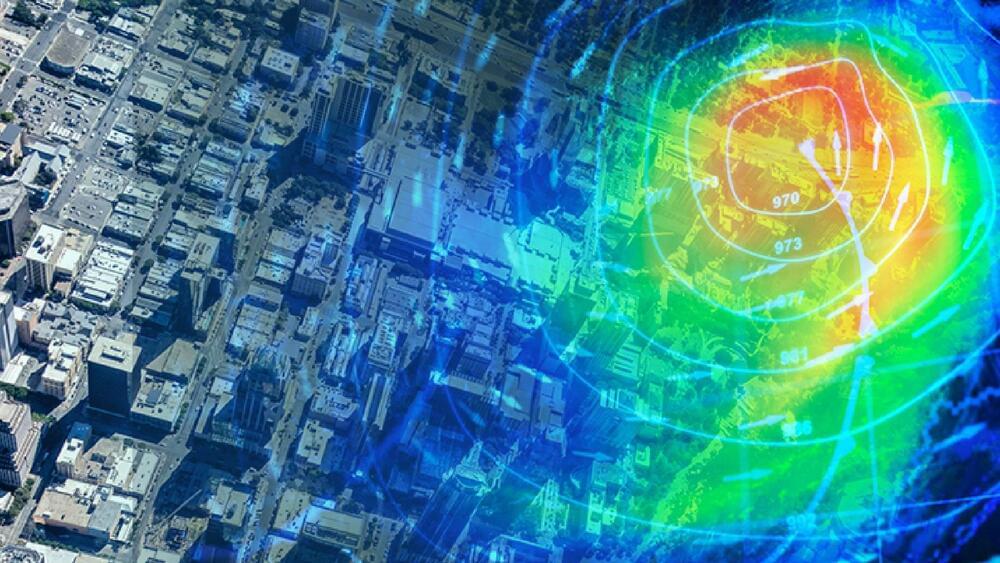
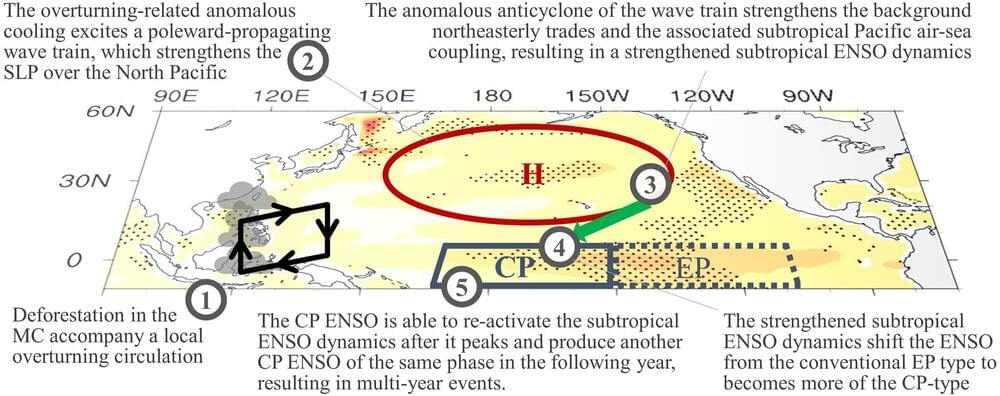
“Regardless of the size of a city, well planned urban land patterns can reduce population exposures to weather extremes.”
Urban planning and design are crucial for creating resilient cities that can withstand and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Now, University of Delaware researcher Jing Gao, assistant professor in the College of Earth, Ocean and Environment and a resident faculty member in the Data Science Institute, and colleague Melissa Bukovsky, associate professor in the Haub School of Environment and Natural Resources at the University of Wyoming, are exploring how future populations’ exposure to weather extremes under climatic circumstances present at the end of the twenty-first century will be impacted by changes in urban design.