Future leather…may be made from fungus! Cool! 😃
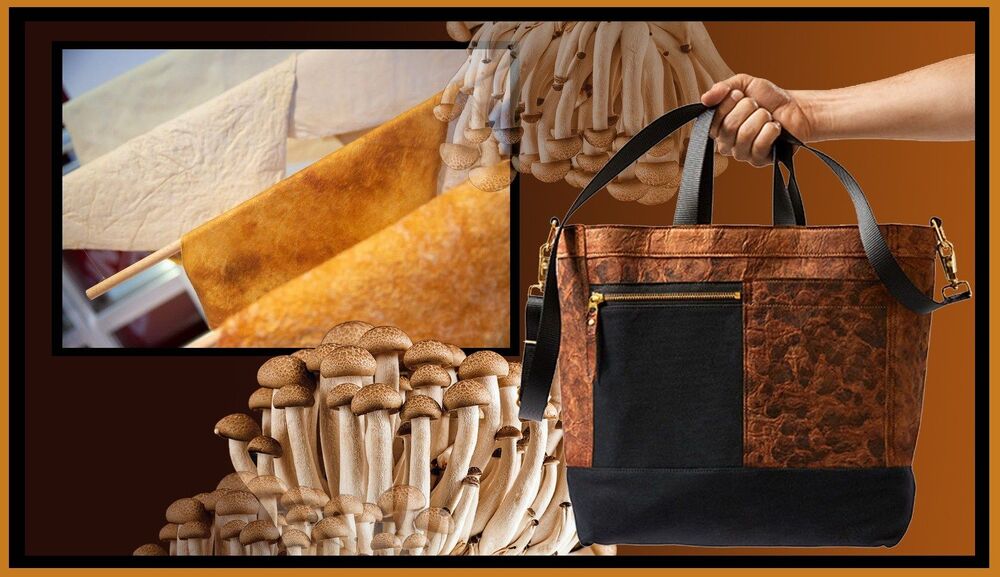
Around five years ago, US companies MycoWorks and Ecovative invented and patented fungus-derived leather technologies. These technologies use the mushroom’s root-like structure, known as mycelium. When mycelium is grown on agricultural waste or sawdust, they produce a thick mat that can be treated to look like leather.
This natural biological process can be conducted anywhere since the roots are used and not the mushrooms. The process doesn’t need light; it turns waste into something useful and stores carbon by collecting it in the growing fungus.
Making fungi leather (or mycelium leather) is an overall significantly quicker process than traditional leather. It takes years to raise a cow to maturity, while going from a single spore to a finished fungi leather takes weeks.