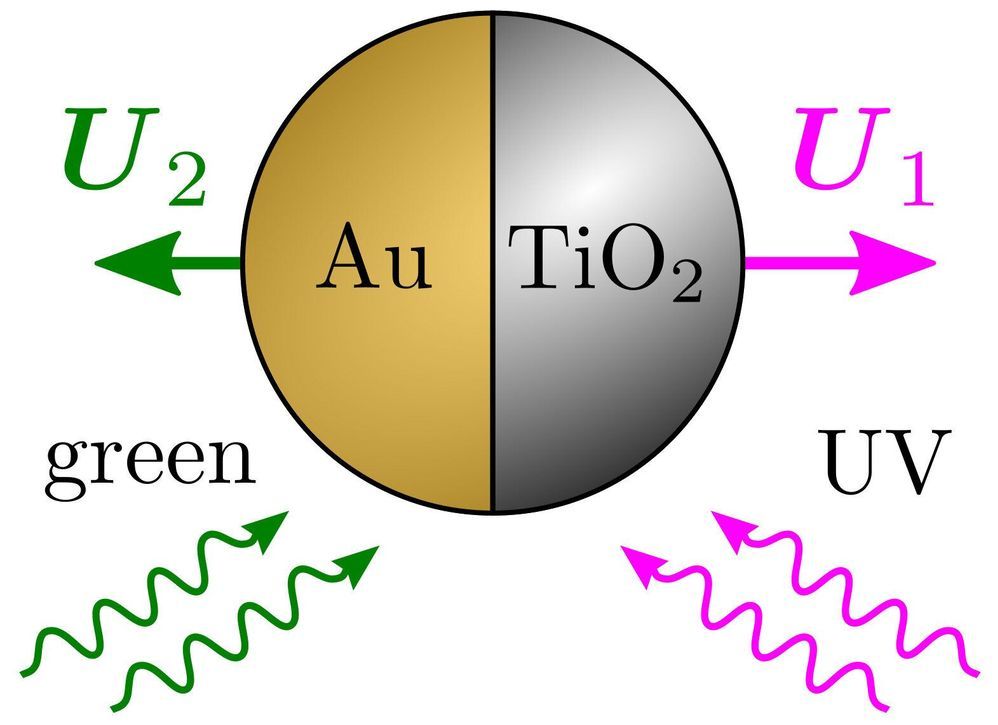
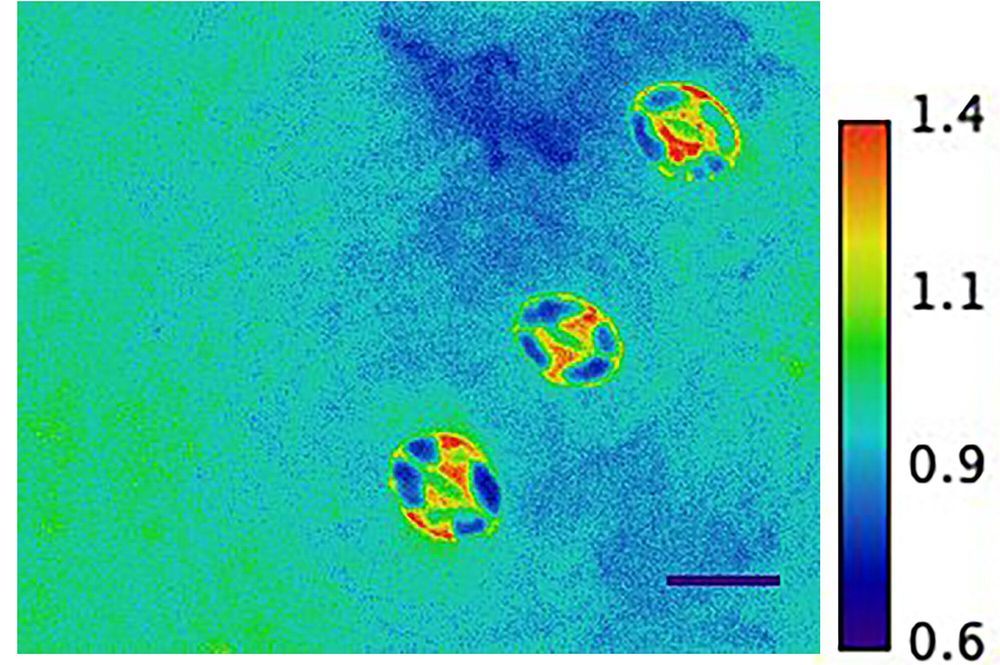
Researchers from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, ETH in Zurich and the University of Cambridge have synthesized and analysed active microparticles self-propelling in a fluid and reversing their propulsion direction depending on the wavelength of illuminating light. A research article summarising their work has recently been published in Nature Communications.
Active matter encompasses systems with self-propelling elements that draw energy from the environment and convert it into kinetic energy. This is currently a lively discipline in physics, spanning across many time and length scales, concerning, e.g., the behaviour of birds in flocks (such as murmurations of starlings), schools of fish (as a form of protection against predators), and also bacteria in biofilms and other aquatic microswimmers. It focuses both on the behaviour of individual elements and understanding their mechanisms of energy conversion, interaction and coupling with the environment so important for the survival, and on the collective effects and emergence of new phenomena in large populations. Both can be successfully described on different levels of precision, starting from simplistic minimal coarse-grained models, and up to refined numerical simulations.
Bacteria, algae, spermatozoa, ciliates and other unicellular organisms are an important group of active swimmers. Exploring the physical basis of their dynamics is often complicated by their immense diversity, biological complexity, and high sensitivity to external conditions. The aquatic microworld is, however, governed by the universal laws of fluid dynamics, which put limitations on all organisms.