The U.S. government has warned for years that products from Chinese tech giant Huawei Technologies Co. pose a national security risk. Now, a Bloomberg investigation has found a key piece of evidence explaining why. Bloomberg’s Jamie Tarabay reports on “Bloomberg Daybreak: Asia.”
Category: cybercrime/malcode – Page 193
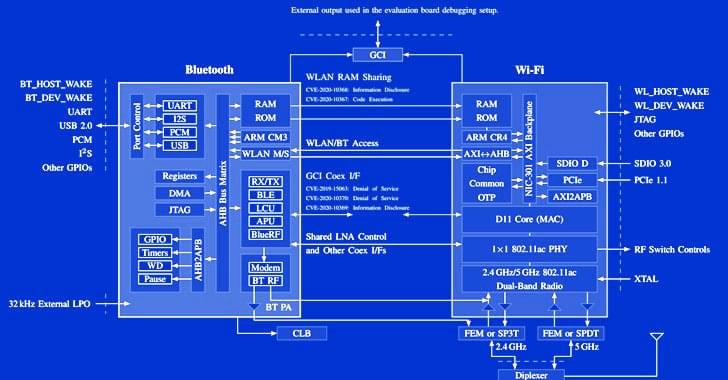
Researchers Uncover New Coexistence Attacks On Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Chips
Cybersecurity researchers have demonstrated a new attack technique that makes it possible to leverage a device’s Bluetooth component to directly extract network passwords and manipulate traffic on a Wi-Fi chip, putting billions of electronic devices at risk of stealthy attacks.
The novel attacks work against the so-called “combo chips,” which are specialized chips that are equipped to handle different types of radio wave-based wireless communications, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LTE.
“We provide empirical evidence that coexistence, i.e., the coordination of cross-technology wireless transmissions, is an unexplored attack surface,” a group of researchers from the Technical University of Darmstadt’s Secure Mobile Networking Lab and the University of Brescia said in a new paper.



Neural networks can hide malware, and scientists are worried
This article is part of our reviews of AI research papers, a series of posts that explore the latest findings in artificial intelligence.
With their millions and billions of numerical parameters, deep learning models can do many things: detect objects in photos, recognize speech, generate text—and hide malware. Neural networks can embed malicious payloads without triggering anti-malware software, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of Illinois have found.
Their malware-hiding technique, EvilModel, sheds light on the security concerns of deep learning, which has become a hot topic of discussion in machine learning and cybersecurity conferences. As deep learning becomes ingrained in applications we use every day, the security community needs to think about new ways to protect users against their emerging threats.




New Cyber Protections Against Stealthy “Logic Bombs” Targeting 3D Printed Drones, Prostheses and Medical Devices
Cyber attackers could target 3D printed objects in health care, aerospace, and other fields.
Cybersecurity researchers at Rutgers University-New Brunswick and the Georgia Institute of Technology have proposed new ways to protect 3D printed objects such as drones, prostheses, and medical devices from stealthy “logic bombs.”
The researchers will present their paper, titled “Physical Logic Bombs in 3D Printers via Emerging 4D Techniques,” at the 2021 Annual Computer Security Applications Conference on December 10, 2021.

Global race to patch critical computer bug
Security experts around the world raced Friday to patch one of the worst computer vulnerabilities discovered in years, a critical flaw in open-source code widely used across industry and government in cloud services and enterprise software.
“I’d be hard-pressed to think of a company that’s not at risk,” said Joe Sullivan, chief security officer for Cloudflare, whose online infrastructure protects websites from malicious actors. Untold millions of servers have it installed, and experts said the fallout would not be known for several days.
New Zealand’s computer emergency response team was among the first to report that the flaw in a Java-language utility for Apache servers used to log user activity was being “actively exploited in the wild” just hours after it was publicly reported Thursday and a patch released.