Brighter with Herbert
Category: economics – Page 19

‘Qubits For Peace’: Researchers Warn Quantum Technology Is Deepening The Global Divide
Countries in the Global South risk being left out of the quantum revolution — along with its economic, technological and security benefits — due to growing export controls, siloed research initiatives and national security concerns, a new policy analysis argues.
In the first of a series of articles on quantum technologies published by the policy journal Just Securit y, researchers Michael Karanicolas, of Dalhousie University, and Alessia Zornetta, of UCLA Law, examine how the geopolitics of emerging quantum technologies are replicating long-standing patterns of technological exclusion. The authors argue that absent meaningful interventions, quantum could become another engine of global inequality, one that threatens to lock poorer nations out of the next era of technological and economic development.
The authors trace the roots of this divide to export control regimes that are quickly expanding in response to the strategic potential of quantum systems. Since 2020, governments in the U.S., EU and China have implemented targeted restrictions on quantum-enabling hardware, software, and communications systems.
The Futurists — EPS_286: The Meaning Economy with David Shapiro
In this week’s episode we interview author, AI theorist and researcher David Shapiro is part philosopher, part theorist with a fair bit of practical wisdom thrown in. With a hit YouTube channel Shapiro travels the globe as a speaker and advisor musing on the longer-term impacts of AI, technology and human adaptability. In this deep conversation with host Brett King, we delve into the ways in which advanced AI might completely transform our way of life, including economics, politics and what it means to be human itself. This is not one you’ll want to miss.
Follow David Shapiro: @DaveShap
ABOUT SHOW
Subscribe and listen to TheFuturists.com Podcast where hosts Brett King and Robert TerceK interview the worlds foremost super-forecasters, thought leaders, technologists, entrepreneurs and futurists building the world of tomorrow. Together we will explore how our world will radically change as AI, bioscience, energy, food and agriculture, computing, the metaverse, the space industry, crypto, resource management, supply chain and climate will reshape our world over the next 100 years. Join us on The Futurists and we will see you in the future!
HOSTS
https://thefuturists.com/info/hosts-b… / brettking & http://brettking.com/
/ superplex &https://roberttercek.com/ SUBSCRIBE & LISTEN https://thefuturists.com/info/listen–… https://open.spotify.com/show/0nvdnEs… https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast… https://blubrry.com/thefuturists/ FOLLOW & ENGAGE
/ futuristpodcast
/ futuristpodcast
/ thefuturistspodcast
/ @thefuturistspodcast GET EVEN MORE https://thefuturists.com/exclusive/
/ brettking & http://brettking.com/
/ superplex & https://roberttercek.com/
SUBSCRIBE & LISTEN
https://thefuturists.com/info/listen–…
https://open.spotify.com/show/0nvdnEs…
https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast…
https://blubrry.com/thefuturists/
FOLLOW & ENGAGE
Tony Seba Predicts Robot Super Abundant Future
Brighter with Herbert
China Lights Up the Sky with a Secret Weapon Test
China conducted a secret weapon test that has caught the US intelligence community off guard. Back in August, China lit up the sky when it tested a nuclear-capable hypersonic missile, which travels faster than the speed of sound. The global shipping supply crisis might affect Christmas, thanks in part to China’s power shortage. And a man in Jiangsu Province takes drastic measures after his daughter fails to solve a math problem correctly. Watch this episode of China Uncensored for that and more of this week’s China news headlines.
Jack ma’s dirty secret | power struggle rips ant financial • jack ma’s dirty secret | power strugg…
China’s POWER SHORTAGE could cause economic collapse • china’s POWER SHORTAGE could cause ec…
YouTube demonetizes our channels, we need your support!
www.patreon.com/ChinaUncensored.
https://chinauncensored.locals.com.
We also accept bitcoin!
https://chinauncensored.tv/bitcoin.
Buy our merchandise!

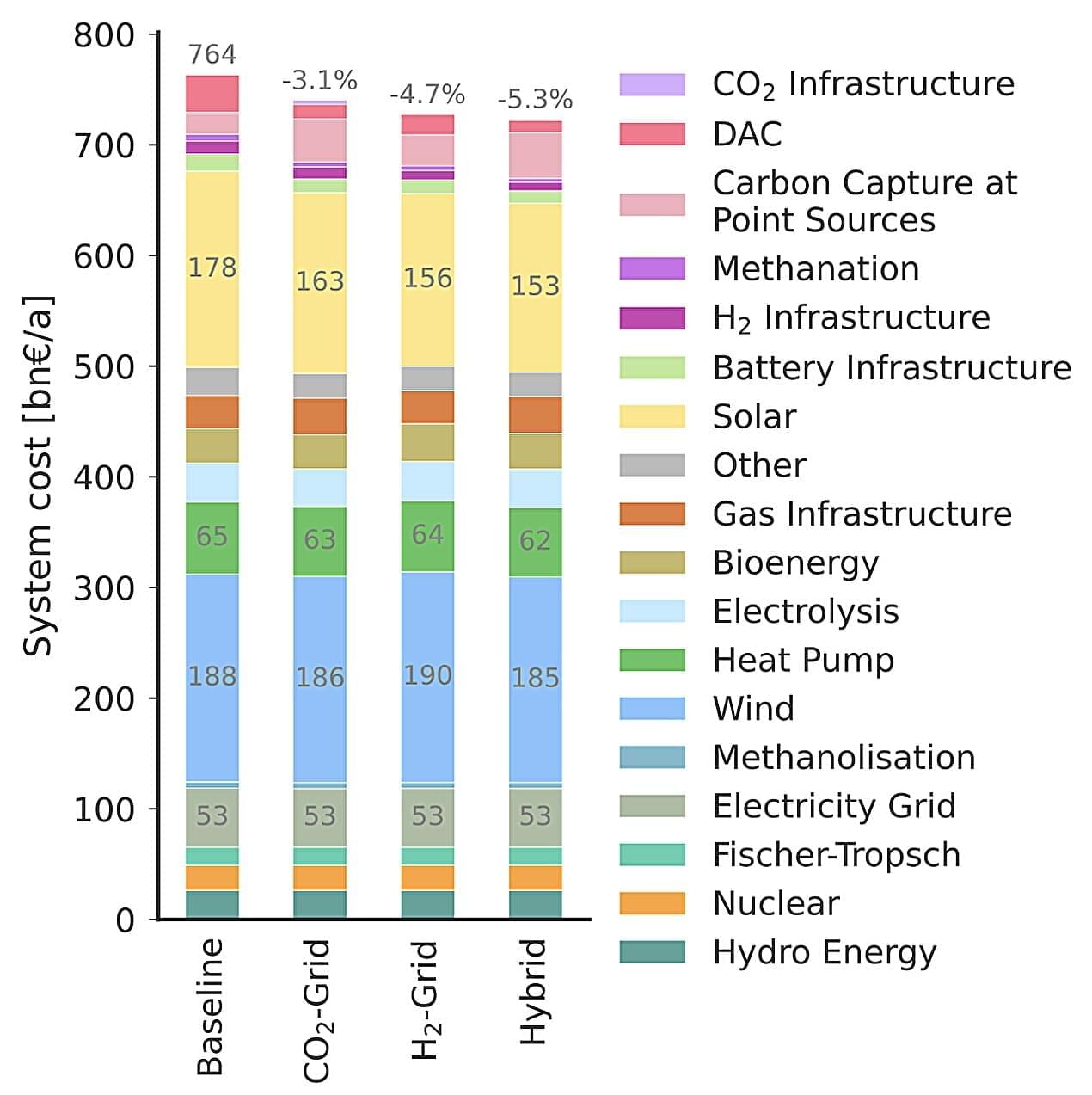
Assessing the potential of hydrogen and carbon dioxide networks for the future of European energy systems
Over the past decades, many countries worldwide have been trying to gradually transform their energy systems, with the aim of reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the adverse effects of climate change. Hydrogen and carbon dioxide (CO2) transport networks, infrastructures designed to transport hydrogen gas and captured CO2, could support the shift towards climate-neutral energy systems.
Researchers at Technical University Berlin carried out a study aimed at better understanding the extent to which hydrogen and CO2 transport networks could contribute to the future de-carbonization of the European energy system. Their paper, published in Nature Energy, suggests that both these types of networks could play a key role in establishing a sustainable and clean European energy system.
“In our view, we are envisioning a climate-friendly economy which relies as little as possible on fossil fuels and respects socio-economic considerations,” Fabian Hofmann, first author of the paper, told Tech Xplore.
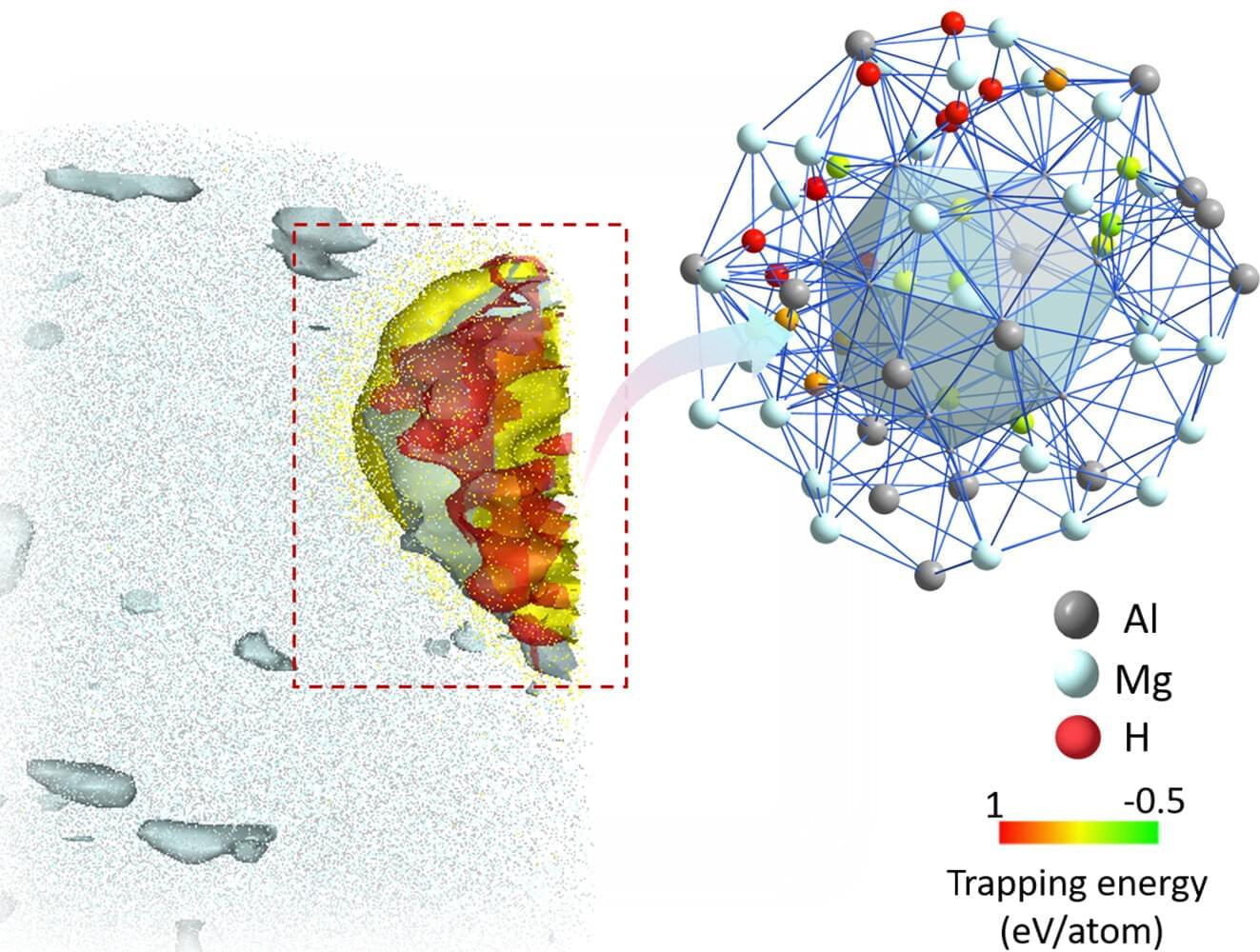
Stronger and safer: New design strategy for aluminum combines strength with hydrogen embrittlement resistance
Aluminum alloys are well-known for their low weight and corrosion resistance, making them ideal candidates for applications in a low-carbon economy—from lightweight automobiles to tanks for storing green hydrogen. However, their widespread application is limited by a key challenge: they suffer from embrittlement leading to cracking and failure when exposed to hydrogen. Until now, alloys resistant to hydrogen embrittlement were rather soft, limiting their application in hydrogen-related technologies that require high strength.
Now, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Sustainable Materials (MPI-SusMat) in Germany, together with partners from China and Japan, have developed a new alloy design strategy that overcomes this dilemma. Their approach enables both exceptional strength and superior resistance to hydrogen embrittlement (HE), paving the way for safer and more efficient aluminum components in the hydrogen economy. They have published their results in the journal Nature.
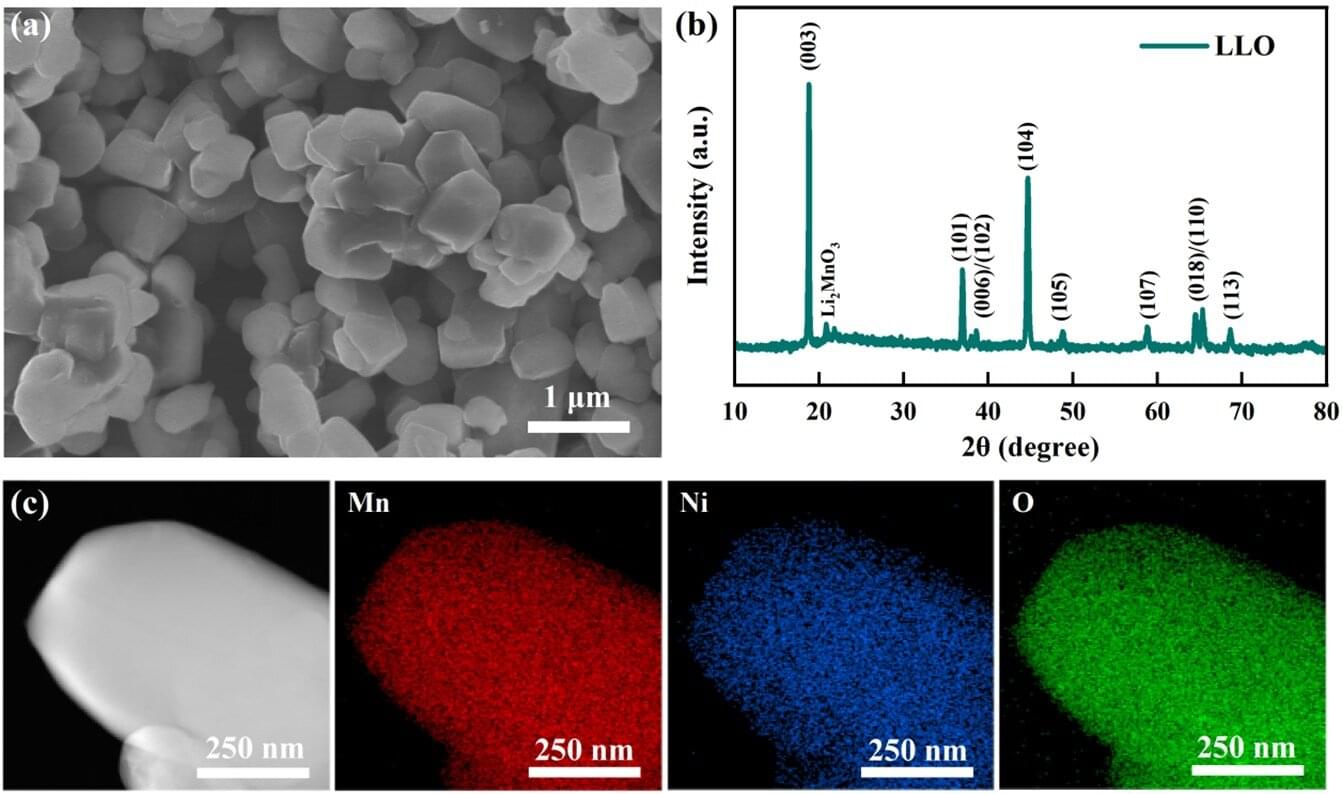
Real-time magnetic structure tracking reveals oxygen redox in Li-rich cathode materials
Recently, a research team achieved real-time tracking of electronic/magnetic structure evolution in Li-rich Mn-based materials during the initial cycling through the self-developed operando magnetism characterization device.
Their study, published in Advanced Materials, elucidated the critical mechanism underlying the oxygen redox reaction. The research team was led by Prof. Zhao Bangchuan from the Institute of Solid State Physics, the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. Zhong Guohua from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology and Prof. Li Qiang from Qingdao University.
With the rise of electric vehicles and the low-altitude economy, the demand for high-energy-density batteries is growing. Li-rich Mn-based materials stand out due to their high capacity, wide voltage range, and cost-effectiveness.