On top of the environmental concerns, Japan has an added motivation for this push towards automation —its aging population and concurrent low birth rates mean its workforce is rapidly shrinking, and the implications for the country’s economy aren’t good.
Thus it behooves the Japanese to automate as many job functions as they can (and the rest of the world likely won’t be far behind, though they won’t have quite the same impetus). According to the Nippon Foundation, more than half of Japanese ship crew members are over the age of 50.
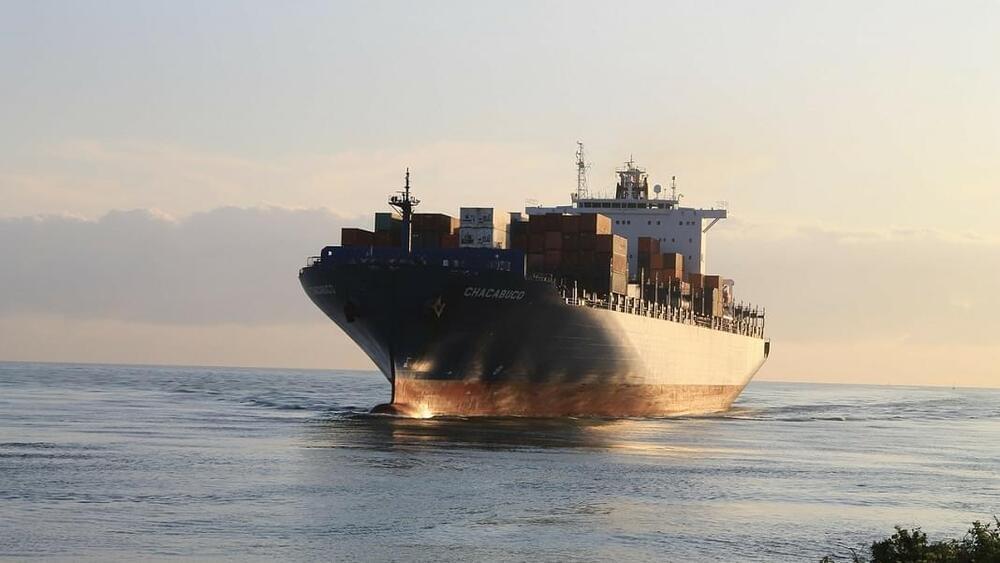
In partnership with Misui OSK Lines Ltd., the foundation recently completed two tests of autonomous ships. The first was a 313-foot container ship called the Mikage, which sailed 161 nautical miles from Tsuruga Port, north of Kyoto, to Sakai Port near Osaka. Upon reaching its destination port the ship was even able to steer itself into its designated bay, with drones dropping its mooring line.