Hurricane forecasters rely on weather data collected and processed by Department of Defense satellites. That data will no longer be available as of Monday, June 30.



Though the last volcanic eruption in Puy-de-Dôme dates back to ancient times, there could be new occurrences in the future within the Central Massif. It is indeed true that a layer of lava lies beneath the region and is expected to eventually resurface.
In France, Puy de Dôme is not only known as a department but primarily as a volcano approximately 11,000 years old, with its last eruption occurring in 5,760 BC. Since then, no lava has flowed within France. However, this might not be a permanent situation, according to Guillaume Boudoire, a volcanologist at the Laboratory of Magmas and Volcanoes at Clermont Auvergne University. Interviewed by the Journal Du Net in an article published in April 2025, Boudoire spoke about a very likely “volcanic reactivation” in the Central Massif.
While the expert is certain of this reactivation, it’s crucial to note that forecasting future eruptions is extremely challenging. However, volcanic activity tends to follow cycles, alternating between active and dormant phases. The activity in the Central Massif is not extinguished but merely slumbering, having been dormant for 7,000 years.
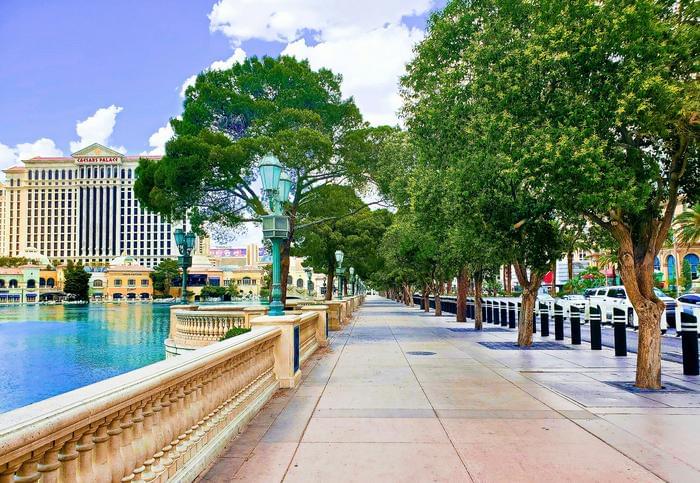

How can trees provide relief from extreme heat in urban climates? This is what a recent study published in Environmental Research Climate hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated using urban street trees to provide shade relief from extreme temperatures, which continue to increase due to climate change. This study has the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, legislators, city planners, and the public better understand the benefits of trees for cooling urban spaces in the face of the increasing threat of climate change.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models between July and August 2022 to simulate how street tree planting in Las Vegas could provide relief from extreme heat and heat exposure. The goal of the study was to ascertain the overall effectiveness of planting non-native trees in an urban setting while estimating the amount of water they would need to survive and provide shade relief from extreme heat. In the end, the researchers found that desert environments are too hot for trees to adequately provide shade relief, primarily due to the trees’ water conservation efforts.
“Urban trees are not a silver bullet for cooling our cities, particularly for desert cities like Las Vegas,” said Dr. Juan Henao, who is a postdoctoral researcher at the Desert Research Institute and lead author of the study. “But they provide significant shade and of course other benefits. I know that I prefer to see trees, and they can help store carbon. We just need to remember that in order to cool the air, they need to release water vapor, and we need to give them enough water to do that. Any hot, dry city will need to consider these tradeoffs and really do their research to identify the right species for planting efforts.”

ESA’s Living Planet Symposium, one of the world’s leading Earth observation conferences, opened today in Vienna.
More than 6,500 participants from almost 120 countries signed up to attend the event. With more than 4,200 scientific presentations and posters, the symposium provides a forum and meeting point for scientists, academics and space industry representatives, as well as students and citizens.
The event takes place every three years and this year the focus is ‘from observation to climate action and sustainability for Earth’
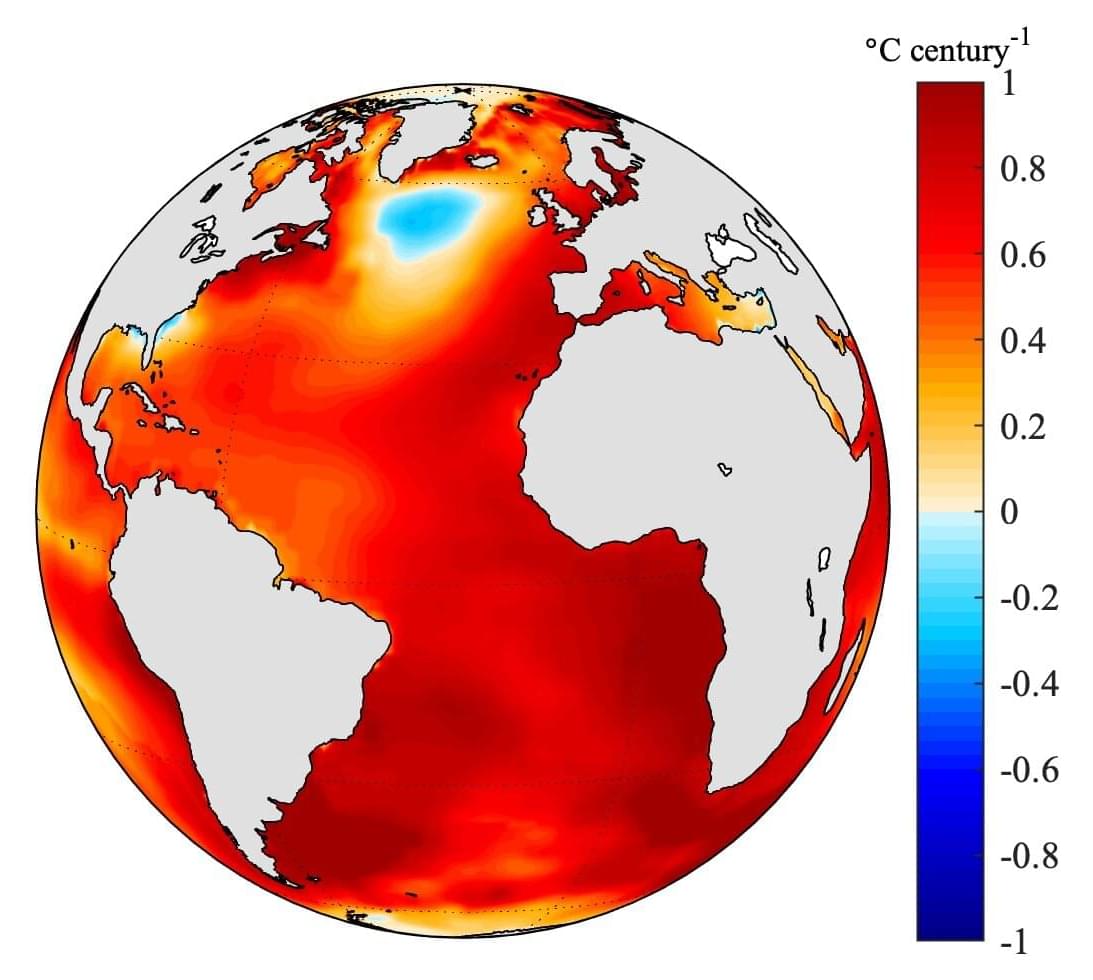
For more than a century, a patch of cold water south of Greenland has resisted the Atlantic Ocean’s overall warming, fueling debate among scientists. A new study identifies the cause as the long-term weakening of a major ocean circulation system.
Researchers from the University of California, Riverside show that only one explanation fits both observed ocean temperatures and salinity patterns: the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC, is slowing down. This massive current system helps regulate climate by moving warm, salty water northward and cooler water southward at depth.
“People have been asking why this cold spot exists,” said UCR climate scientist Wei Liu, who led the study with doctoral student Kai-Yuan Li. “We found the most likely answer is a weakening AMOC.”

TOQUERVILLE, Washington County — The Hurricane-based robotics company IME Automation recently announced the purchase of 6.5 acres of land at Anderson Junction in Toquerville, where the company has broken ground for its new 20,000-square-foot facility.
IME Automation develops custom robotic systems for manufacturing operations worldwide. This new facility will expand its capabilities and footprint in the region.
The land was acquired approximately eight months ago during the summer of 2024, brokered by sales agent Brandon Price with the commercial real estate agency NAI Excel. Price said he delayed putting out information about the acquisition until IME Automation was completely ready to break ground.
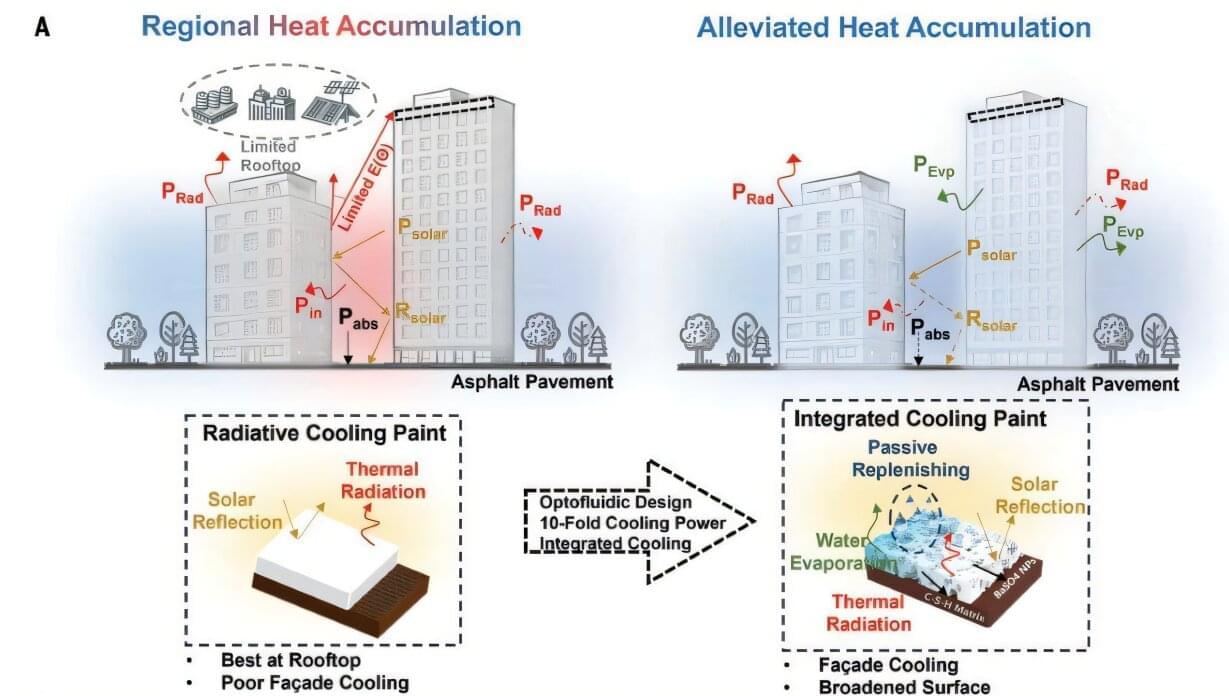
A new cement-based paint can cool down the building by sweating off the heat. The cooling paint, named CCP-30, was designed by an international team of researchers and features a nanoparticle-modified porous structure composed of a calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel network.
This design enabled it to achieve superior cooling by combining both radiative, evaporative and reflective cooling mechanisms, which allowed it to reflect 88–92% of sunlight, emit 95% of the heat as infrared radiation, and hold about 30% of its weight in water, making it a paint ideal for keeping spaces cool throughout the day and across seasons.
As per the findings published in Science, the paint provides 10 times the cooling power of commercial cooling paints in tropical climates, resulting in electricity savings of 30 to 40%.


Every day, tons of CO₂ are released into the atmosphere, but what if we could transform it using clean energy? This is the question explored in a recent Politecnico di Milano study, which was featured on the cover of the journal ACS Catalysis. The research focuses on a process that transforms carbon dioxide and hydrogen into methane using carefully engineered nickel nanoparticles.
Entitled “Deciphering Size and Shape Effects on the Structure Sensitivity of the CO₂ Methanation Reaction on Nickel,” the study by Gabriele Spanò, Matteo Ferri, Raffaele Cheula, Matteo Monai, Bert M. Weckhuysen and Matteo Maestri investigates how the size and shape of nickel nanoparticles influence the rate at which carbon dioxide is converted into methane.
Researchers at the Laboratory of Catalysis and Catalytic Processes (LCCP) at Politecnico di Milano’s Department of Energy are tackling a key climate challenge: reusing CO₂ to produce sustainable fuels. The LCCP is an internationally recognized leader in heterogeneous catalysis, driving forward practical solutions for cleaner energy.
In this in-depth interview, Joscha Bach shares his insights into AI: what it illuminates about consciousness, how it will develop, and what it means for humanity.
Is AI our only chance at achieving real understanding?
With a free trial, you can watch our full archive of Joscha Bach’s talks and debates at https://iai.tv/home/speakers/joscha-b… Introduction 00:08 What is Artificial General Intelligence, and how far away are we from creating it? 01:08 Do you consider AI humanlike now? 02:43 Why do you defend a computational perspective? 03:44 Is AI the method for the universe to understand itself? 04:26 How is AI transforming society now, and how will it transform society in the next few years? 05:20 Do you think we have the capacity to reconceive how our institutions will function in light of these changes? 06:17 How could AI help us solve the climate crisis, when our biggest problem is inaction? 08:24 Have we become less critical, as a species? 10:40 Would you agree that social media has been detrimental to our society? 12:58 How do you think AGI will be realised? 18:46 What are the differences between evolved systems and designed systems? 20:31 What did you think of the infamous open letter about AI safety? 24:24 How can we solve AI’s misalignment to human values? 25:43 Do you have hope for the future? 27:33 Do you think it’s possible to build a machine that understands? 30:32 Do you think that we are living in base reality? Join cognitive scientist and AI researcher Joscha Bach in this exclusive interview on the limits, risks, and future of AI. From the potential of Artificial General Intelligence to the alignment problem and the fundamental ways AI learns differently from humans, Bach explores whether AI might one day grasp reality on a deeper level than we can. He also examines the systemic failures of institutions in tackling the climate crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, arguing that the internet’s potential for collective intelligence remains largely untapped. Might AI help us overcome these challenges, or does it merely reflect our own limitations? Interviewed by Darcy Bounsall. #ai #agi #artificialintelligence #artificialgeneralintelligence #consciousness #computerscience Joscha Bach is a cognitive scientist, AI researcher, and philosopher whose research aims to bridge cognitive science and AI by studying how human intelligence and consciousness can be modelled computationally. The Institute of Art and Ideas features videos and articles from cutting edge thinkers discussing the ideas that are shaping the world, from metaphysics to string theory, technology to democracy, aesthetics to genetics. Subscribe today! https://iai.tv/subscribe?utm_source=Y… For debates and talks: https://iai.tv For articles: https://iai.tv/articles For courses: https://iai.tv/iai-academy/courses.
00:00 Introduction.
00:08 What is Artificial General Intelligence, and how far away are we from creating it?
01:08 Do you consider AI humanlike now?
02:43 Why do you defend a computational perspective?
03:44 Is AI the method for the universe to understand itself?
04:26 How is AI transforming society now, and how will it transform society in the next few years?
05:20 Do you think we have the capacity to reconceive how our institutions will function in light of these changes?
06:17 How could AI help us solve the climate crisis, when our biggest problem is inaction?
08:24 Have we become less critical, as a species?
10:40 Would you agree that social media has been detrimental to our society?
12:58 How do you think AGI will be realised?
18:46 What are the differences between evolved systems and designed systems?
20:31 What did you think of the infamous open letter about AI safety?
24:24 How can we solve AI’s misalignment to human values?
25:43 Do you have hope for the future?
27:33 Do you think it’s possible to build a machine that understands?
30:32 Do you think that we are living in base reality?
Join cognitive scientist and AI researcher Joscha Bach in this exclusive interview on the limits, risks, and future of AI. From the potential of Artificial General Intelligence to the alignment problem and the fundamental ways AI learns differently from humans, Bach explores whether AI might one day grasp reality on a deeper level than we can. He also examines the systemic failures of institutions in tackling the climate crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, arguing that the internet’s potential for collective intelligence remains largely untapped. Might AI help us overcome these challenges, or does it merely reflect our own limitations?
Interviewed by Darcy Bounsall.