Finally, they may have a chance as we have seen the prediction of the phasing out of smartphones by 2021. Although not all will be phased out by then; the continue struggle of companies trying to play catch up with smartphones is not an ideal route to take anymore especially with technologies such as the AR Contacts with Bluetooth headsets, other things such as BMI technology, etc. it is smart to focus in the next 3 to 5 years on these technologies instead of playing catch up with Apple.
He says the company’s “pivot to software is taking hold”, pointing to the recent launch of BlackBerry Radar, an asset tracking system, and BlackBerry Hub+ for Android, a set of productivity apps.
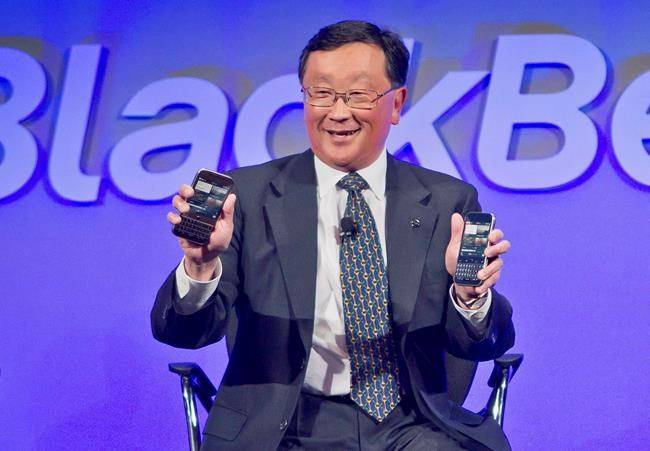
BlackBerry may not be designing its own smartphones anymore, but that doesn’t mean we won’t see new devices sporting the BlackBerry logo. The company plans to end all internal hardware development and will outsource that function to partners.
It’s been a long wait, but BlackBerry has decided pulled the plug on its ailing hardware business and will now focus on its software business instead. That’s if we can trust BlackBerry to ensure that future hardware partners maintain its high standards for design and build quality, of course.