motors commonly used in most electric vehicles today. The Dark Matter replaces the previous motor used in the Gemera, called the Quark.
Both the Quark and the Dark Matter are “raxial flux” motors, which combine features of two common types of electric motors: radial flux and axial flux. Radial flux motors offer more power but less torque, while axial flux motors are known for providing high torque but with less power. The key difference between these two designs is how the magnetic field travels through the motor. In a radial flux motor, the magnetic field path is longer, creating more power. In an axial flux motor, the magnetic field follows a shorter, more direct path, giving the motor more torque.
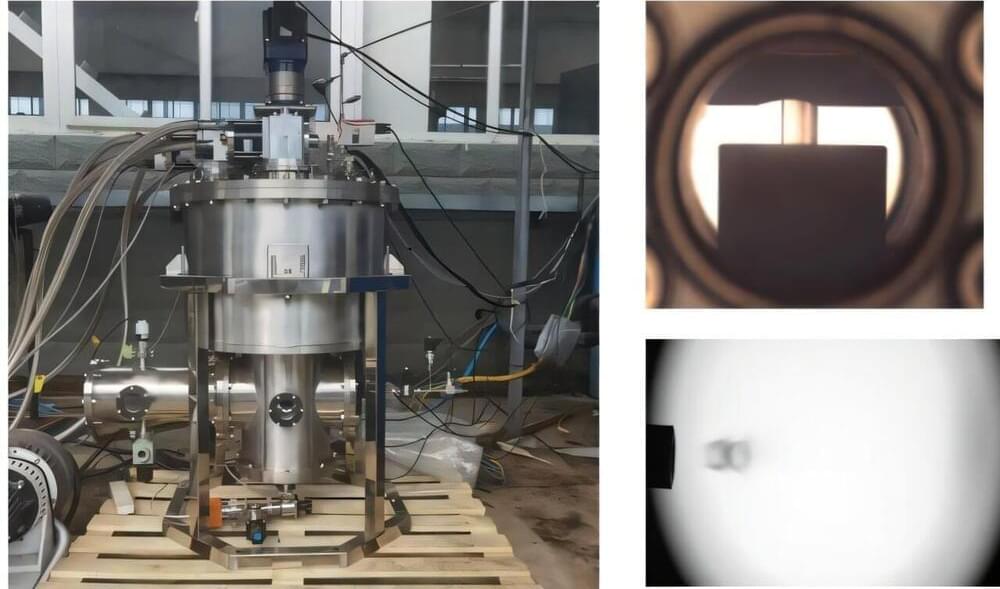

A joint research team from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully developed a continuous cryogenic pellet injection system for tokamak fueling. This innovative system addresses key technical challenges associated with cryogenic ice formation, pellet cutting, and launching.
Cryogenic pellet injection is a state-of-the-art technique in fusion research. It involves condensing hydrogen isotopic gases into solid ice pellets, which are then accelerated and injected into plasma. This method allows for deep particle injection and high fueling efficiency, making it crucial for the future of fusion reactors.
It is recognized as a critical fueling technology for next-generation fusion devices, including the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), the China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor (CFETR), and the European Demonstration Fusion Reactor (EU-DEMO).
How can computer models help medical professionals combat antibiotic resistance? This is what a recent study published in PLOS Biology hopes to address as a team of researchers from the University of Virginia (UVA) developed computer models that can be used to target specific genes in bacteria to combat antimicrobial resistant (AMR) bacteria. This study has the potential to help scientists, medical professionals, and the public better understand innovative methods that can be used to combat AMR with bacterial diseases constantly posing a risk to global human health.
For the study, the researchers used computer models to produce an assemblage of genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions (GENREs) diseases to identify key genes in stomach diseases that can be targeted with antibiotics to circumvent AMR in these bacterial diseases. The researchers validated their findings with laboratory experiments involving microbial samples and found that a specific gene was responsible for producing stomach diseases, thus strengthening the argument for using targeted antibiotics to combat AMR.
“Using our computer models we found that the bacteria living in the stomach had unique properties,” said Emma Glass, who is a PhD Candidate in Biomedical Engineering at UVA and lead author of the study. “These properties can be used to guide design of targeted antibiotics, which could hopefully one day slow the emergence of resistant infections.”
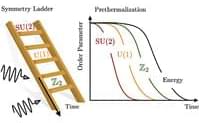
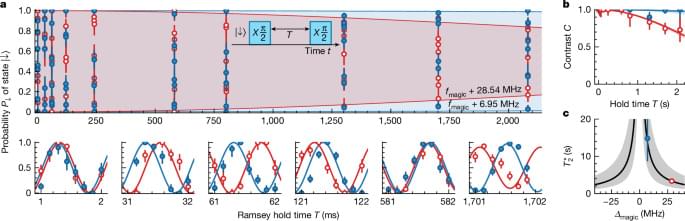
Symmetry plays a crucial role in understanding fundamental phenomena such as conservation laws, the classification of phases of matter, and their transitions. Recently, researchers have been exploring ways to manipulate symmetries in quantum many-body systems with time-dependent driving protocols and, in particular, engineering new symmetries that do not naturally occur. This significantly enriches the toolbox for quantum simulation and computation, and has led to many exciting discoveries of nonequilibrium phases such as discrete time crystals. However, controlling multiple symmetries—especially in a simple and experimentally friendly way—has remained a challenge. In this work, we propose a novel method to engineer hierarchical symmetries by time-dependent protocols.
By carefully controlling how symmetry-indicating observables evolve over time, we show how to create a sequence of symmetries that emerge one after another, each with distinct properties. Our method relies on a recursive construction that hierarchically minimizes the effects of symmetry-breaking processes. This leads to a corresponding sequence of prethermal steady states with controllable lifetimes, each exhibiting a lower symmetry than the preceding one. We illustrate this protocol with several examples, demonstrating how different types of order can emerge through hierarchical symmetry breaking.
This toolbox of hierarchical symmetries opens a new path to stabilizing quantum states and controlling unwanted symmetry-breaking effects, which can be particularly useful in quantum computing and quantum simulation. The construction applies to classical and quantum, fermionic and bosonic, interacting and noninteracting systems. The underlying mechanism generalizes state-of-the-art dynamical decoupling techniques and is implementable on present-day quantum simulation platforms.
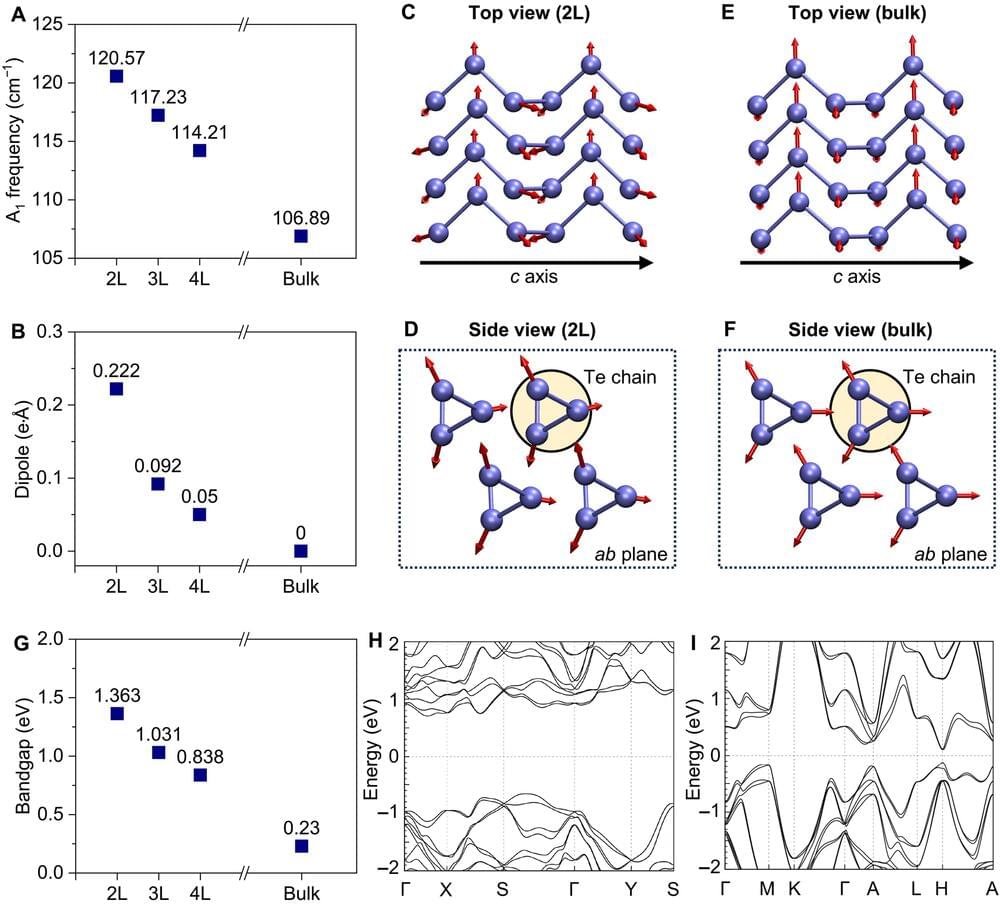
To describe how matter works at infinitesimal scales, researchers designate collective behaviors with single concepts, like calling a group of birds flying in sync a “flock” or “murmuration.” Known as quasiparticles, the phenomena these concepts refer to could be the key to next-generation technologies.
In a recent study published in Science Advances, a team of researchers led by Shengxi Huang, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering and materials science and nanoengineering at Rice, describe how one such type of quasiparticle—polarons—behaves in tellurene, a nanomaterial first synthesized in 2017 that is made up of tiny chains of tellurium atoms and has properties useful in sensing, electronic, optical and energy devices.
“Tellurene exhibits dramatic changes in its electronic and optical properties when its thickness is reduced to a few nanometers compared to its bulk form,” said Kunyan Zhang, a Rice doctoral alumna who is a first author on the study. “Specifically, these changes alter how electricity flows and how the material vibrates, which we traced back to the transformation of polarons as tellurene becomes thinner.”