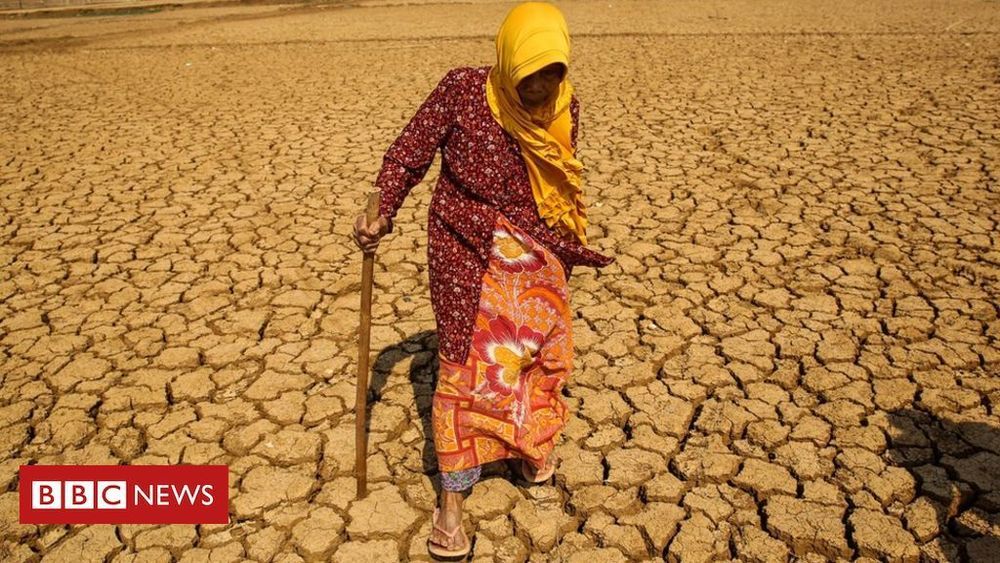
Researchers plan for new centre to explore refreezing the poles, sucking out CO2 and ocean greening.
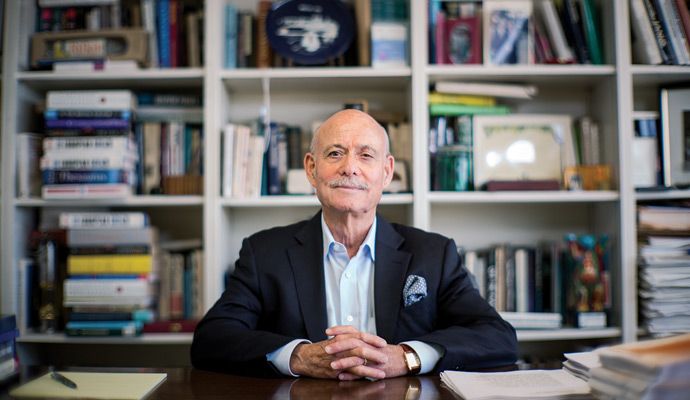



Get ready for a future in which most things you need to live, food, housing, transportation, and information, are free or nearly free.
The influential economic theorist looks ahead to a world of virtually free energy and zero marginal cost production, and to a desperate race against climate change.
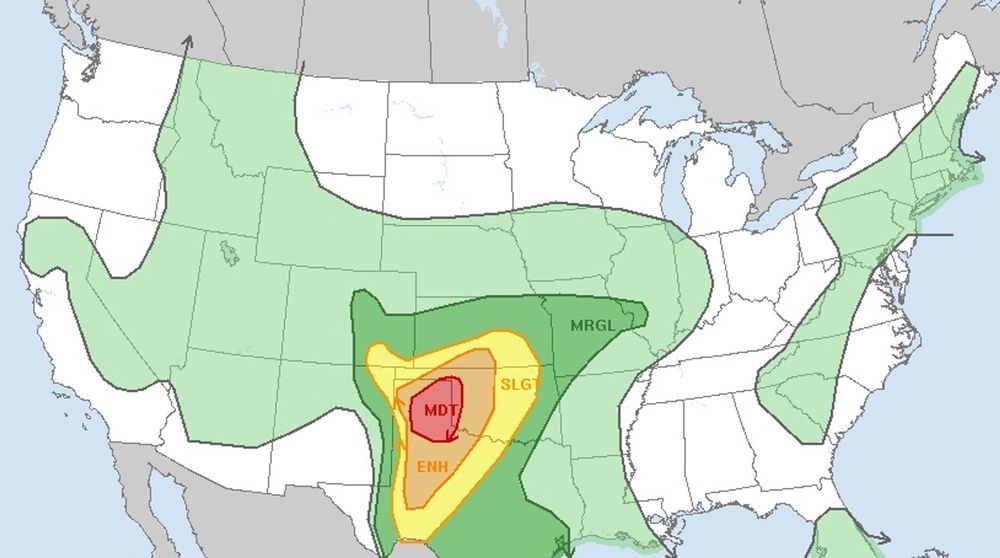
Tornado warnings were issued in the Panhandle of Texas Tuesday afternoon, the first salvo in what’s predicted to be a violent night of weather across the southern Plains.
“Severe thunderstorms are likely into tonight, particularly across the Texas Panhandle and western Oklahoma,” the Storm Prediction Center warned. “A couple of strong tornadoes, very large hail, and damaging winds will all be possible.”
Hail nearly the size of baseballs was reported to be slamming into Fritch, Texas, as of late afternoon, the center reported. That’s about 20 miles northeast of Amarillo.
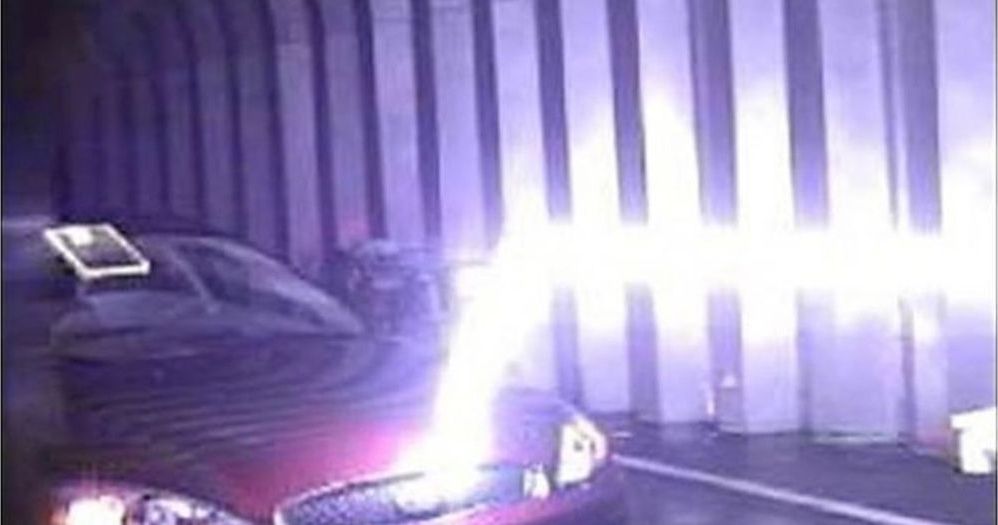

Over at Picatinny Arsenal, the research and development facility and proving ground for the U.S. Army’s weaponry, engineers are developing a device that shoots lighting bolts along a laser beam to annihilate its target. That’s right: lighting bolts shot down laser beams. This story could easily end right here and still be the coolest thing we’ve written today, but for the scientifically curious we’ll continue.
The Laser-Induced Plasma Channel (LIPC) can be used to destroy anything that conducts electricity better than the air or ground surrounding it (unexploded ordnance seems a good candidate here). It works off of some pretty basic principles of physics, using a laser to carve an electromagnetic path through the air that accommodates a high-voltage beam. Create that path, crank up the voltage, and your target is toast.
It works like this: a high intensity, super-short duration (maybe two-trillionths of a second) laser pulse will actually use air like lens—surrounding air focuses the beam, keeping the laser pulse nice and tight rather than scattering it. If the pulse is strong enough, it actually creates an electromagnetic field around itself that’s so powerful it strips electrons from air molecules, essentially creating a channel of plasma through the air. Since air is composed of neutral particles (that act as insulators) and the plasma channel is a good conductor (relative to the un-ionized air around it) the path of the laser beam becomes a kind of filament.


Dear Colleagues.
ReWheel, Inc. was founded to save energy based on a simple truth that wasting energy is extremely not smart … as well as very damaging to our planet’s health.
Most of us are either scientists or believe in science. And that is how we know that we are losing the war against climate change. This war will not be won by any one technology but by our combined efforts. To protect our planet for our children and their children, and those who comes after, we need to act.
“Astronauts at the international space station expecting a delivery on Monday that private company SpaceX launched a cargo capsule loaded with supplies from Cape Canaveral early this morning the shipment. The company’s seventeenth to the orbiting outpost includes a new instrument to measure CO two in the atmosphere. Then peers Rebecca hersher reports it will be attached. To the space station measuring how much carbon dioxide is. In the atmosphere is really fundamental for understanding how the climate is changing. But it’s difficult for one thing. The amount of co two varies each day and each season and each year and measurements have to be both global and extremely precise. The new instrument can do both. It’s designed to scan the earth measuring not only how much co two is entering the atmosphere. But how much of the greenhouse gas is being absorbed by plants and oceans the instrument is called the orbiting carbon observatory three two other versions. Have previously been launched. Overall. NASA says the ability to measure co two from space has already helped scientists better understand our climate and predict how it will change”
KQED Radio
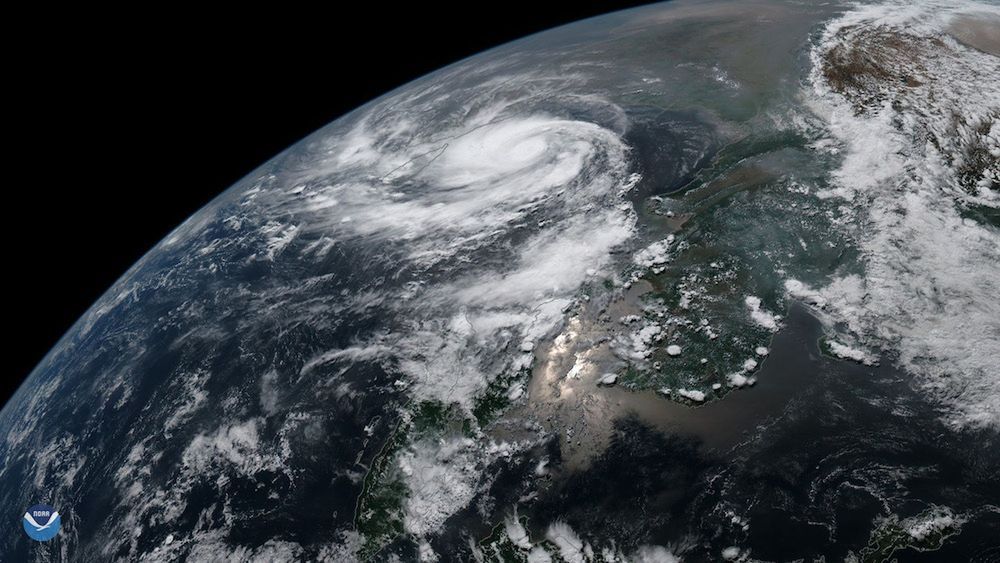


A massive cyclone is set to batter India over the next few days, spurring the biggest evacuation in the country’s history.
The extremely severe cyclone, dubbed “Fani,” is pummeling the Bay of Bengal and is projected to make landfall by Thursday night with approximately 120 mph (190 km/h) winds, with gusts up to 130 mph (210 km/h), according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD). Fani is also likely to bring “phenomenal” sea conditions in parts of the Bay of Bengal, according to the IMD.
More than 100 million people are in the path of the devastating cyclone, and nearly 900,000 people have been ordered to evacuate, the Associated Press reported. About 100,000 of those people are from the city of Puri, in the state of Odisha, which is home to the 858-year-old Jaganath Temple, the BBC reported. Officials fear that this ancient temple could be damaged by the cyclone.
