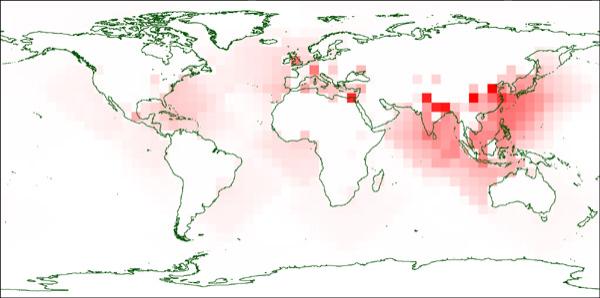
Using maps of population density, the researchers charted the places likely to suffer the most casualties from asteroids. As might be expected, countries with large coastal populations turned out to be most vulnerable, with China, Indonesia, India, Japan and the US in the top five spots.
The team focused on smaller asteroids because they hit the Earth more frequently. An asteroid a few hundred metres across hits the planet about once every 10,000 years, on average, while those larger than 1 kilometre hit only every 100,000 years or so. Small asteroids are also harder to spot. They considered a range of impact energies corresponding to asteroids between 100 and 500 metres across, striking with typical solar system speeds of about 20,000 kilometres per second.
Simulations show the asteroid impact locations that would produce the most casualties in red. The Pacific coast of Asia is a particularly deadly place for an asteroid to strike because of tsunamis, while a direct strike on some densely populated inland areas could also cause a heavy toll (Illustration: Nick Bailey et al/University of Southampton)
The US faced the worst potential economic losses, since it has a lot of infrastructure on coastlines facing two different oceans. China was second, followed by Sweden, Canada, and Japan.
The Lifeboat asteroid shield project helps to address these risks and Tsunami warning and response systems would also help mitigate loss of life from ocean impacts.