After a decade studying thousands of supernovae, astronomers are still perplexed by the enigma that led Einstein to his ‘greatest mistake’
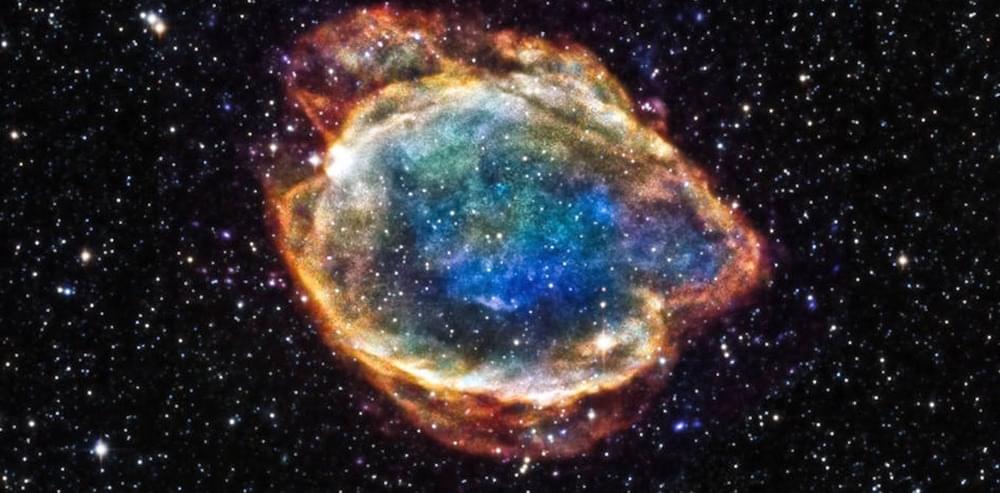


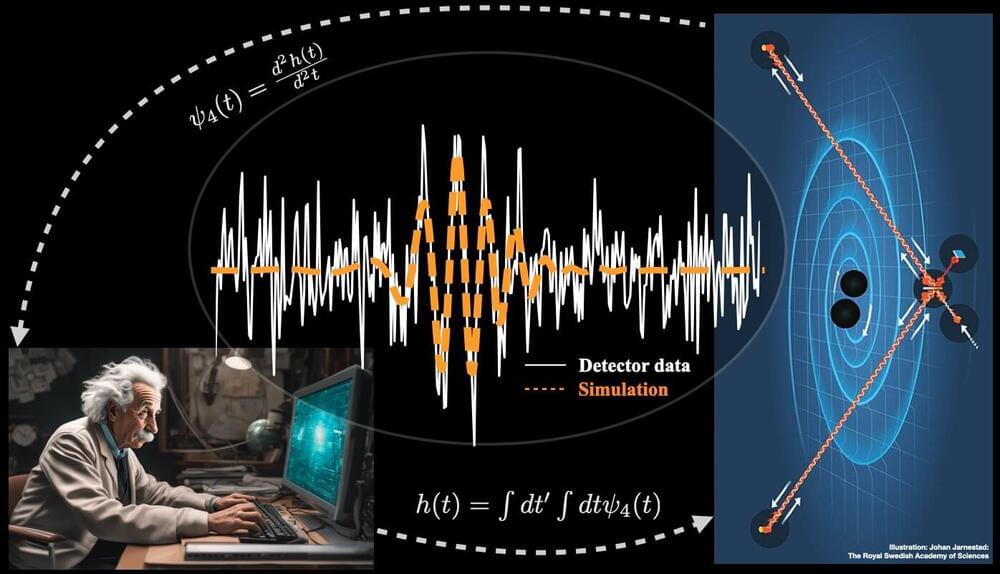
Thanks to the LIGO and Virgo detectors, researchers now regularly observe ripples in spacetime known as gravitational waves, which are caused by catastrophic cosmic events such as black-hole mergers, star explosions, or the big bang itself.
Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of spacetime that travel at the speed of light. These are produced in some of the most violent events in the universe, such as black-hole mergers, supernovae, or the Big Bang itself. Since their first detection in 2015, and after three observing runs, the Advanced LIGO and Virgo detectors have detected around 100 such waves.
Thanks to these observations, we are starting to unveil the black-hole population of our universe, study gravity in its most extreme regime and even determine the formation of elements like gold or platinum during the merger of neutron stars.
The LIGO and Virgo detectors are nothing but the most precise rulers ever built by humankind, able to measure the subtle squeezing and stretching of spacetime produced by gravitational waves.
Over the past few decades, it has become quite obvious that humans are not the only living organisms with intelligence.
The story of intelligence you are about to experience goes back 13.8 billion years, back to the moment the universe was born: the Big Bang. It’s a story of time and space, matter and energy. It is a story of unfolding, It’s the story of how the very nature of the physical universe from its very inception led to the universe getting to know itself and eventually, to reflect.
Complexity, Evolution, and Intelligence is comprised of five parts, each corresponding to a movement in Dan Forrest’s “Requiem For The Living.” This composition was performed August 2, 2013 in Raleigh, NC by Bel Canto, conducted by Dr. Bill Young.

The problem is known as the Hubble tension, and it centers around figuring out a number for the universe’s expansion rate, called the Hubble constant. To find it, scientists have pored over tiny fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) — an ancient relic of the universe’s first light — and built cosmic distance ladders to remote, pulsating stars called Cepheid variables.
But the best experiments using these two methods disagree. The difference in results may have seemed small, but it was enough to spark a major crisis in cosmology.
Wendy Freedman, an astrophysicist at the University of Chicago, has spent four decades studying the Hubble constant.
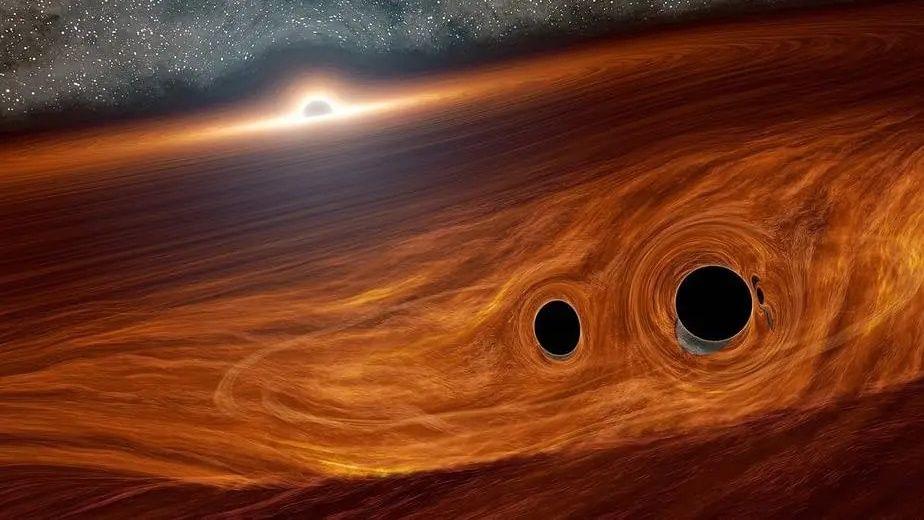

To that end, Caplan is part of a crew that posits the dark matter portion of the dark universe could very well be made up of not particles like we imagine, but instead a huge number of atom-size black holes produced during the dawn of the universe, each of which is about as massive as a typical asteroid in our own solar system. “I think all dark matter candidates are just a little bit wild,” Caplan, who is an assistant professor of physics at Illinois State University, told Space.com. “Some guesses are better than others, and primordial black holes are taken seriously. I’ll go so far as to say I think they’re popular.”
But to turn the hypothesis into fact, he says, scientists have to actually find one of these miniscule ancient voids — which brings us to this new black-hole-sun conversation. Potentially, Caplan and his co-authors say in their papers, some of those ultrasmall black holes might’ve gotten caught up in dust clouds in the midst of forming stars. Potentially, they might’ve ended up literally lodged in those eventual sparkling oceans of plasma. Potentially, they might still be there.
So, no, there is probably not a black hole in the center of our star — but there might be other stars gallivanting through space with black holes indeed wedged within their hearts.
Get your 12,020 SPACE Calendar here: https://shop.kurzgesagt.org/
WORLDWIDE SHIPPING IS AVAILABLE!
This year’s calendar focuses on the future of humanity and how we will explore space in the next 10,000 years.
We want to get you the best shipping fees. So If you’re located in the EU, please order from our EU-warehouse. If you’re located anywhere else in the world, please go to our World Wide Shop. (The link is the same you will be asked to choose your location once you are there.)
Thanks to everyone for the support!
Sources: https://sites.google.com/view/sources-neutron-stars/
Neutron stars are one of the most extreme and violent things in the universe. Giant atomic nuclei, only a few kilometers in diameter but as massive as stars. And they owe their existence to the death of something majestic.
OUR CHANNELS
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
German Channel: https://kgs.link/youtubeDE
Spanish Channel: https://kgs.link/youtubeES
HOW CAN YOU SUPPORT US?
One of the greatest challenges of modern physics is to find a coherent method for describing phenomena, on the cosmic and microscale. For over a hundred years, to describe reality on a cosmic scale we have been using general relativity theory, which has successfully undergone repeated attempts at falsification.
Albert Einstein curved space-time to describe gravity, and despite still-open questions about dark matter or dark energy, it seems, today, to be the best method of analyzing the past and future of the universe.
To describe phenomena on the scale of atoms, we use the second great theory: quantum mechanics, which differs from general relativity in basically everything. It uses flat space-time and a completely different mathematical apparatus, and most importantly, perceives reality radically differently.

A new study reveals that magnetic fields are common in star systems with large blue stars, challenging prior beliefs and providing insights into the evolution and explosive nature of these massive stars.
Astronomers from the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP), the European Southern Observatory (ESO), and the MIT Kavli Institute and Department of Physics have discovered that magnetic fields in multiple star systems with at least one giant, hot blue star, are much more common than previously thought by scientists. The results significantly improve the understanding of massive stars and their role as progenitors of supernova explosions.
Characteristics of O-type Stars.
2023 was a landmark year in space exploration for the European Space Agency (ESA), marked by significant missions like Juice’s journey to Jupiter, the launch of the Euclid space telescope for dark matter research, and the decommissioning of ESA’s Aeolus mission.
The year also saw advancements in Earth observation technologies, initiatives to address space debris, and collaborative efforts in asteroid impact studies. Notably, the Galileo satellite system’s new high-accuracy service and the first hardware tests for its second generation of satellites were significant milestones.
