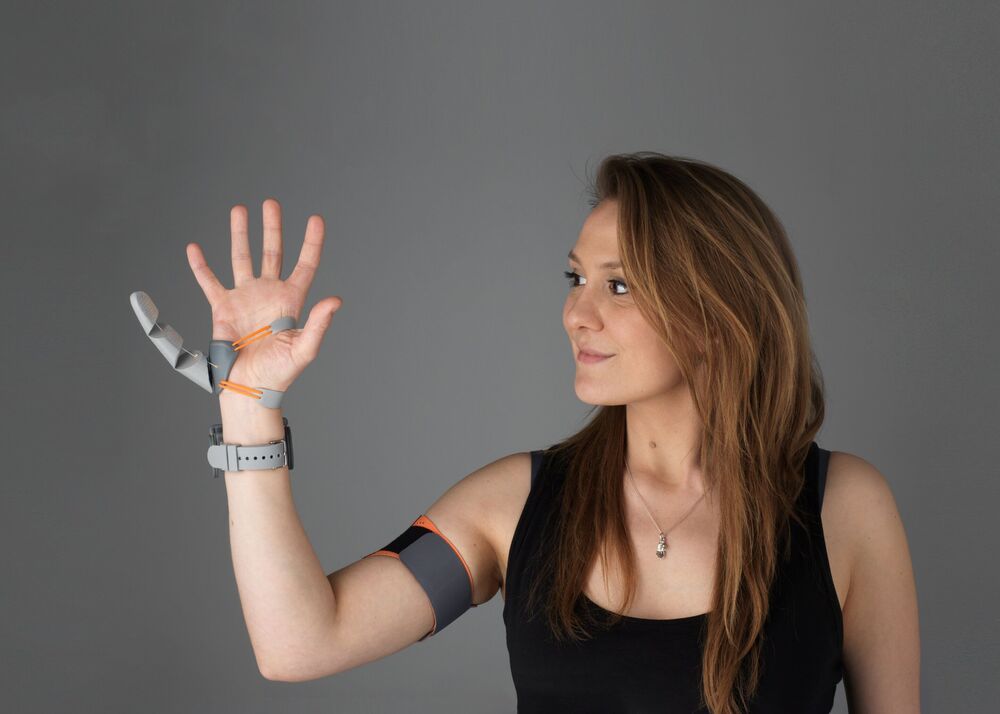
Using a robotic ‘Third Thumb’ can impact how the hand is represented in the brain, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The team trained people to use a robotic extra thumb and found they could effectively carry out dextrous tasks, like building a tower of blocks, with one hand (now with two thumbs). The researchers report in the journal Science Robotics that participants trained to use the thumb also increasingly felt like it was a part of their body.
Designer Dani Clode began developing the device, called the Third Thumb, as part of an award-winning graduate project at the Royal College of Art, seeking to reframe the way we view prosthetics, from replacing a lost function, to an extension of the human body. She was later invited to join Professor Tamar Makin’s team of neuroscientists at UCL who were investigating how the brain can adapt to body augmentation.