🤔🧐🤷♂️🤦♂️
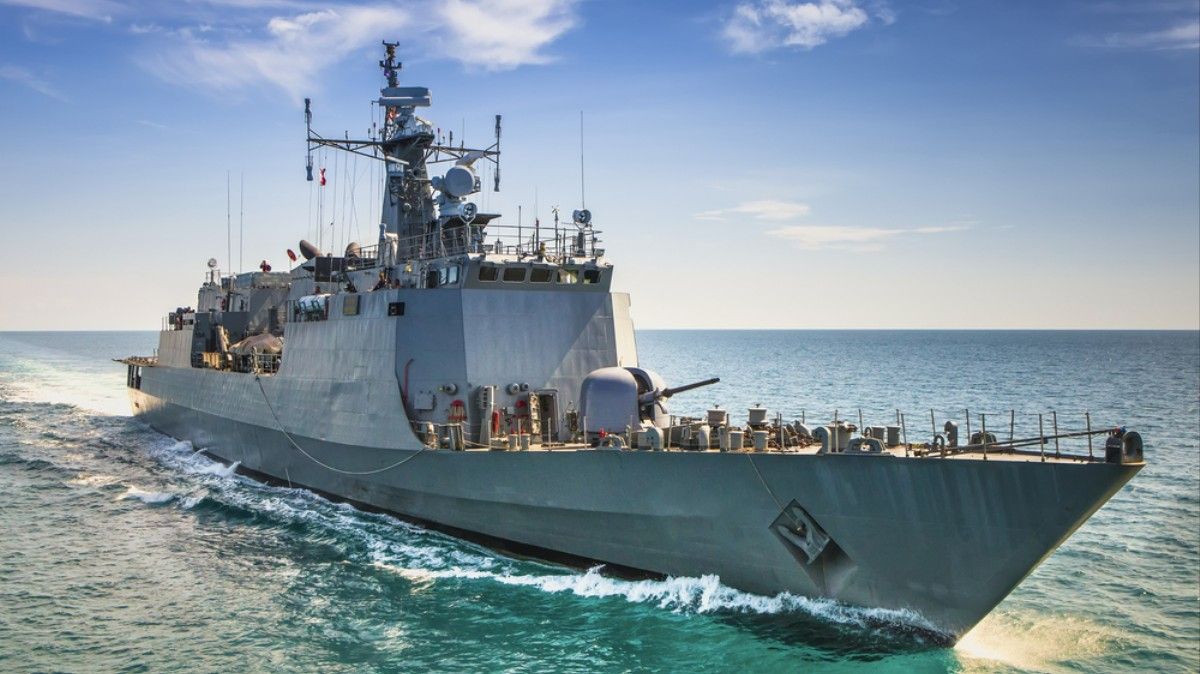
The effort is part of a $45 million program across all the branches of the armed forces to figure out military applications for genetic engineering.
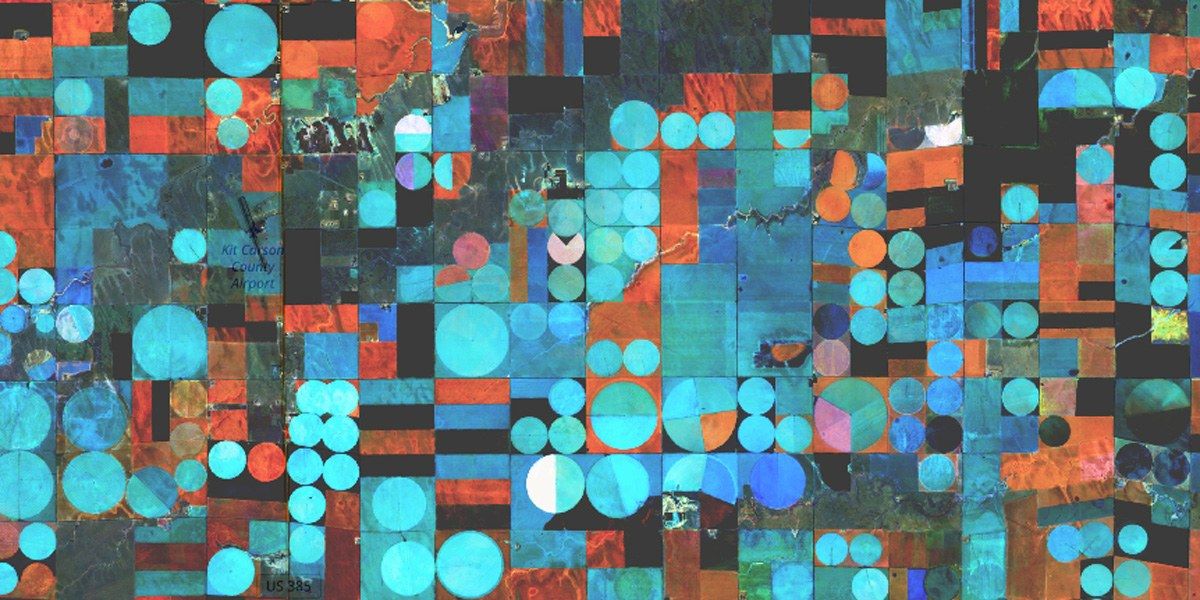


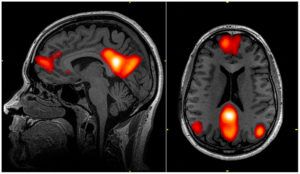

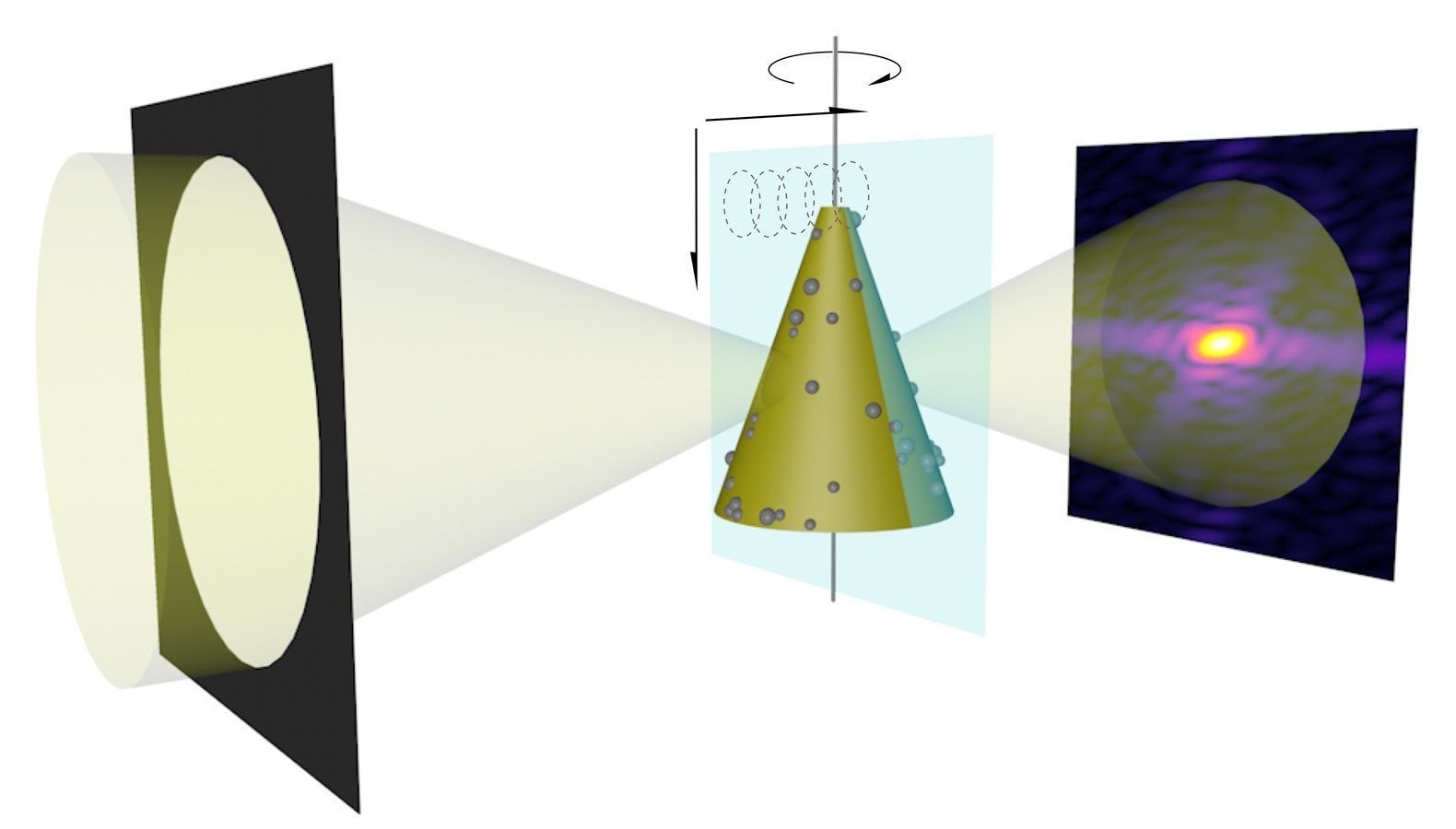
A longstanding problem in optics holds that an improved resolution in imaging is offset by a loss in the depth of focus. Now, scientists are joining computation with X-ray imaging as they develop a new and exciting technique to bypass this limitation.
The upcoming Advanced Photon Source Upgrade (APS-U) project at Argonne will put this problem under one of the brightest spotlights imaginable. The upgrade will make the APS, a Department of Energy Office of Science User Facility, 500 times brighter than it is today, further enhancing the capabilities of its X-rays to study the arrangements of atoms and molecules in a wide range of biological and technological materials.
“A whole variety of X-ray imaging experiments ultimately will need something like this as they all push the resolution to finer length scales in the future,” said Chris Jacobsen, an Argonne Distinguished Fellow and professor of physics at Northwestern University. With the Upgrade in place, the APS’s X-rays could allow scientists to study systems like the brain’s full network of synaptic connections, or the entire volume of an integrated circuit down to its finest details.

Advancement in technology will continue to impact the way we work, eat, and even take care of ourselves. A new report from Scientific American takes a look at some of the top emerging technologies that range from the field of biology to computer science. The publication’s chief science editor Seth Fletcher talked to Cheddar about what’s next when it comes to tech.
WATCH NEXT
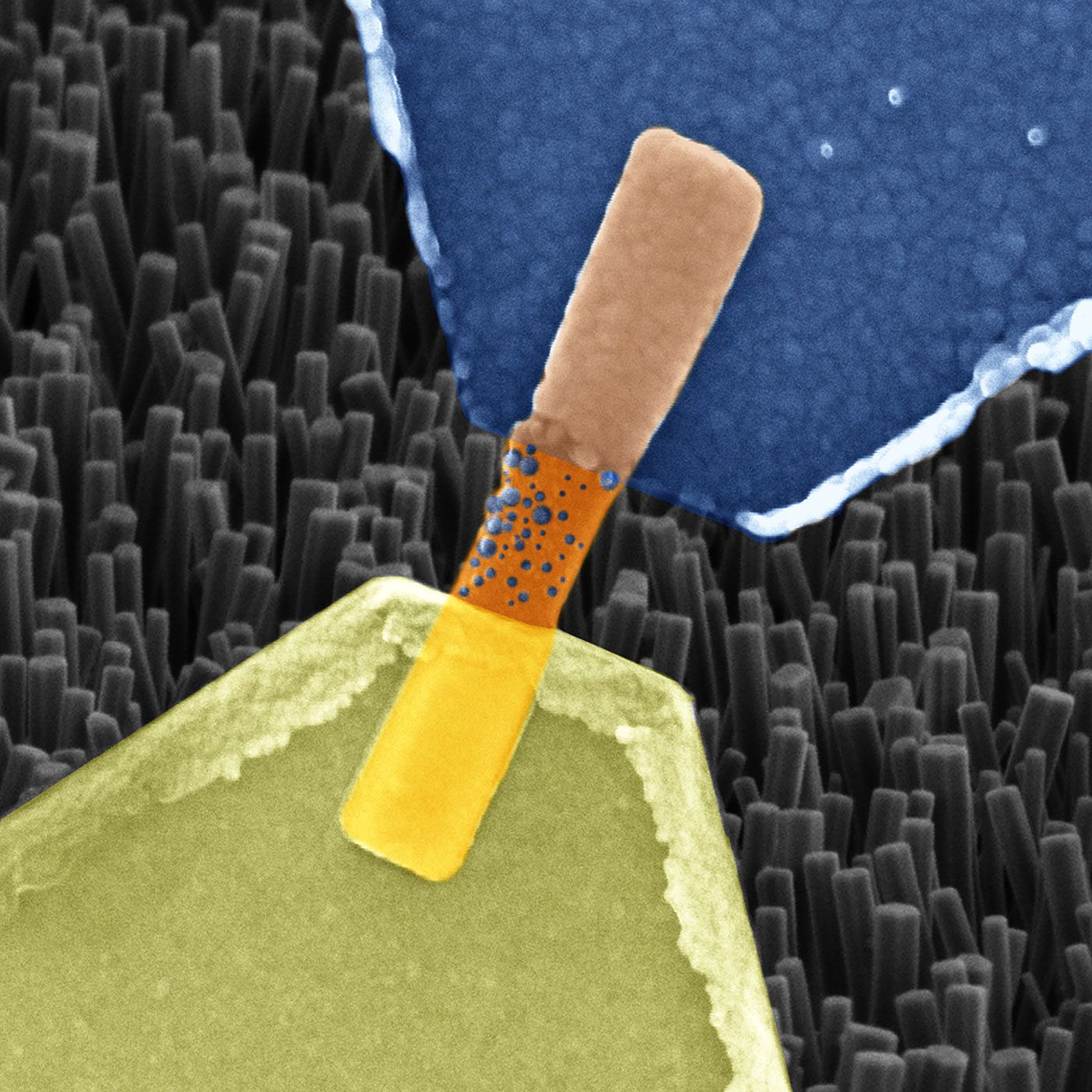
Scientists from Jülich together with colleagues from Aachen and Turin have produced a memristive element made from nanowires that functions in much the same way as a biological nerve cell. The component is able to save and process information, as well as receive numerous signals in parallel. The resistive switching cell made from oxide crystal nanowires is thus an ideal candidate for use in building bioinspired “neuromorphic” processors, able to take over the diverse functions of biological synapses and neurons.
That was pretty interesting…
Presented December 4th 2018 by Prof. Michael Levin (Allen Discovery Center at Tufts University)
Michael Levin
Vannevar Bush Professor
Director, Allen Discovery Center at Tufts.
Director, Tufts Center for Regenerative and Developmental Biology.
Morphological and behavioral information processing in living systems.
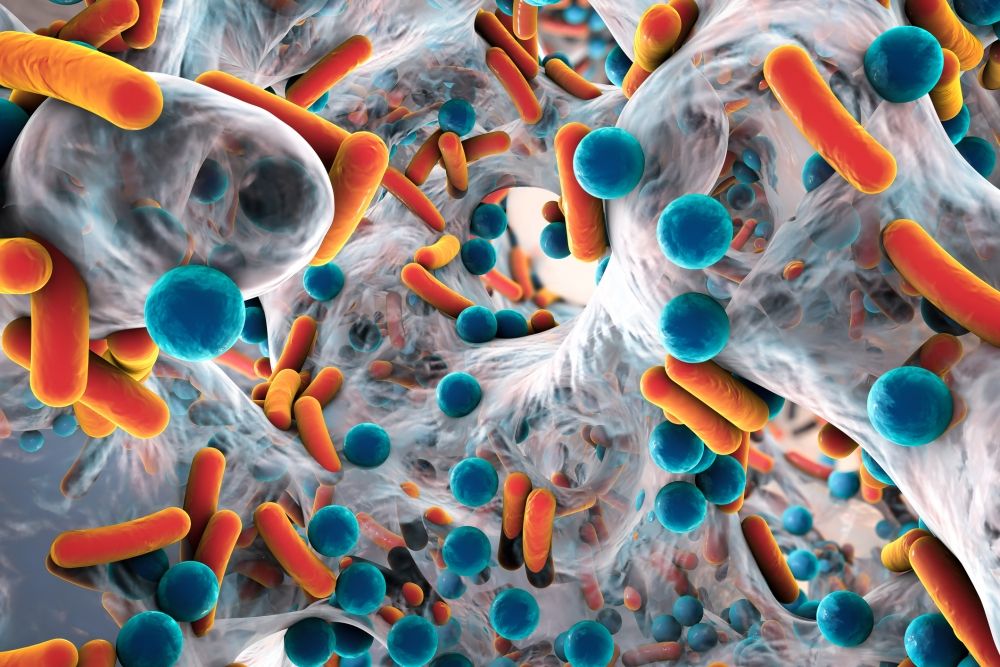
What the study shows, the researchers said, is that the interactions between the bacterial populations are as significant to the host’s overall fitness as their presence — the microbiome’s influence cannot be solely attributed to the presence or absence of individual species. “In a sense,” said Jones, “the microbiome’s influence on the host is more than the sum of its parts.”
The gut microbiome — the world of microbes that inhabit the human intestinal tract — has captured the interest of scientists and clinicians for its critical role in health. However, parsing which of those microbes are responsible for effects on our wellbeing remains a mystery.
Taking us one step closer to solving this puzzle, UC Santa Barbara physicists Eric Jones and Jean Carlson have developed a mathematical approach to analyze and model interactions between gut bacteria in fruit flies. This method could lead to a more sophisticated understanding of the complex interactions between human gut microbes.
Their finding appear in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
What would it be like to live through our own species’ evolution? The biological process of natural selection that gave rise to every species on Earth takes hundreds of generations to turn one species into another, but what if that process could be skipped entirely?
A look at the future of transhumanist technologies and what their evolution will mean for our society.