The most jaw-dropping pictures of space this year.
From the Pillars of Creation to the Milky Way’s black hole, 2022 has been full of incredible photos from space. Here are the best space pictures of 2022.


How could we one day travel between the stars with real physics? Perhaps the greatest challenge to interstellar flight is energetics — it takes vast amounts of energy to accelerate even small ships to 20% the speed of light. But what if we could steal that energy from where? Perhaps even a black hole. Enter the “halo drive”, a video by Prof David Kipping based on his new peer-reviewed research paper on the subject.
This video is based on research conducted at the Cool Worlds Lab at Columbia University, New York. You can now support our research program directly here: https://www.coolworldslab.com/support.
Further reading and resources:
► Kipping, David (2018), “The Halo Drive: Fuel Free Relativistic Propulsion of Large Mases via Recycled Boomerang Photons”, JBIS, 71458: https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.03423
► Dyson, Freeman (1963), “Gravitational Machines”, in A.G.W. Cameron, ed., Interstellar Communication, New York Benjamin Press: https://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/~barnes/ast242_s14/Dyson_Machines.pdf.
► Breakthrough Starshot homepage: https://breakthroughinitiatives.org/initiative/3
► Our Cool Worlds video giving some background on Breakthrough Starshot: https://youtu.be/Ksb6Vh0BT_E
► Our Cool Worlds video on relativistic moving mirrors: https://youtu.be/msK9d9k6K0E
► Our Cool Worlds video on mirror distortion effects: https://youtu.be/1iNA-GTocI0
► Columbia University Department of Astronomy: http://www.astro.columbia.edu.
► Cool Worlds Lab website: http://coolworlds.astro.columbia.edu.
There’s an error in the video at around 8:30, 2 trillion joules is the cumulative energy output of a typical nuclear power station after 2000 seconds, not 20 days.
Music is largely by Chris Zabriskie (http://chriszabriskie.com/) and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), in order of appearance;
► Cylinder Five (http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/)
► Music from Neptune Flux, “We Were Never Meant to Live Here” (http://chriszabriskie.com/neptuneflux/)
► Music from Neptune Flux, “That Hopeful Future Is All I’ve Ever Known” (http://chriszabriskie.com/neptuneflux/)
► Cylinder Four (http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/)
► The Sun is Scheduled to Come Out Tomorrow (https://soundcloud.com/chriszabriskie/the-sun-is-scheduled-to-come)
In addition, music from OneGuitarOrchestra, acoustic cover of Hans Zimmer’s “No Time For Caution”: https://youtu.be/vau08Z_pN8s.
Video materials used:
Backwards through time? We travel forwards every day, but traveling back could let us change our past, visit old friends, or manipulate the timeline to our benefit… Although our knowledge of space and time remains incomplete, we can still use what we know to consider possible time machines. But what kind of paradoxes would this entail and how can we resolve them? Join us today on a special journey through time.
An educational video written and presented by Professor David Kipping.
This video is based on research conducted at the Cool Worlds Lab at Columbia University, New York. You can now support our research program directly here: https://www.coolworldslab.com/support.
All music used is licensed by SoundStripe.com or through Creative Commons:
► “It’s Always Darkest Before the Dawn” by Hill, licensed through SoundStripe.com: https://app.soundstripe.com/songs/7441
► “Waking Up” by Atlas, licensed through SoundStripe.com: https://app.soundstripe.com/songs/3984
► Cylinder Four (http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/) by Chris Zabriskie (http://chriszabriskie.com/); licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
► “Always Dreaming” by Caleb Etheridge, licensed through SoundStripe.com: https://app.soundstripe.com/songs/5534
► Cylinder Two (http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/) by Chris Zabriskie (http://chriszabriskie.com/); licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
► “Fable” by Stephen Keech, licensed through SoundStripe.com: https://app.soundstripe.com/songs/6312
► “Selha” by Stephen Keech, licensed through SoundStripe.com: https://app.soundstripe.com/songs/7102
Further reading and resources:
► Echeverria, F., Klinkhammer, G. & Thorne, K. S. (1991), “Billiard balls in wormhole spacetimes with closed timelike curves: Classical theory”, Phys. Rev. D., 44, 1077: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1991PhRvD…44.1077E/abstract.
► S. Kalyana Rama & Siddhartha Sen (1994), “Inconsistent Physics in the Presence of Time Machines”: https://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9410031v1
► Stephen Hawking (1992), “Chronology protection conjecture”, Phys. Rev. D., 46603: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1992PhRvD…46…603H/abstract.
► Max Tegmark (1997), “On the dimensionality of space time”, CQG, 14, L69: https://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9702052
Films clips used:

A study reveals that light from these galaxies traveled for 13.4 billion years.
A study by an international team of astronomers has identified a group of the earliest galaxies confirmed to date. The team based its findings on the data processed by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The galaxies are estimated to be less than 400 million years after the big bang, and light from these sources has taken roughly 13.4 billion years to reach the Earth’s atmosphere.
Sololos/iStock.
Astronomer and co-author, Emma Curtis-Lake from the University of Hertfordshire in the United Kingdom said that “it was crucial to prove that these galaxies do, indeed, inhabit the early universe. It’s very possible for closer galaxies to masquerade as very distant galaxies.”

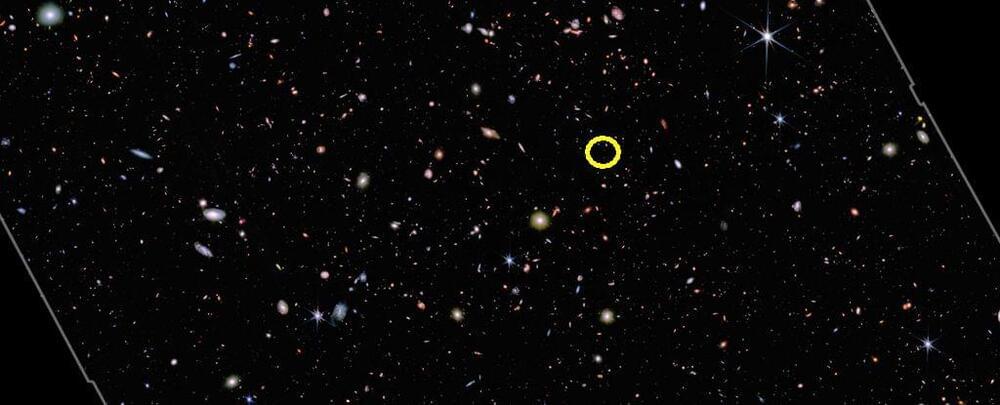
Light that has traveled for over 13.4 billion years to reach our neighborhood of space has been confirmed as originating from the earliest, most distant galaxy detected yet.
That places the most distant of these four very young objects at the very dawn of the Universe, just a short time after the Big Bang – a time period when the Universe was still foggy and bleary and the first rays of light were penetrating the darkness.
So detailed are the JWST’s long spectroscopic observations that researchers can not only measure the distance the light of these galaxies has traveled, they can also infer some of the galaxies’ properties.

Life is really weird. From the vantage point of a physicist, it is even stranger. Life is unlike any other phenomenon in physics. Stars, electrons, and black holes are all amazing in their own ways. But only life invents, and the first thing life invents is itself.
Life is creative in a way that no other physical system can be, and its unique use of information may be the key to understanding what makes it different from other physical systems. Now, thanks to a new grant my colleagues and I have received from the Templeton Foundation, we are going to be exploring exactly how information allows life to work its magic. I’m very excited about the project, and this essay is my first report from the frontier as we plunge into terra incognita.
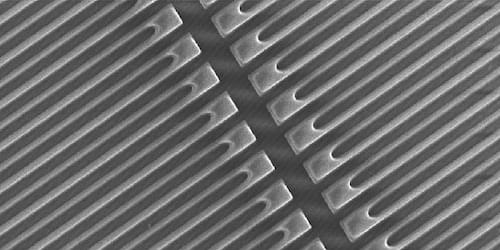
Hunting for lightweight dark matter particles requires detectors with much lower signal thresholds than traditional experiments. This requirement has prompted novel detection techniques, including probing the faint interactions that occur between sub-MeV particles and electrons. In a 180-hour-long experiment, Yonit Hochberg of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and her colleagues demonstrate a device that distinguishes hypothetical sub-MeV dark matter from background noise with record sensitivity [1]. Their experiment places the strongest constraints yet on interactions between lightweight dark matter and regular matter.
Hochberg and her colleagues etched an array of nanowires in a 7-nm-thick tungsten-silicide film to produce a superconducting nanowire single-photon detector, a sensor that is sensitive to extremely small energy inputs. When energy above some threshold is deposited on a superconducting nanowire, the wire briefly becomes a regular conductor, resulting in a voltage pulse.
The team circulated a fixed current through their device and sealed it in a light-tight box for 180 hours. They counted four voltage pulses, each corresponding to a deposited energy of at least 0.73 eV. Absent any other detectable energy source, these dark counts could be attributed to cosmic-ray-generated muons or high-energy particles excited by radioactive decay.

A massive blast of light considered extremely rare and is believed to have been triggered by the collision of stars with a black hole that hit the Earth recently and which could help change our understanding of the universe, scientists revealed.
The event called a gamma-ray burst (GRB), which lasted for only 50 seconds, came from a nearby galaxy in December 2021. These blasts are considered to be the most powerful explosions in the universe.
Earlier, it was believed that GRBs only resulted from the destruction of massive stars, but astronomers now believe that it can come from the combination of two neutron stars.