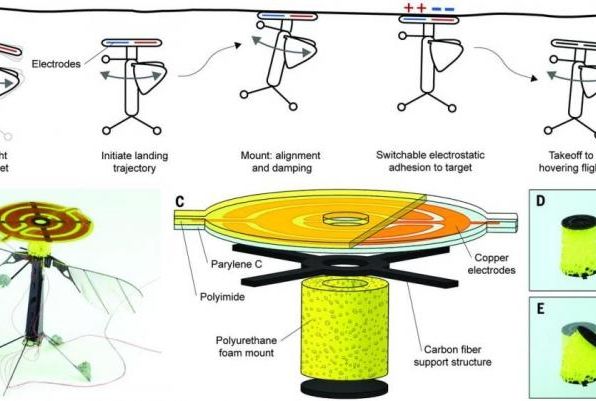
BOSTON, May 19 (UPI) — Engineers at MIT and Harvard have designed a tiny bee-like robot capable of pausing mid-flight to perch on a variety of objects before once again taking to the air. The robot uses static electricity to momentarily cling to the underside of objects.
Robots designed for aerial surveys and related observational tasks, like quadcopters, are currently limited by short flight times. They tend to run out of battery rather quickly. While perching won’t extend a drone’s actual time in the air, the technology could empower UAVs to employ their power more strategically — periodically taking a moment to rest their wings, or blades.
Researchers tested their technology on RoboBee, a bug-like flying robot no bigger than a quarter. A small jolt of static electricity emitted through a tiny foam patch on the bee’s head allows it to land on and adhere to the underside of a plant or to the ceiling.