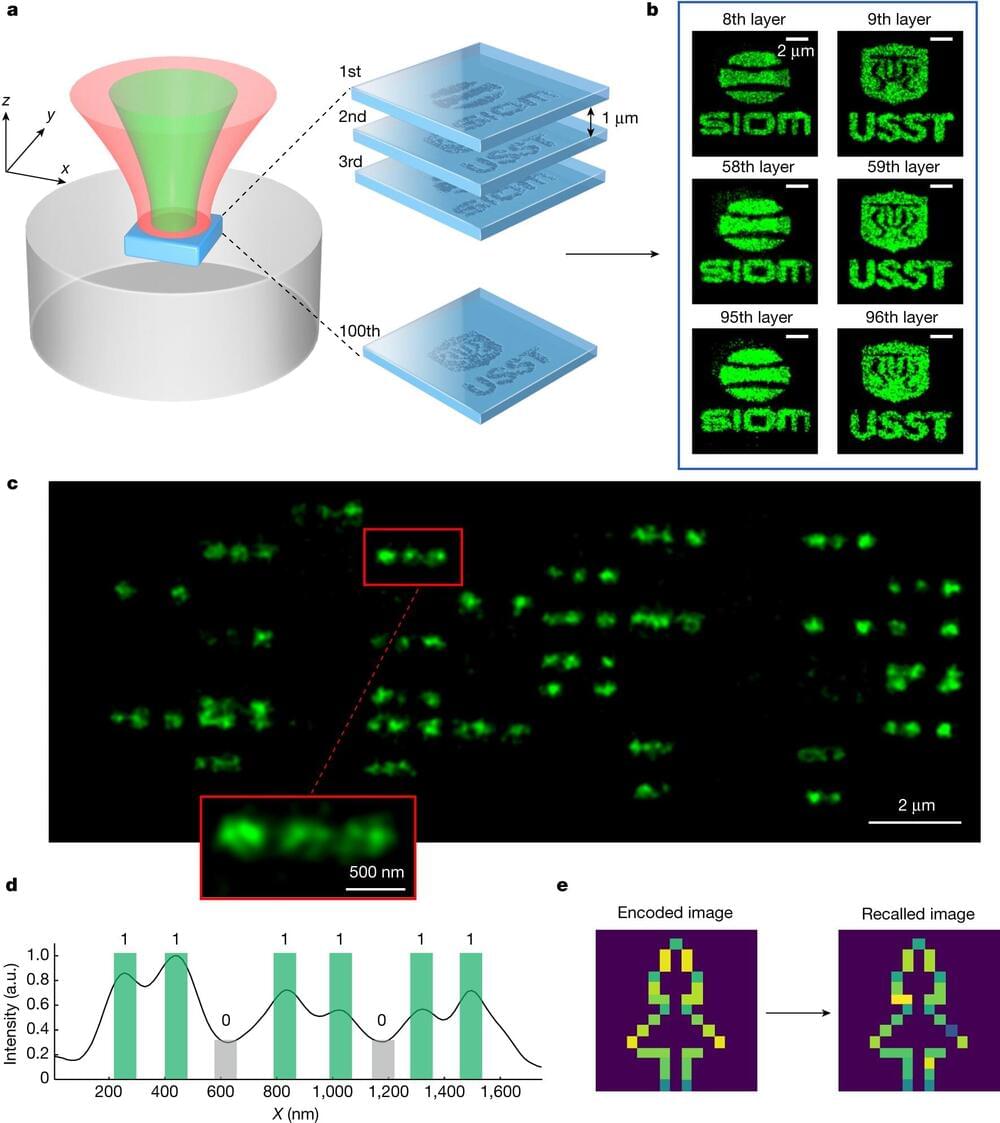
Year 2023 face_with_colon_three
Recycling nutrients is essential for closing nutrient loops within a circular economy. Using locally available resources such as human excreta to produce bio-based recycling fertilizers can substitute mineral fertilizers and thereby promote environmentally friendly food production. To better understand the fertilizer potential and nitrogen value of human excreta, three novel and safe recycling products were evaluated in a field experiment. Two nitrified urine fertilizers (NUFs) and one fecal compost were applied alone or in combination, and compared against the commercial organic fertilizer vinasse. In addition, the uptake of pharmaceuticals was assessed for treatments with compost application. White cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata f. alba) was cultivated in plots in three different soil types (sand, loam or silt) treated with the fertilizers according to plant needs and mineral soil nitrogen content. The two NUFs resulted in marketable yields similar to those of vinasse in all soil types. Combining fecal compost with a NUF led to increased marketable yield compared to compost alone. The highest yield was recorded from the sandy soil, where vinasse and NUF treatments led to comparable yields, as expected in organic productions systems (up to 72 t ha−1). The cabbage yield and total aboveground fresh biomass followed the following trend in all soils: NUFs ∼ vinasse ≥ compost + NUF ≥ compost. Nitrogen uptake in the cabbage heads and total biomass was significantly higher in sand (69.5–144 kg ha−1) than loam (71.4–95.8 kg ha−1). All compost treatments alleviated the effect of soil type and resulted in comparable nitrogen uptake and yield in all soil types. Plant uptake of pharmaceuticals (Carbamazepin) was higher in sand than in loam, and concentration in the edible part was lower than in the outer leaves. In conclusion, NUF alone appears to be a promising successful fertilizer substitute in horticultural food production. The combined application of NUF and compost led to slightly lower crop yields, but may increase soil carbon content in the long term, promoting climate-friendly food production.
In view of a growing world population and the human alteration of nutrient cycles, including nitrogen (N) and phosphorus ℗ (Rockström et al., 2009), transforming food production is a major challenge of this century (Springmann et al., 2018). Both N and P are essential nutrients for healthy plant growth in crop production; however, their addition to synthetic fertilizers is currently organized in a linear economy. The Haber-Bosch process, used to generate plant-available N from its airborne unreactive form, is energy intensive, depending on fossil fuels such as natural gas, and associated with high greenhouse gas emissions (Wang et al., 2021). P is obtained from finite, depleting phosphate rock resources and its mining is increasingly more expensive and polluting (Desmidt et al., 2015). This background emphasize the need for significant improvements of nutrient management in agriculture and for alternative, circular N and P sources to achieve global food security (Gerten et al.