The weird, faint star system—the tiniest Milky Way satellite ever found—could be under the influence of dark matter.
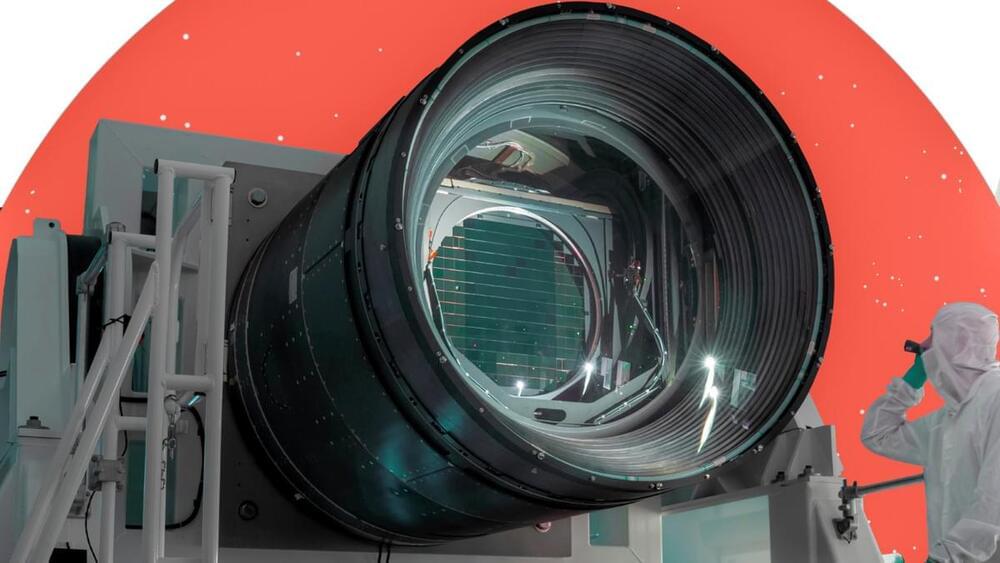



The 3,200-megapixel LSST camera is the size of a compact car and weighs in at 3 metric tons, which is about half the weight of a male African bush elephant. The LSST’s wide-field view will attempt to solve lingering mysteries surrounding dark energy, the force that accounts for around 70% of our universe’s matter-energy content and causes the expansion of the cosmos to accelerate.
The LSST will also investigate dark matter, the mysterious substance that accounts for around 85% of all stuff in the cosmos despite being invisible to us, as well as answer other astronomical questions as it creates what Željko Ivezić, Director of Rubin Observatory’s construction, describes as the “greatest movie of all time and the most informative map of the night sky ever assembled.”
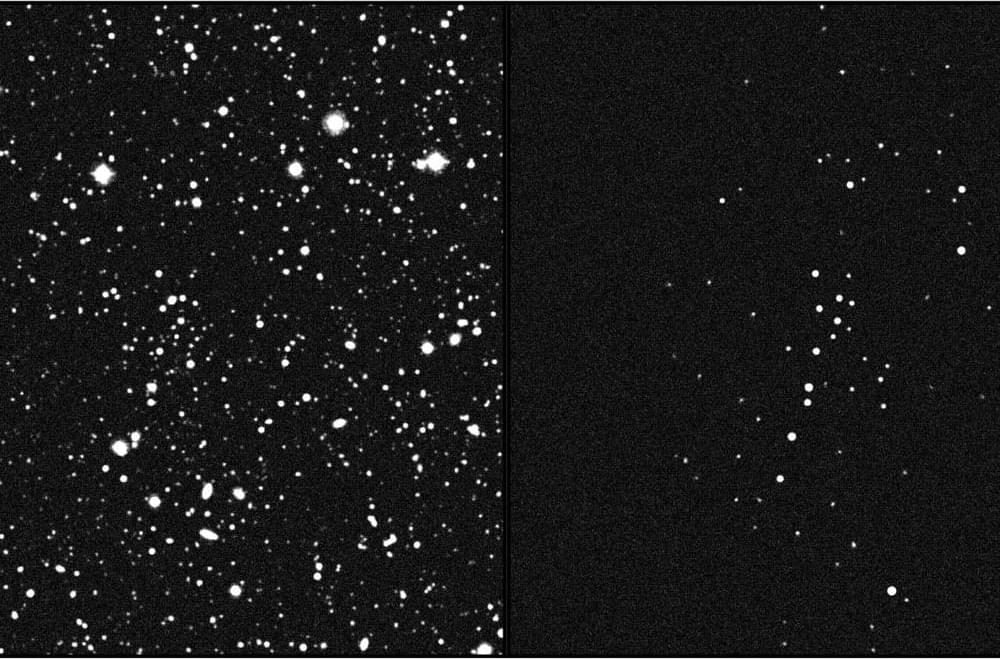


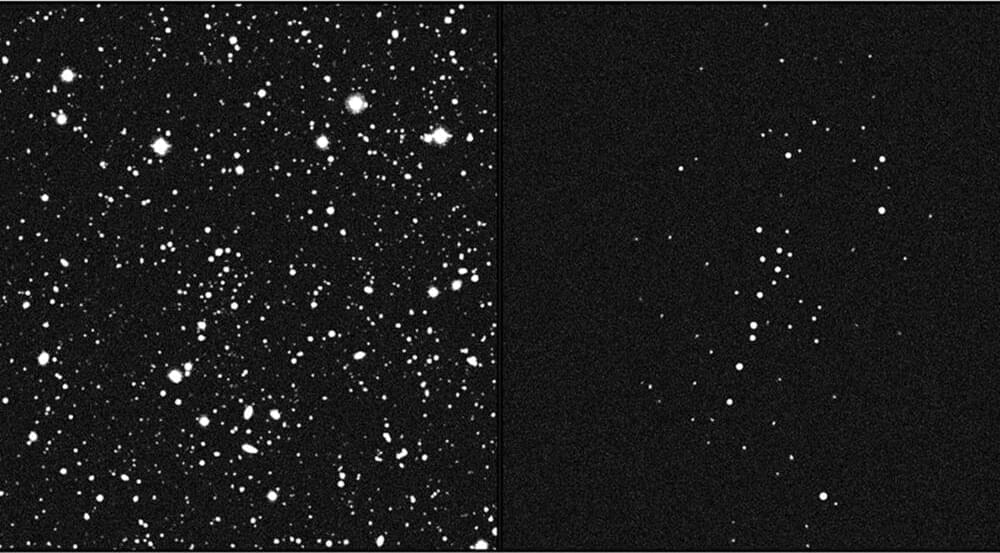
A tiny clump of stars orbiting our galaxy should have been ripped apart by the Milky Way, but its continued existence hints it may be held together by a massive amount of dark matter.
By Leah Crane
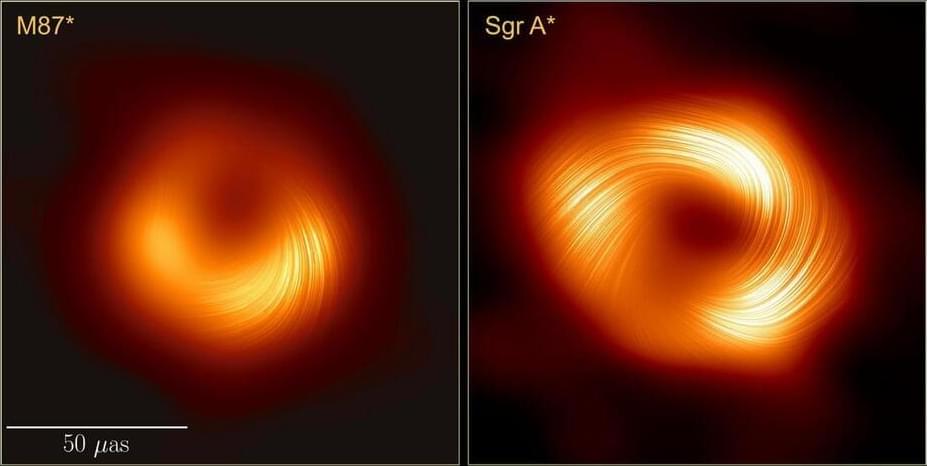
Black holes are one of the most elusive objects in the space, but this simulation created by researchers in Netherlands might help us know more about their mysteries.
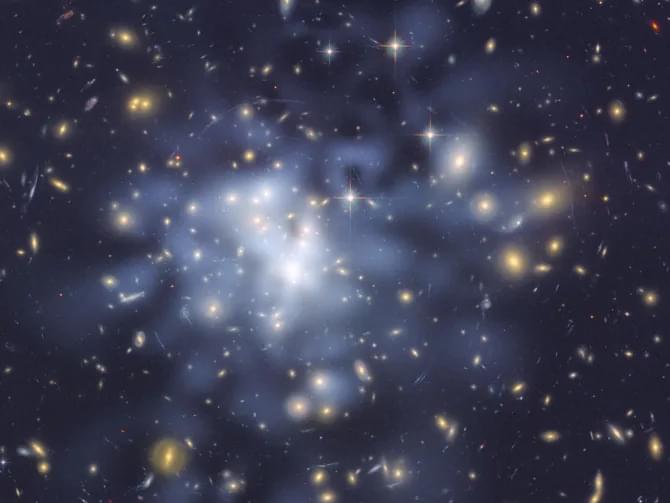

Dark matter is one of science’s greatest mysteries. It doesn’t absorb, reflect or emit light, so we can’t see it. But its presence is implied by the gravitational effects it appears to have on galaxies.
Although dark matter makes up about 85% of the cosmos, scientists know very little about its fundamental nature.
Theories abound, and research by Clemson University postdoctoral fellow Alex McDaniel provides some of the most stringent constraints on the nature of dark matter yet. His research also reveals a small hint of a signal that if real, could be confirmed sometime in the next decade or so.

Our universe is getting bigger and bigger really fast — something all the theories about space agree on, but none of them can totally explain. Now, there’s a new idea in town: Maybe our universe is expanding because it keeps bumping into and soaking up “baby” universes.
When scientists look at the afterglow of the Big Bang, known as the cosmic microwave background, they see that our universe is swelling up quicker and quicker. To make sense of this, physicists use something called the Standard Cosmological Model, which says there’s this weird stuff called dark energy pushing the universe to expand.


Utilizing data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, scientists have unveiled the earliest starlight spectra, revealing low-mass galaxies’ central role in the universe’s dawn. Credit: SciTechDaily.com.
Groundbreaking JWST observations reveal the pivotal role of low-mass galaxies in the early universe’s reionization, challenging existing cosmic evolution theories.
Scientists working with data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have obtained the first full spectra of some of the earliest starlight in the universe. The images provide the clearest picture yet of very low-mass, newborn galaxies, created less than a billion years after the Big Bang, and suggest the tiny galaxies are central to the cosmic origin story.