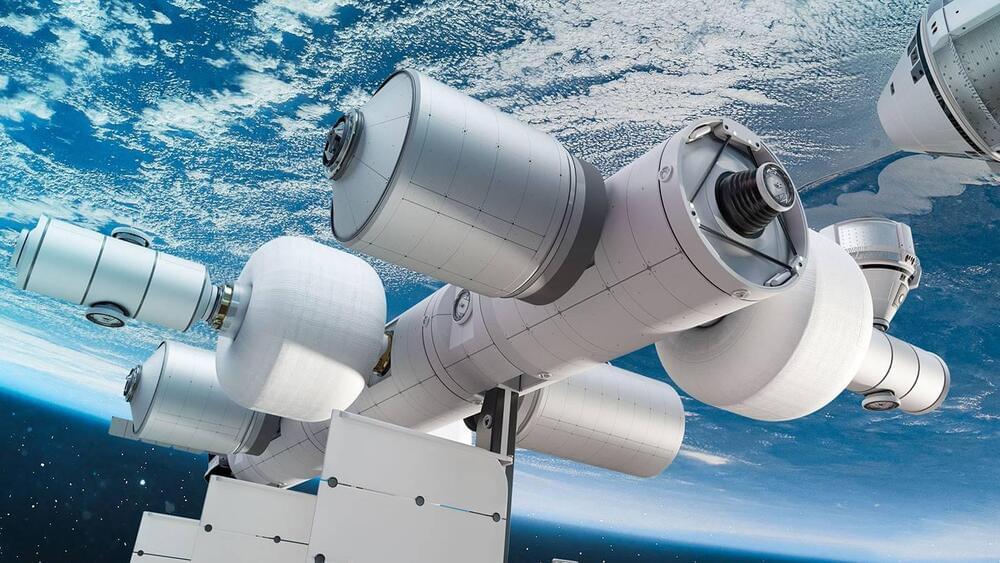
Following October’s news that Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin spaceflight company planned to build its own commercial space station in low Earth orbit, NASA announced on Thursday it has selected the program for funding through a Space Act Agreement to further develop the station’s design. The funding is part of NASA’s Commercial LEO Development program, which aims to “develop a robust commercial space economy in LEO, including supporting the development of commercially owned and operated LEO destinations.”
“We are pleased that NASA supports the development of Orbital Reef, a revolutionary approach to making Earth orbit more accessible to diverse customers and industries,” Brent Sherwood, Senior Vice President of Advanced Development Programs for Blue Origin, said in a prepared statement. The station would be an orbital “mixed-use space business park” that would offer any number of turnkey services as well as reduced operational costs for burgeoning low-g industries “in addition to meeting the ISS partners’ needs.”
Blue Origin is partnering with Sierra Space in this project with the former focusing on the architecture and infrastructure of the station — everything from its design and construction to managing lift logistics using the New Glenn heavy launch system — while the latter is tasked with developing the station’s LIFE (Large Integrated Flexible Environment). Boeing is also helping out, designing the operations-maintenance-science module and leveraging its Starliner crew capsule. Genesis Engineering Solutions is involved as well. It’s working on a single person spacecraft that tourists and employees alike will be able to putter around in.