Over 70,000 jobs will be created through the rising battery manufacturing in Europe within the next years, new studies predict.
The energy supply in Germany and Europe has never been more in flux. As the success of renewable energies continues to mount, another technology is coming into focus. Energy storage technologies and battery storage systems in particular are becoming increasingly important with the advancement of the energy transition. This development also has significant implications for Germany as an economic center, since battery production is expected to create thousands of jobs here in the future.
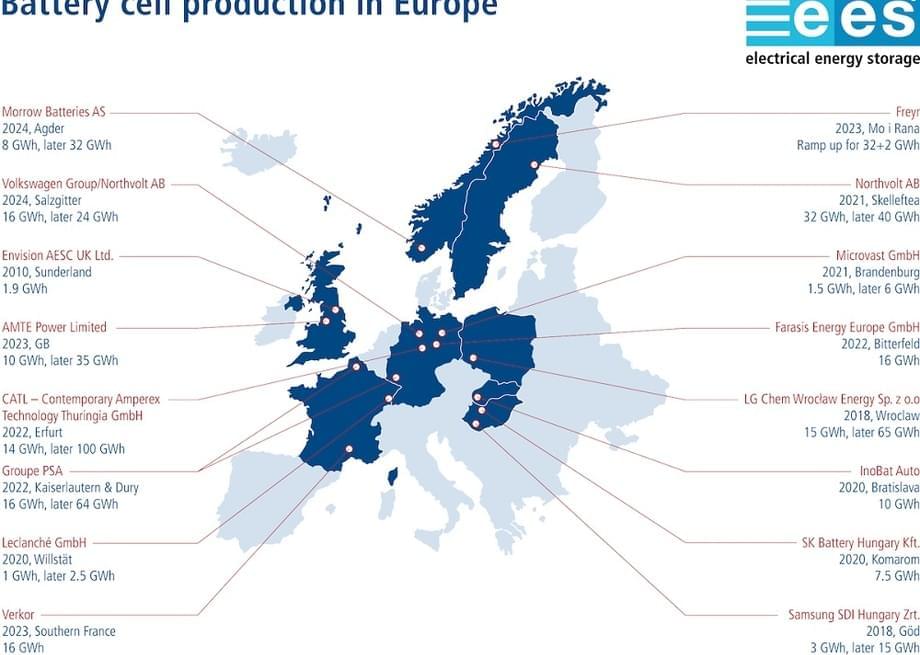
Europe has not traditionally played a very significant role as a site for battery cell production, but technical advances, favorable political conditions and an especially promising sales market are making the continent increasingly attractive for battery production. A look at the key role that battery cell production plays in upstream value chains – throughout the renewable energy supply sector and especially in the manufacture of electric vehicles – makes its significance clear. Battery cells represent approximately 40 percent of the value added in the production of an electric vehicle. So it is no wonder that production capacities for lithium-ion batteries are growing faster in Europe than in any other region of the world. Current forecasts predict that the continent’s share in this global manufacturing business will increase from around 6 percent now to 16 to 25 percent by 2030.
Numerous battery cell manufacturing plants are currently being built in Europe. According to Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, Europe is expected to host manufacturing facilities capable of producing more than 300 gigawatt hours (GWh) of battery capacity by 2029. The meta-study “Batteries for electric cars: Fact check and need for action,” commissioned by VDMA and carried out by Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI, even suggests that production capacities of 300 to 400 GWh could be achieved by 2025. The website Battery-News.de anticipates that the German market alone will account for more than 170 GWh of production capacity. By way of comparison, Europe currently has around 30 GWh of production capacity.