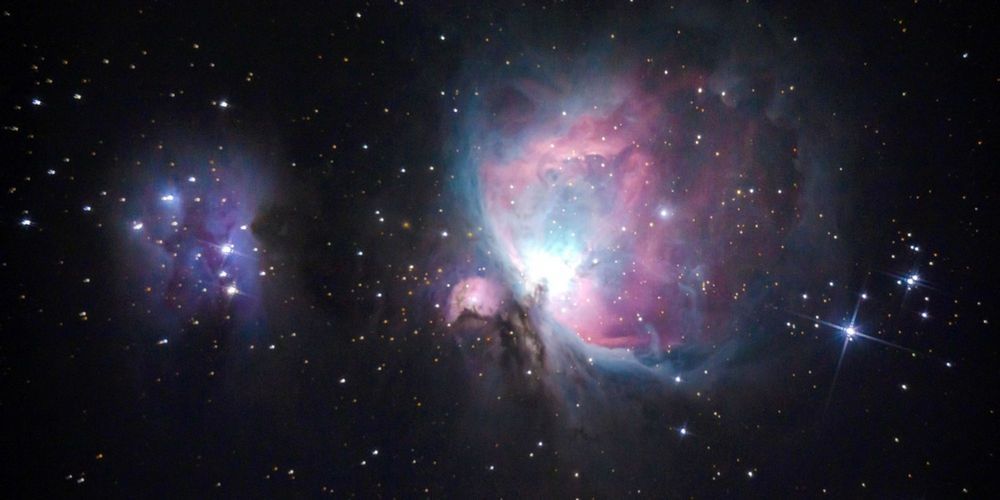
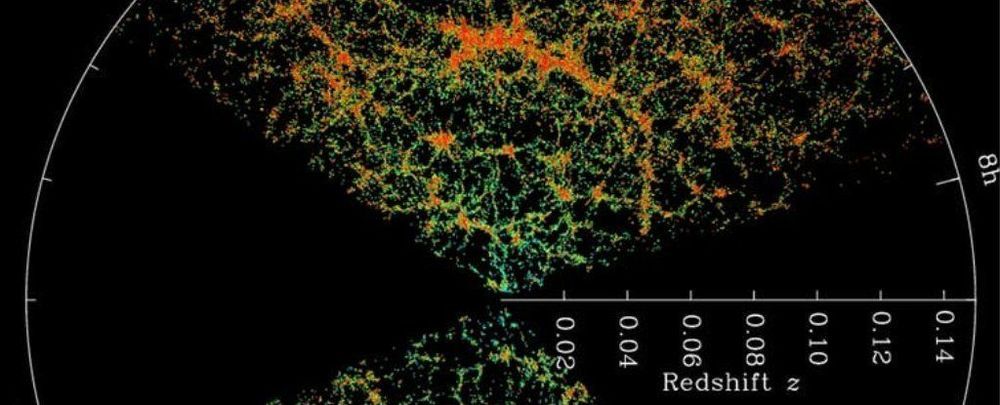
While it seems we are making great strides in unlocking the mysteries of the Universe, there is a sizable hole in what we know – up to 95% of the cosmos appears to be missing. We are talking about dark matter and dark energy, two useful, groundbreaking, but yet-to-be-directly-observed explanations for the vast majority of what exists. While there have been various attempts to pin down these ideas, inferred from their gravitational effects, a recent theory from a University of Oxford scientist claims to do away with them entirely. Instead, his model proposes something which may be even more unusual – what if the Universe is actually filled with a “dark fluid” possessing “negative mass”?
Dark matter takes up 27% of the known Universe (per NASA), while dark energy, a repulsive force that makes the Universe expand, gets 68%. Only 5% of the Universe is the observable world, including us and our planet. According to the model, proposed by Dr. Jamie Farnes, both dark matter and dark energy are unified in a fluid which has “negative gravity”. It repels all other material away.
“Although this matter is peculiar to us, it suggests that our cosmos is symmetrical in both positive and negative qualities,” wrote Farnes, astrophysicist, cosmologist and data scientist who worked at Oxford at the time of publishing his paper, and has since moved on to Faculty, a leading AI company.