Researchers have taken the wraps off “Symbiote,” what they call a “nearly-impossible-to-detect” Linux malware that’s targeting the financial sector.
Category: cybercrime/malcode – Page 176
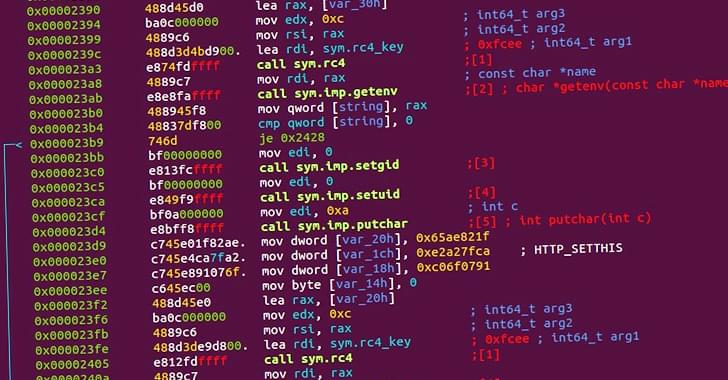
Symbiote: A Stealthy Linux Malware Targeting Latin American Financial Sector
Cybersecurity researchers have taken the wraps off what they call a “nearly-impossible-to-detect” Linux malware that could be weaponized to backdoor infected systems.
Dubbed Symbiote by threat intelligence firms BlackBerry and Intezer, the stealthy malware is so named for its ability to conceal itself within running processes and network traffic and drain a victim’s resources like a parasite.
The operators behind Symbiote are believed to have commenced development on the malware in November 2021, with the threat actor predominantly using it to target the financial sector in Latin America, including banks like Banco do Brasil and Caixa, based on the domain names used.

Ethereum Moves Closer to Blockchain Revamp After Milestone Test
Ethereum, the world’s most used cryptocurrency blockchain network, passed a milestone test ahead of a highly anticipated technical upgrade without any major glitches.
Developers ran the latest software for the upgrade known as the Merge on Ropsten, which is one of the oldest so-called testnets of the network. The testnets are used by developers to find potential bugs and glitches before moving their applications to the blockchain. While the Merge has been carried out on other testnets earlier this year, Ropsten was seen as providing the most realistic technical environment and the best estimate for the outcome of the final process.

Chinese hacking group Aoqin Dragon quietly spied orgs for a decade
Žilvinas DeveikaIt’s much sooner than that. My prediction (that is almost 10 years old now) of an “early” appearance of a strong AGI is 2029. I am completely sure that it will either emerge or will already be there in 2030s.
24 Replies.
Marc O MonfilsAnd what strategies do we have in place to guarantee humanity’s continued relevance in the era of super intelligent machines?
Empathy? Never saved any tribe in the past…
Human services and interaction? For what, to keep our irrelevance engaged?… See more.
5 Replies.
View 9 more comments.
Gone in 130 seconds: New Tesla hack gives thieves their own personal key
You may want to think twice before giving the parking attendant your Tesla-issued NFC card.

“Firehose” of raw data: Twitter agrees to provide complete ‘Fake Accounts’ data to Elon Musk
According to multiple news reports, Twitter plans to give Elon Musk access to its “firehose” of raw data on hundreds of millions of daily tweets in an effort to speed up the Tesla billionaire’s $44 billion acquisition of the social media platform. The data-sharing agreement was not confirmed by the lawyers involved in the deal. Musk was silent on Twitter, despite having previously expressed his displeasure with various aspects of the deal.
Twitter declined to comment on the reports, pointing to a statement released on Monday in which the company stated that it is continuing to “cooperate” and share information with Musk, who in April entered into a legally binding agreement to purchase Twitter, claims that the transaction cannot go forward until the firm discloses more information on the frequency of bogus accounts on its network. He claims, without providing evidence, that Twitter has grossly underestimated the number of “spam bots” on its platform, which are automated accounts that typically promote scams and misinformation.
On Monday, the Attorney General of the State of Texas, Ken Paxton, said that his office will be investigating “possible false reporting” of bot activity on Twitter as part of an inquiry against Twitter for allegedly failing to disclose the scale of its spam bot and fake account activity. According to a source familiar with the situation, Twitter’s plan to give Musk full access to the firehose was first reported by the Washington Post. According to other reports, the billionaire may only have limited access.
Radio waves for the detection of hardware tampering
As far as data security is concerned, there is an even greater danger than remote cyberattacks: namely tampering with hardware that can be used to read out information—such as credit card data from a card reader. Researchers in Bochum have developed a new method to detect such manipulations. They monitor the systems with radio waves that react to the slightest changes in the ambient conditions. Unlike conventional methods, they can thus protect entire systems, not just individual components—and they can do it at a lower cost. The RUB’s science magazine Rubin features a report by the team from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB), the Max Planck Institute for Security and Privacy and the IT company PHYSEC.
Paul Staat and Johannes Tobisch presented their findings at the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, which took place in the U.S. from 23 to 25 May 2022. Both researchers are doing their Ph.D.s at RUB and conducting research at the Max Planck Institute for Security and Privacy in Bochum in Professor Christof Paar’s team. For their research, they are cooperating with Dr. Christian Zenger from the RUB spin-off company PHYSEC.

Musk will drop Twitter deal if data on bots not provided
In a new letter, Elon Musk threatens to walk away from $44 Billion Twitter deal if the management doesn’t provide more data on total bot counts.
According to a letter sent by Elon Musk’s legal team to Twitter, “Twitter refused to provide the information that Mr. Musk has repeatedly requested since May 9, 2022 to facilitate his evaluation of spam and fake accounts on the company’s platform” and “It’s effort to characterize it otherwise is merely an attempt to obfuscate and confuse the issue”.
The letter also reminded that Musk does not believe the company’s lax testing methodologies are adequate so he must conduct his own analysis and “The data he has requested is necessary to do so”. The letter also said “Mr. Musk is entitled to seek, and Twitter is obligated to provide information and data”.

Automatic debugging of software
Circa 2016
Computer programs often contain defects, or bugs, that need to be found and repaired. This manual “debugging” usually requires valuable time and resources. To help developers debug more efficiently, automated debugging solutions have been proposed. One approach goes through information available in bug reports. Another goes through information collected by running a set of test cases. Until now, explains David Lo from Singapore Management University’s (SMU) School of Information Systems, there has been a “missing link” that prevents these information gathering threads from being combined.
Dr Lo, together with colleagues from SMU, has developed an automated debugging approach called Adaptive Multimodal Bug Localisation (AML). AML gleans debugging hints from both bug reports and test cases, and then performs a statistical analysis to pinpoint program elements that are likely to contain bugs.
“While most past studies only demonstrate the applicability of similar solutions for small programs and ‘artificial bugs’ [bugs that are intentionally inserted into a program for testing purposes], our approach can automate the debugging process for many real bugs that impact large programs,” Dr Lo explains. AML has been successfully evaluated on programs with more than 300,000 lines of code. By automatically identifying buggy code, developers can save time and redirect their debugging effort to designing new software features for clients.
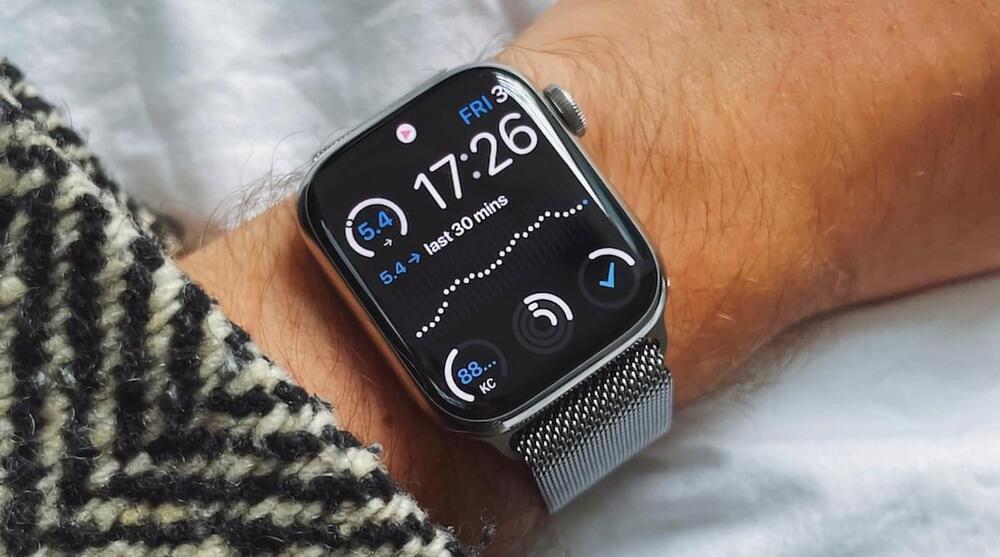

Homebrew project adds continuous glucose monitoring to the Apple Watch
An Apple Watch owner has created a complication and watchOS app that works with a glucose monitor, so they can keep track of their blood glucose level from their wrist.
Numerous rumors have claimed Apple is actively working on some form of glucose monitoring sensor for the Apple Watch, but has so far yet to add it to the wearable device. In the case of one Apple Watch owner, they managed to hack together their own solution.
The project, outlined by Harley Turan, effectively takes the data from a continuous glucose monitoring system and imports and interprets it in a way that it can be viewed on an Apple Watch. In doing so, the project creates a reasonably low-cost solution for the problem.