Researchers make significant progress toward proving a critical mathematical test of the theory of general relativity.
- By Kevin Hartnett, Quanta Magazine on August 27, 2018

Researchers make significant progress toward proving a critical mathematical test of the theory of general relativity.


This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com’s Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
Philosophers have debated the nature of “nothing” for thousands of years, but what has modern science got to say about it? In an interview with The Conversation, Martin Rees, Astronomer Royal and Emeritus Professor of Cosmology and Astrophysics at the University of Cambridge, explains that when physicists talk about nothing, they mean empty space (vacuum). This may sound straightforward, but experiments show that empty space isn’t really empty – there’s a mysterious energy latent in it which can tell us something about the fate of the universe.
Rees was interviewed for The Conversation’s Anthill podcast on Nothing. This Q&A is based on an edited transcript of that interview.
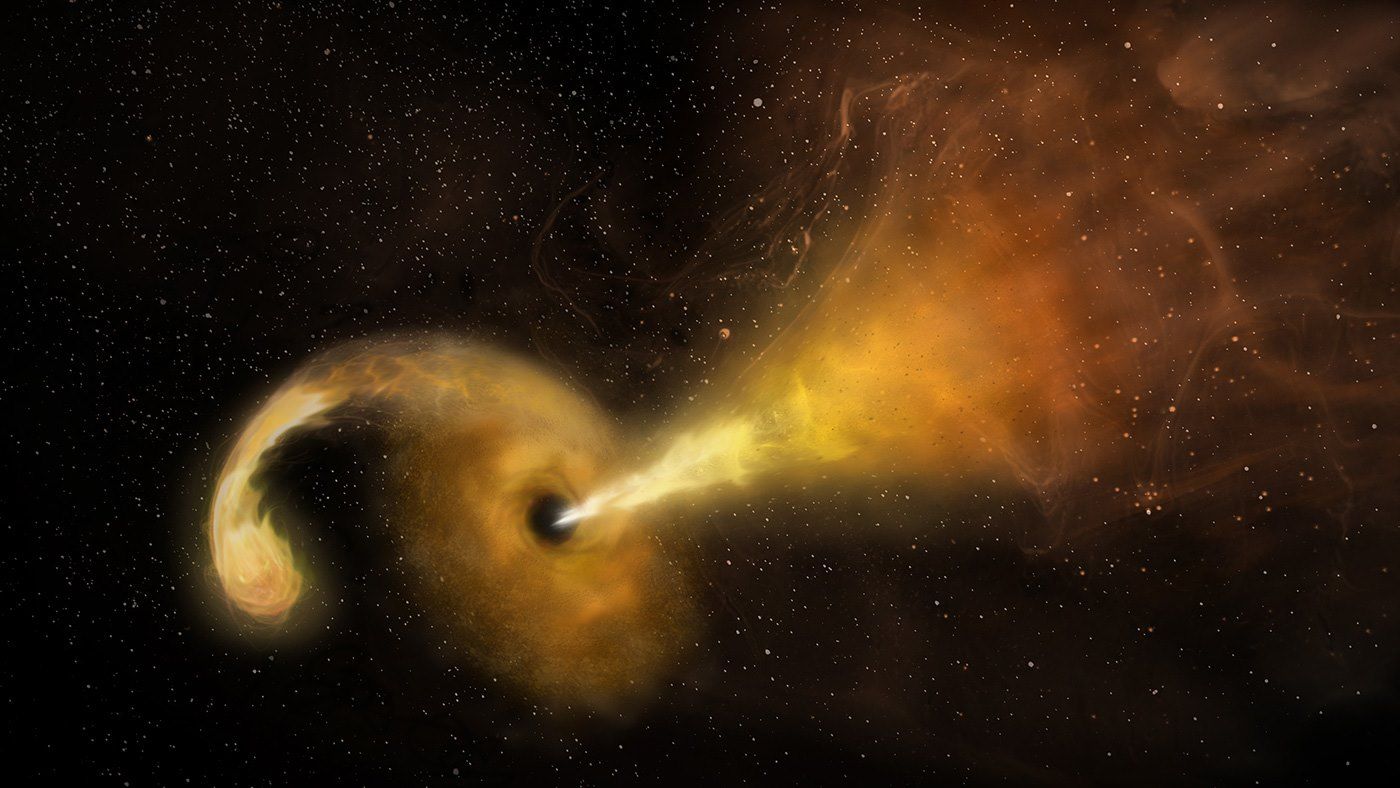

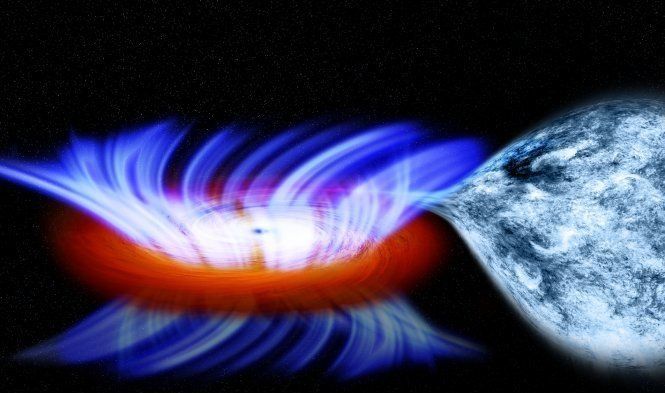
Astronomers used radio & infrared telescopes to image the distant eruption of this cosmic duel. Details: https://go.nasa.gov/2JMkZWF
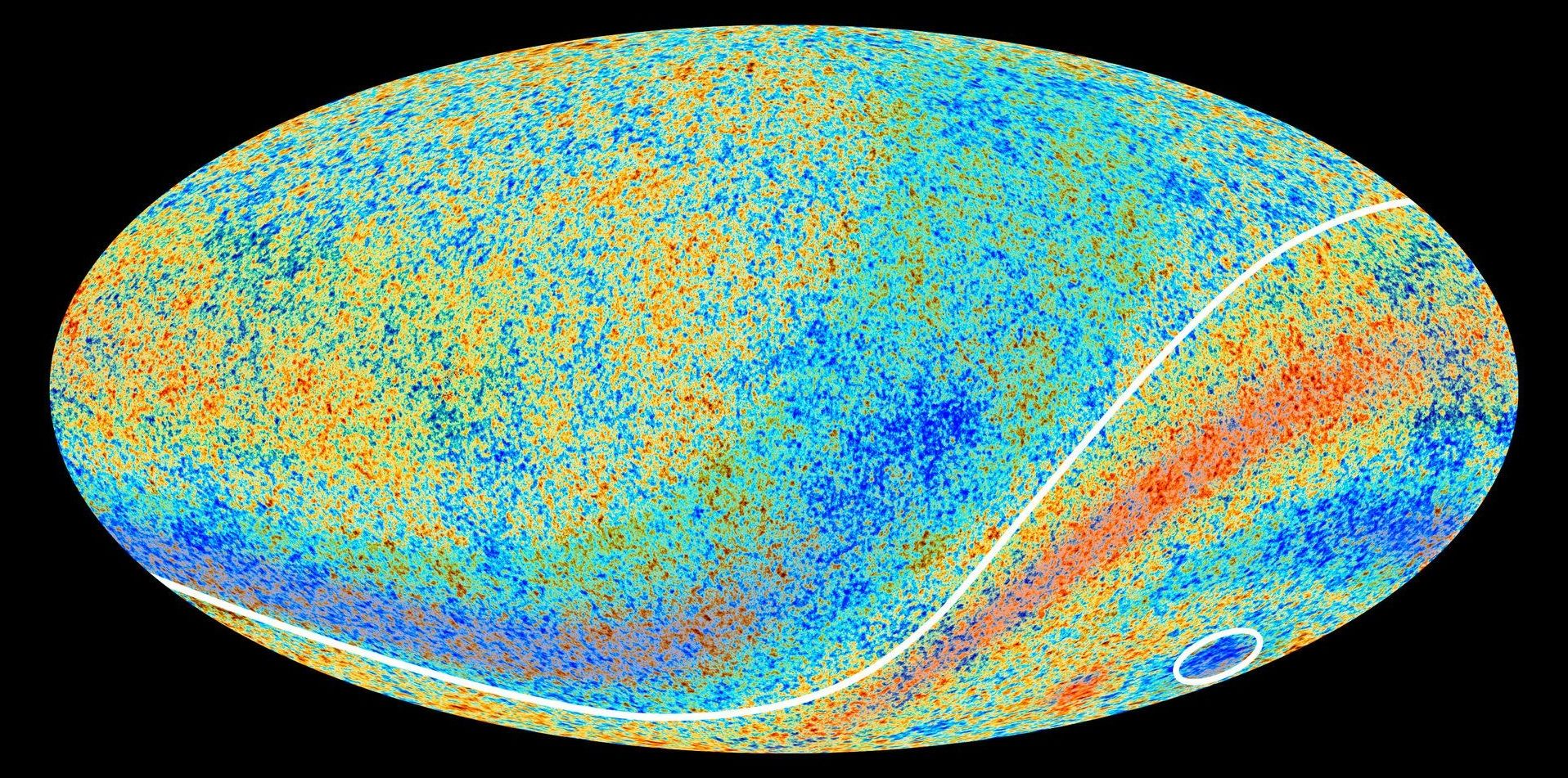
The Universe’s earliest epochs appear to be written into the small dwarf galaxies orbiting our own galactic home, the Milky Way.
A team of researchers studying dark matter noticed a strange trend in the brightness of the satellite galaxies around the Milky Way. There seem to be two classes of these orbiting dwarf galaxies—dim ones and bright ones—with few in the middle range. The researchers propose that this kink, when viewed on a graph, could be explained by a period early on in the Universe’s history called the re-ionization era.
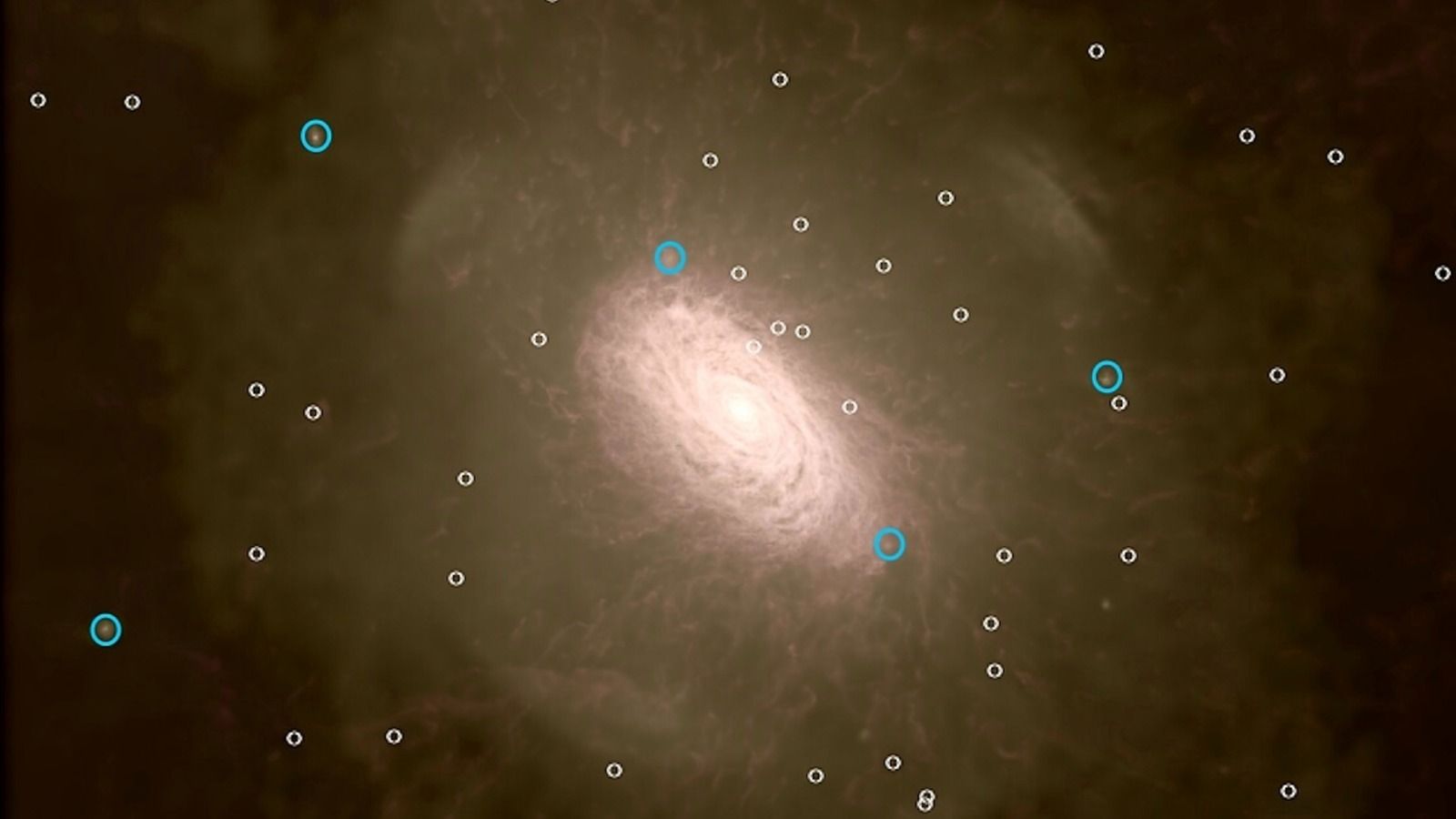
A trio of researchers with The University of Hong Kong, Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics in Taiwan and Northwestern University in the U.S., has come up with an alternative theory to explain how some stellar-mass black holes can grow bigger than others. In their paper published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Shu-Xu Yi, K.S. Cheng and Ronald Taam describe their theory and how it might work.
Since the initial detection of gravitational waves three years ago, five more detections have been observed—and five of the total have been traced back to emissions created by two stellar-mass black holes merging. The sixth was attributed to neutron stars merging. As part of their studies of such detections, space researchers have been surprised by the size of the stellar-mass black holes producing the gravity waves—they were bigger than other stellar-mass black holes. Their larger size has thus far been explained by the theory that they grew larger because they began their lives as stars that contained very small amounts of metal—stars with traces of metals would retain most of their mass because they produce weaker solar winds. In this new effort, the researchers suggest another possible way for stellar-mass black holes to grow larger than normal.
The new theory starts out by noting that some supermassive black holes at the hearts of galaxies are surrounded by a disk of gas and dust. In such galaxies, there are often stars lying just outside the disk—stars that could evolve to become stellar-mass black holes. The researchers suggest that it is possible that sometimes, pairs of these stars wind up in the disk as they evolve into black holes. Such stellar-mass black holes would pull in material from the disk, causing them to grow larger. The researchers note that if such a scenario were to play out, it is also possible that the two merging stars could wind up with a synchronized spin resulting in a stellar-mass black hole that produces more gravity waves than if the spins had not been synchronized, making them easier for researchers to spot.

Forget the Higgs: theorists have uncovered a missing link that explains dark matter, what happened in the big bang and more. Now they’re racing to find it.
By Michael Brooks
911? It’s an emergency. The most important particle in the universe is missing. Florian Goertz knows this isn’t a case for the police, but he is still waiting impatiently for a response. This 911 isn’t a phone number, but a building on the northern edge of the world’s biggest particle accelerator.
By Chelsea Whyte
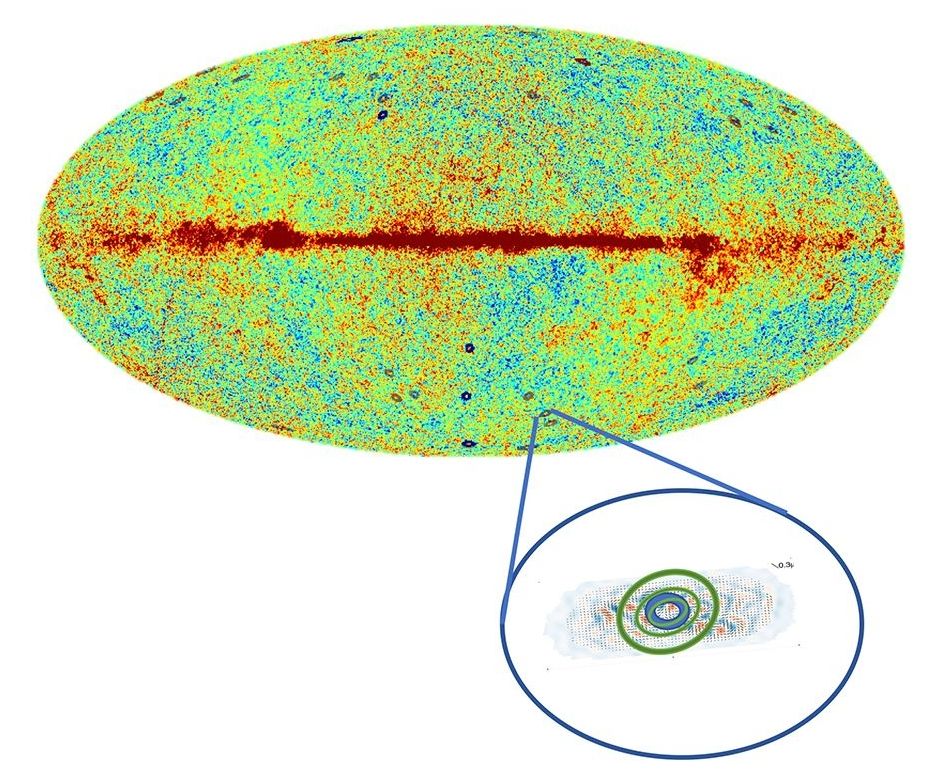
Swirling patterns in the sky may be signs of black holes that survived the destruction of a universe before the big bang.
“What we claim we’re seeing is the final remnant after a black hole has evaporated away in the previous aeon,” says Roger Penrose, a mathematical physicist at the University of Oxford.

A kiwi physicist has discovered the energy difference between two quantum states in the helium atom with unprecedented accuracy, a ground-breaking discovery that contributes to our understanding of the universe and space-time and rivals the work of the world’s most expensive physics project, the Large Hadron Collider.
Our understanding of the universe and the forces that govern it relies on the Standard Model of particle physics. This model helps us understand space-time and the fundamental forces that hold everything in the universe in place. It is the most accurate scientific theory known to humankind.
But the Standard Model does not fully explain everything, for example it doesn’t explain gravity, dark matter, dark energy, or the fact that there is way more matter than antimatter in the universe.