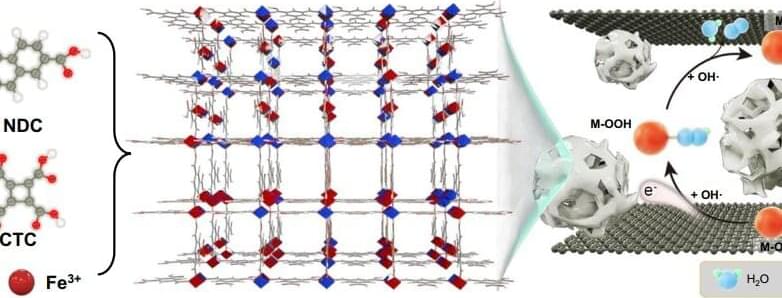
Prof. Zhang Tao’s group at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. Hou Yang from Zhejiang University and Prof. Xiao Jianping from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of CAS, proposed a novel two-dimensional (2D) nanoconfinement strategy to strongly enhance the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of low-conductivity metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Results were published in Nature Communications.
The development of high-efficiency electrocatalysts for the electrochemical conversion of water to generate environmentally friendly and sustainable hydrogen energy has drawn tremendous attention for decades.
Despite the crucial role the OER plays in water splitting, OER at the anode requires a relatively high thermodynamic potential to accelerate water splitting kinetics. Thanks to the large surface area, tunable porosity, diverse compositions and metal centers, MOFs have emerged as promising candidates for efficient OER electrocatalysts. However, the intrinsically poor conductivity of the most MOFs seriously impede their catalytic activity.