Podo is a small HD camera capable of attaching to a variety of surfaces.
Selfie sticks are about to go bye-bye.
Podo is a small HD camera capable of attaching to a variety of surfaces.
Selfie sticks are about to go bye-bye.

Has anyone seen “The Yes Men” youtube video where they present to the WTO their proposed employee monitoring suit to ensure employees were working and performing while the supervisor is at the beach. This reminds me a little of that same scenario; except this time it’s the employees wearing the wearable monitor to measure & track their performance.
Working in the intelligence community can be stressful. The IC’s research arm wants to use sensors to evaluate how people respond to the demands of the job.

Ah, science. wink
In the right hands, broken electronics can be turned into something useful again. But useful isn’t the best way to describe Drake Anthony’s 200-watt laser bazooka made from a bunch of old DLP projectors he bought off eBay. Words like incredibly dangerous, do-not-try-this-at-home, or “are you crazy?” seem more appropriate.
For comparison, the handheld laser pointers used during PowerPoint presentations measure in at a measly 0.005-watts, while the FDA limits the lasers that most consumers can buy to a maximum power rating of 0.5-watts. That means that Drake’s creation, which focuses four 50-watt lasers through a massive lens—is 400 times more powerful than what the FDA will let you play with. And those rules are there for a good reason. Lasers can be deadly!


A “huge” stash of helium discovered in East Africa could ease a decades-long shortage of the rare and valuable gas.
Researchers in the United Kingdom and Norway say the newly discovered helium gas field, found in the East African Rift Valley region of Tanzania, has the potential to ease a critical global shortage of helium, a gas that is vital to many high-tech applications, such as the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners used in many hospitals.
The researchers say the discovery is the result of a new approach to searching for helium that combines prospecting methods from the oil industry with scientific research that reveals the role of volcanic heat in the production of pockets of helium gas. [Elementary, My Dear: 8 Elements You Never Heard Of].

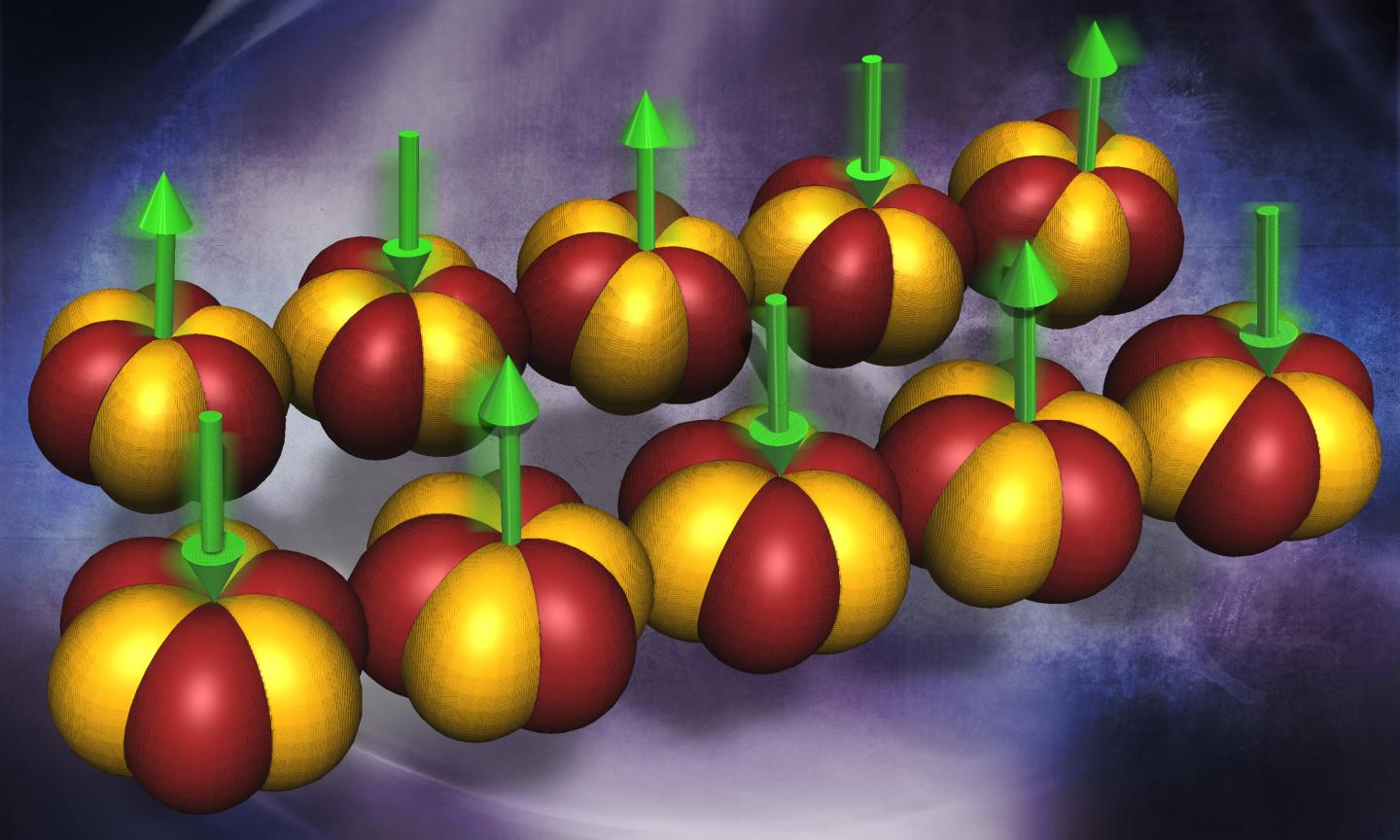
More news on ORNL’s efforts around magnetic excitations in the metallic compound ytterbium-platinum-lead (Yb2Pt2Pb).
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and their collaborators used neutron scattering to uncover magnetic excitations in the metallic compound ytterbium-platinum-lead (Yb2Pt2Pb). Surprisingly, this three-dimensional material exhibits magnetic properties that one would conventionally expect if the connectivity between magnetic ions was only one-dimensional. Their research is discussed in a paper published in the journal Science.
An electron can theoretically be understood as a bound state of three quasiparticles, which collectively carry its identity: spin, charge and orbit. It has been known that the spinon, the entity that carries information about electron spin, can “separate” itself from the others under certain conditions in one-dimensional chains of magnetic ions such as copper (Cu2+) in an insulating host. Now, the new study reveals that spinons are also present in metallic Yb2Pt2Pb.
The experimental team included ORNL postdoctoral researcher and lead author Liusuo Wu, Georg Ehlers, and Andrey Podlesnyak, instrument scientists at ORNL’s Spallation Neutron Source (SNS), a DOE Office of Science User Facility. The team made use of the neutrons’ sensitivity to magnetic fluctuations at the atomic scale and the world-leading capabilities of the SNS Cold Neutron Chopper Spectrometer (CNCS) instrument.

Featuring backside-illuminated sensor technology providing 95% quantum efficiency, the Prime 95B from 2016 Innovators Awards silver-level honoree Photometrics is reportedly three times more sensitive than the current generation of sCMOS cameras. The camera features a GSENSE400BSI-TVISB scientific CMOS (sCMOS) sensor from Gpixel Inc., which is a 1.44 MPixel sensor with a 11 µm square pixel size that can achieve a frame rate of 41 fps in 16-bit and 82 fps in 12-bit. The Prime 95B, according to Photometrics, is optimized for low-light microscopy and life sciences imaging applications because of its ability to collect nearly all available light, and maximize the signal-to-noise ratio of the experiment while minimizing cellular photo damage. Additionally, the camera features forced air or liquid cooling options, as well as a PCIe and USB 3.0 interfaces.
America Future Secrets Military Weapons #Mind Blow (Full Documentary)
MOST FEARED Weapons Technology for US Military (Message to world) 2016.
This Documentary contains related tags:
The Top Secret World of Killing Weapons New (Full Documentary),history, documentary, secret,

Silicon forms the basis of everything from solar cells to the integrated circuits at the heart of our modern electronic gadgets. However the laser, one of the most ubiquitous of all electronic devices today, has long been one component unable to be successfully replicated in this material. Now researchers have found a way to create microscopically-small lasers directly from silicon, unlocking the possibilities of direct integration of photonics on silicon and taking a significant step towards light-based computers.
Whilst there has been a range of microminiature lasers incorporated directly into silicon over the years, including melding germanium-tin lasers with a silicon substrate and using gallium-arsenide (GaAs) to grow laser nanowires, these methods have involved compromise. With the new method, though, an international team of researchers has integrated sub-wavelength cavities, the basic components of their minuscule lasers, directly onto the silicon itself.
To help achieve this, a team of collaborating scientists from Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, the University of California, Santa Barbara, Sandia National Laboratories and Harvard University, first had to find a way to refine silicon crystal lattices so that their inherent defects were reduced significantly enough to match the smooth properties found in GaAs substrate lasers. They did this by etching nano-patterns directly onto the silicon to confine the defects and ensure the necessary quantum confinement of electrons within quantum dots grown on this template.