Among startups, the race to start mining asteroids is underway. Their pioneering work could transform our economy – and one day, our ability to explore the universe.


➡🖒⛧Well worth a listen!⛧🖒⬅.
Robots moving deeper into the American workplace—how much decision-making will we turn over to machines?
For all the change that has come with the digital revolution – in the ways we work and communicate and do business – the real impact still lies ahead. Computers – machines themselves – are become smarter all the time. That intelligence is being wired into real world action. That’s overturning giant companies. It’s moving in on what we thought only humans could do. Andrew McAfee and Eric Brynjolfsson are on it. It’s exciting. And terrifying. This hour On Point: intelligent machines move in. — Tom Ashbrook
Guests
Andrew McAfee, co-author of the forthcoming “Machine, Platform, Crowd: Harnessing our Digital Future.” Co-director of the MIT Initiative on the Digital Economy. (@amcafee)

The two academic authors from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, who became the pin-up boys of the Davos crowd for their previous book on The Second Machine Age (2014), do a neat job of scanning the technological horizon and highlighting significant landmarks. This is a clear and crisply written account of machine intelligence, big data and the sharing economy. But McAfee and Brynjolfsson also wisely acknowledge the limitations of their futurology and avoid over-simplification. No one can really have much idea how the business world is going to evolve or predict the precise interplay between all these fast-changing forces.
A new book by the authors of ‘The Second Machine Age’ suggests that digital disruption is coming to the corner office.
Interview with Dr. Jose Luis Cordeiro at the International Longevity and Cryopreservation Summit in Madrid.
During the recent International Longevity and Cryopreservation Summit in Madrid, LEAF Board member Elena Milova had the opportunity to speak with Dr. Jose Luis Cordeiro new fellow of the World Academy of Art and Science (WAAS) and long-term proponent of innovation technologies in many fields. Jose shared his vision on how public perception of rejuvenation technologies is changing over time and what are the main outcomes of the groundbreaking show he and his team managed to organize.
Dr. Cordeiro got his B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees in Mechanical Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, USA, with a minor in Economics and Languages. He is President Emeritus of the Future World Society (Venezuela) and since its foundation about two decades ago Jose managed to become an influential futurist. He is a founding faculty at NASA created Singularity University in Silicon Valley. The goal of the research centre is to tackle global problems such as health, nutrition, poverty and education using the medium of technology. He is also on the board of directors for the Lifeboat Foundation. Jose is part of Fundacion VidaPlus, promoting rejuvenation technologies as well as cryonics, as he believes that people who are too old to make use of the emerging biotechnologies should be granted a plan B in form of cryopreservation. Apart from traveling all over the world to promote innovative ideas in his inspiring talks, Jose has written more than 10 books and co-written over 20 more in five languages, including sections of the State of the Future by the Millennium Project. His extensive associations and achievements are far too numerous to list in this short article, and we invite you to read more about Jose here and also watch his awesome TEDx talk here.

Lifeboat Foundation readers are aware that the world has become progressively more chaotic. Part of the danger comes from centralized points of failure. While large institutions can bear great stress, they also cause more harm when they fail. Because there are so few pillars, if one collapses, the whole system is destroyed.
For instance, prior to the federal reserve system, bank runs we extremely common. However, since the financial system consisted of small, competing institutions, failure was confined to deficient banks. So while failure was frequent, it was less impactful and systemic. In contrast, after the establishment of the federal reserve, banks became fewer and larger. Failures, while more infrequent, were large scale catastrophes when they occurred. They affected the whole economy and had longer impact.
This is even more important in political systems, which are the foundation of how a society operates. In order to have a more robust, antifragile social order, systems must be decentralized. Rather than a monopolistic, static political order, there must be a series of decentralized experiments. While failures are inevitable, it can be localized to these small experiments rather than the whole structure.
We call these small, experimental governments “startup societies”. Examples include smart cities, seasteading, eco-villages, special economic zones, intentional communities, microstates, private cities, Ect. The Startup Societies Foundation studies these experiments, promotes them to the public, and hold conferences.
The Startup Societies Foundation is partnering with D10e to host our biggest conference yet. The Startup Societies Summit is a trade show that unites 300–500 engineers, policy experts, technologists, urban planners, economists, entrepreneurs, and investors interested in building new societies. Attendees with startups related to new societies can engage with investors to push their ideas to fruition. By networking together and sharing valuable information, our guests will be at the forefront starting new societies. The Summit will take place in City College San Francisco on August 11th-12th. If you are interested in buying tickets or becoming a sponsor, here is a link to our crowdfunding campaign.
Like a startup, a startup society begins small and scales when it produces a better service through technology. 65% of the earth’s population will live in cities by 2040. This presents an unprecedented opportunity for entrepreneurs. They can become innovators of the greatest wealth creation tool: cities. Join us and gain an edge in the growing, exciting field of innovative governance.
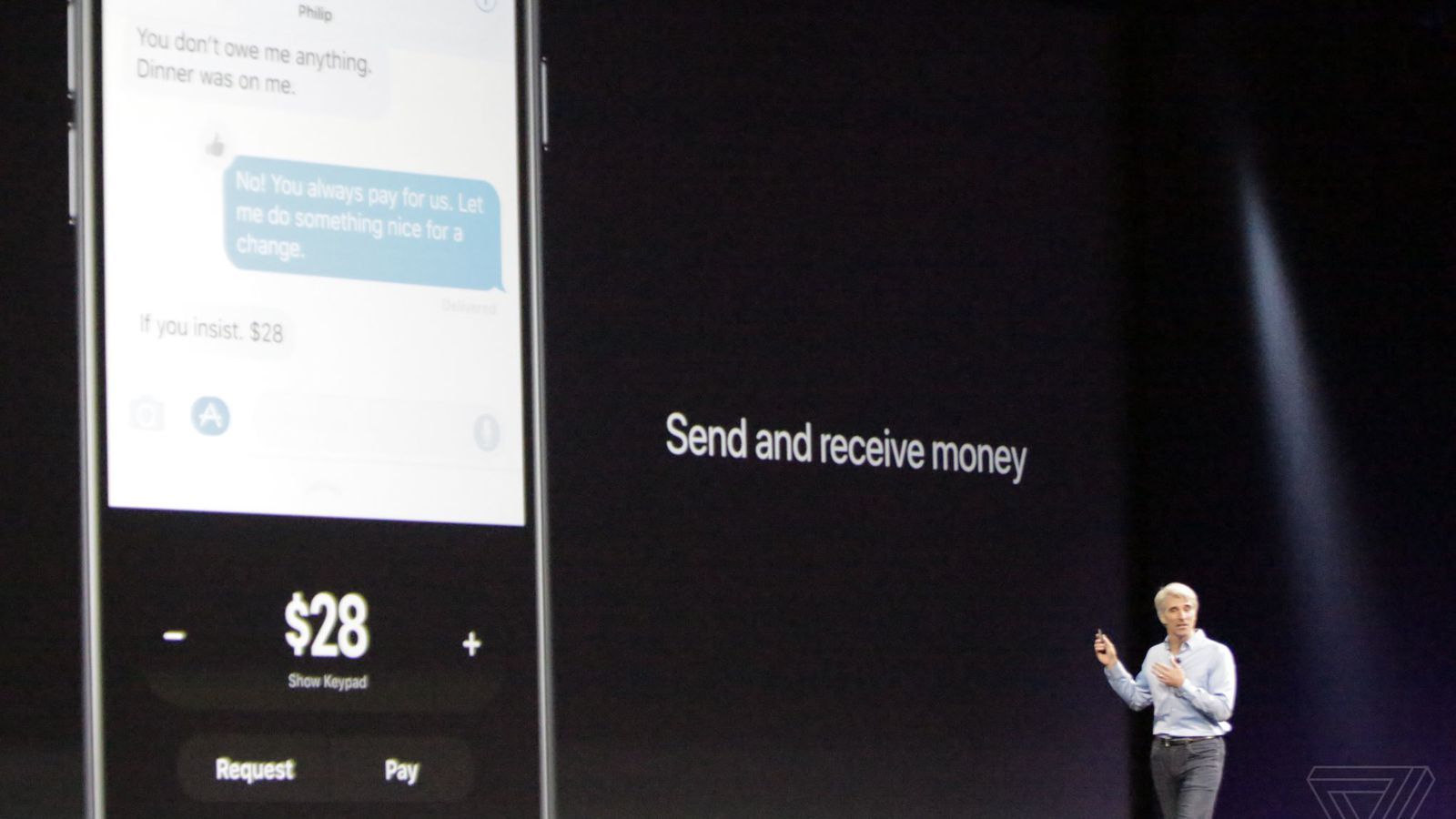
Apple just announced onstage at its Worldwide Developer’s Conference that Apple Pay is getting person-to-person payments. The feature will come in iOS 11, which was announced onstage, and will be available later this year.
It’s an obvious swipe at the part of the payments market that apps like Venmo, PayPal, and Square Cash have cornered. But there’s a catch — P2P payments with Apple Pay will live inside iMessage, and it’s unclear if Apple will let users perform them outside of its messaging app. Also, the money will be transferred to something called an “Apple Pay Cash Card,” which can then be sent to your bank account. That means Apple is not only coming for the Venmos of the world, but maybe the banks themselves.
I’m super excited to share a (via NowThis Op-Ed) video of my bipartisan plan to fund a Basic Income, which I call a Federal Land Dividend. This is a main platform issue of my California Libertarian Governor run. This plan can forever end poverty and lack of health care in California and America—and perhaps even end poverty and lack of health care around the world if adopted by foreign governments.
This futurist has a plan to bring basic income to America.
A mantra of these data-rife times is that within the vast and growing volumes of diverse data types, such as sensor feeds, economic indicators, and scientific and environmental measurements, are dots of significance that can tell important stories, if only those dots could be identified and connected in authentically meaningful ways. Getting good at that exercise of data synthesis and interpretation ought to open new, quicker routes to identifying threats, tracking disease outbreaks, and otherwise answering questions and solving problems that previously were intractable.
Now for a reality check. “Today’s hardware is ill-suited to handle such data challenges, and these challenges are only going to get harder as the amount of data continues to grow exponentially,” said Trung Tran, a program manager in DARPA’s Microsystems Technology Office (MTO). To take on that technology shortfall, MTO last summer unveiled its Hierarchical Identify Verify Exploit (HIVE) program, which has now signed on five performers to carry out HIVE’s mandate: to develop a powerful new data-handling and computing platform specialized for analyzing and interpreting huge amounts of data with unprecedented deftness. “It will be a privilege to work with this innovative team of performers to develop a new category of server processors specifically designed to handle the data workloads of today and tomorrow,” said Tran, who is overseeing HIVE.
The quintet of performers includes a mix of large commercial electronics firms, a national laboratory, a university, and a veteran defense-industry company: Intel Corporation (Santa Clara, California), Qualcomm Intelligent Solutions (San Diego, California), Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (Richland, Washington), Georgia Tech (Atlanta, Georgia), and Northrop Grumman (Falls Church, Virginia).

I finally found a copy of my radio interview at Stanford University last month discussing how I’d pay for a #basicincome by leasing out federal land (called a “Federal Land Dividend”). It’s an hour long interview with a guests asking questions: We discuss transhumanism too.
In this April 18, 2017 episode, we speak with Zoltan Istvan, who ran for President in the Transhumanist party, and is now running for California Governor as a Libertarian. He proposes a Universal Basic Income, funded by the leasing of federal lands. How does this compare to the Georgist ideal of a citizen’s dividend funded by land rents?
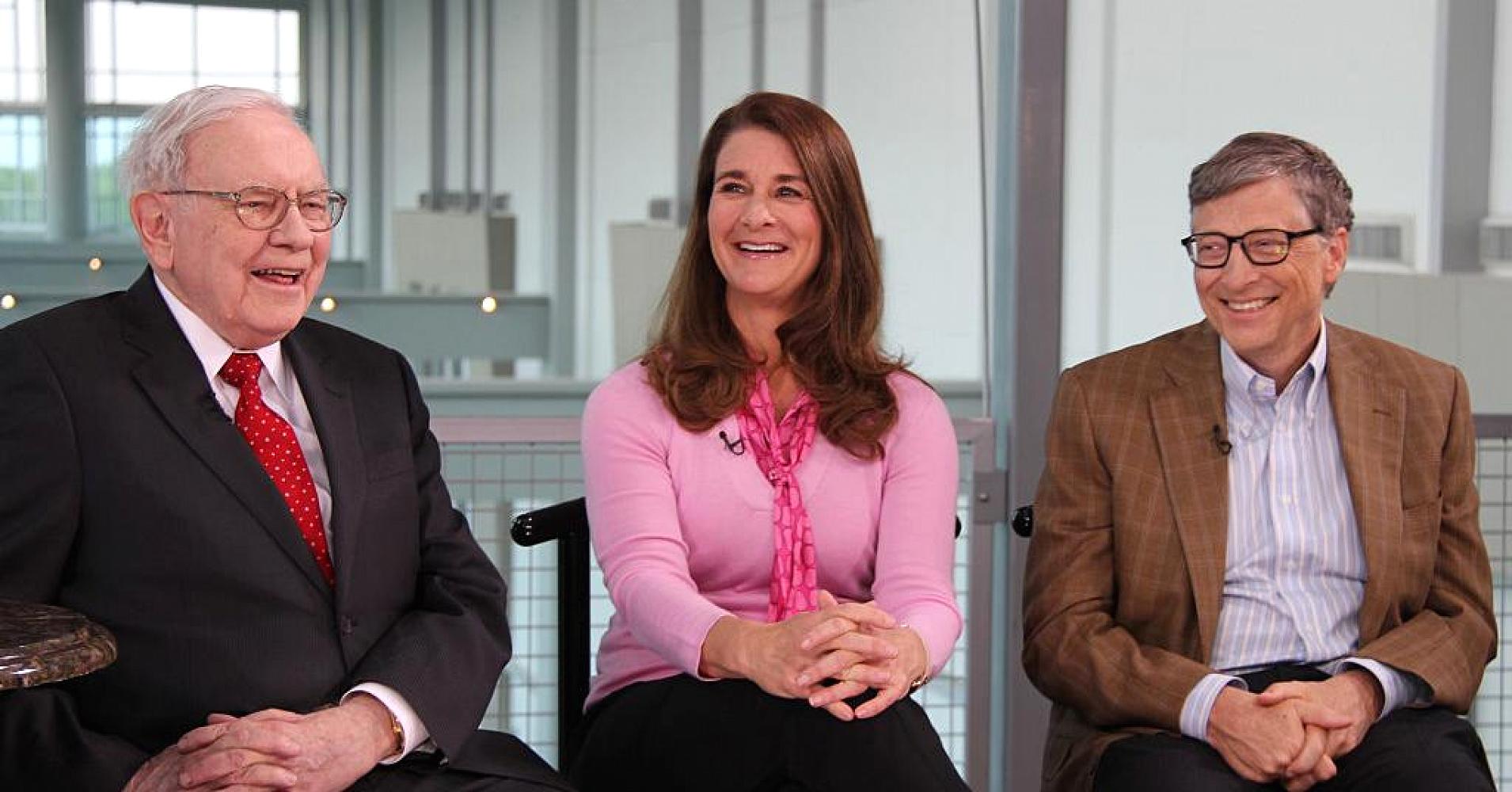

Started in 2010 by Bill and Melinda Gates, worth $88.5 billion, and Warren Buffett, worth $74.2 billion, the Giving Pledge is a commitment by wealthy individuals and families to give away more than half of their wealth to causes including including poverty alleviation, refugee aid, disaster relief, global health, education, women and girls’ empowerment, medical research, arts and culture, criminal justice reform and environmental sustainability.
Started in 2010, the Giving Pledge now includes 168 wealthy individuals and couples from 21 countries.