How will artificial intelligence, molecular manufacturing, biological engineering and distributed additive manufacturing change the economics of the production of goods and services?



Lighter than air! Stronger than steel! More flexible than rubber! No, it’s not an upcoming superhero flick: It’s the latest marvelous formulation of carbon nanotubes–at least as reported by the creators of the new super-material. Researchers working on artificial muscles say they’ve created nanotech ribbons that make our human muscles look puny by comparison. The ribbons, which are made of long, entangled 11-nanometer-thick nanotubes, can stretch to more than three times their normal width but are stiffer and stronger than steel… They can expand and contract thousands of times and withstand temperatures ranging from −190 to over 1,600 °C. What’s more, they are almost as light as air, and are transparent, conductive, and flexible [Technology Review].
The material is made from bundles of vertically aligned nanotubes that respond directly to electricity. Lengthwise, the muscle can expand and contract with tremendous speed; from side-to-side, it’s super-stiff. Its possibilities may only be limited by the imaginations of engineers. [The material’s composition] “is akin to having diamond-like behavior in one direction, and rubber-like behavior in the others” [Wired], says material scientist John Madden, who wasn’t involved in the research.
When voltage is applied to the material, the nanotubes become charged and push each other away, causing the material to expand at a rate of 37,000 percent per second, tripling its width. That’s 10 times as far and 1000 times as fast as natural muscle can move, and the material does so while generating 30 times as much force as a natural muscle [IEEE Spectrum]. The researchers put together a video to illustrate the concept, and will publish their work in Science tomorrow.
I agree with the need to prepare.
Yea…maybe. We may see a US stock market crash this year. Truth is we are way over do for a market correction and when it does hit, this may cause a major financial crisis and recession in the US and globally. Are you prepared? 🤔
🔥Recommended Survival Gear🔥
{Support the channel with these affiliate links }
◼ESEE 5P Black Tactical Survival Knife w/ Sheath.

“Very dependent on volume, but I’m confident moving to Mars (return ticket is free) will one day cost less than $500k & maybe even below $100k,” he wrote. “Low enough that most people in advanced economies could sell their home on Earth & move to Mars if they want.”
The extraordinary ambition of Musk’s prediction wasn’t lost on some Twitter users. “Fyre Festival Part Deux,” one replied.
Maybe that skepticism is why, in a follow –up reply, Musk seemed to hedge his bets.
“Just planning on keeping the public informed about progress & setbacks,” he wrote. “Will be some [Rapid Unscheduled Disassemblies] along the way, but excitement is guaranteed!”
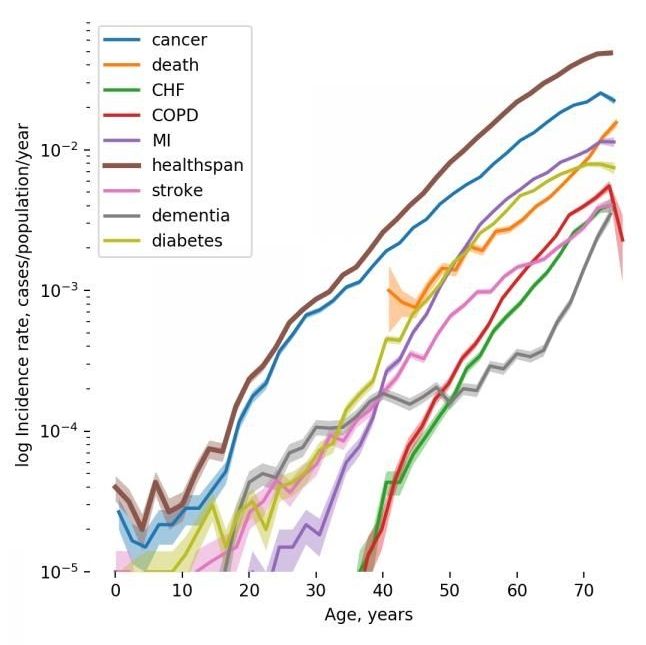
The global population aged 60 or over is growing faster than all younger age groups and faces the tide of chronic diseases threatening their quality of life and posing challenges to healthcare and economy systems. To better understand the underlying biology behind healthspan — the healthy period of life before the first chronic disease manifestation — the scientists from Gero and MIPT collaborated with the researchers from PolyOmica, the University of Edinburgh and other institutes to analyze genetic data and medical histories of over 300,000 people aged 37 to 73 made available by UK Biobank.
The study published today in Communications Biology was lead by Dr. Peter Fedichev and Prof. Yurii Aulchenko. It shows that the most prevalent chronic conditions such as cancer, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, dementia, and some others apparently share the common underlying mechanism that is aging itself.
«According to Gompertz mortality law, the risk of death from all causes increases exponentially after the age of 40 and doubles approximately every 8 years», explains Peter Fedichev, founder and CSO of Gero. «By analyzing the dynamics of disease incidence in the clinical data available from UKB, we observed that the risks of age-related diseases grow exponentially with age and double at a rate compatible with the Gompertz mortality law. This close relation between the most prevalent chronic diseases and mortality suggests that their risks could be driven by the same process, that is aging. This is why healthspan can be used as a natural proxy for investigation of the genetic factors controlling the rate of aging, the “holy grail” target for anti-aging interventions».


The researchers found that people have a moral preference for supporting good causes and not wanting to support harmful or bad causes. However, depending on the strength of the monetary incentive, people will at one point switch to selfish behavior. When the authors reduced the excitability of the rTPJ using electromagnetic stimulation, the participants’ moral behavior remained more stable.
“If we don’t let the brain deliberate on conflicting moral and monetary values, people are more likely to stick to their moral convictions and aren’t swayed, even by high financial incentives,” explains Christian Ruff. According to the neuroeconomist, this is a remarkable finding, since: “In principle, it’s also conceivable that people are intuitively guided by financial interests and only take the altruistic path as a result of their deliberations.”
Our actions are guided by moral values. However, monetary incentives can get in the way of our good intentions. Neuroeconomists at the University of Zurich have now investigated in which area of the brain conflicts between moral and material motives are resolved. Their findings reveal that our actions are more social when these deliberations are inhibited.
When donating money to a charity or doing volunteer work, we put someone else’s needs before our own and forgo our own material interests in favor of moral values. Studies have described this behavior as reflecting either a personal predisposition for altruism, an instrument for personal reputation management, or a mental trade-off of the pros and cons associated with different actions.
Impact of electromagnetic stimulation on donating behavior
A research team led by UZH professor Christian Ruff from the Zurich Center for Neuroeconomics has now investigated the neurobiological origins of unselfish behavior. The researchers focused on the right Temporal Parietal Junction (rTPJ) — an area of the brain that is believed to play a crucial role in social decision-making processes. To understand the exact function of the rTPJ, they engineered an experimental set-up in which participants had to decide whether and how much they wanted to donate to various organizations. Through electromagnetic stimulation of the rTPJ, the researchers were then able to determine which of the three types of considerations — predisposed altruism, reputation management, or trading off moral and material values — are processed in this area of the brain.

US$190 million in investors’ money has been locked since Cotten died in December. His widow says she doesn’t know his passwords.
About US$190 million in cryptocurrency has been locked away in a online black hole after the founder of a currency exchange died, apparently taking his encrypted access to their money with him.
Investors in QuadrigaCX, Canada’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, have been unable to access their funds since its founder, Gerald Cotten, died last year.


Behold the new black gold. Dark and warm, it oozes water and teems with beneficial properties. It even harbors precious metals.
And boy does it stink.
Call it the excrement economy. Between the rise of fecal transplants and water strained from latrine sludge, the poop market is hot. Besides removing toxic waste, the commodification of crap could mean big bucks, especially in the developing world. Sounds crazy, but look at what happened with used cooking oil — now processed into biofuel instead of dumped into landfills — which went from being worth nothing in the early 2000s to $3.30 a gallon in 2011, according to the Utah Biodiesel Supply.
