From the discovery of microorganisms in the field of biology to imaging atoms in the field of physics, microscopic imaging has improved our understanding of the world and has been responsible for many scientific advances. Now, with the advent of spintronics and miniature magnetic devices, there is a growing need for imaging at nanometer scales to detect quantum properties of matter, such as electron spins, magnetic domain structure in ferromagnets, and magnetic vortices in superconductors.
Typically, this is done by complementing standard microscopy techniques, such as scanning tunneling microscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM), with magnetic sensors to create “scanning magnetometry probes” that can achieve nanoscale imaging and sensing. However, these probes often require ultrahigh vacuum conditions, extremely low temperatures, and are limited in spatial resolution by the probe size.
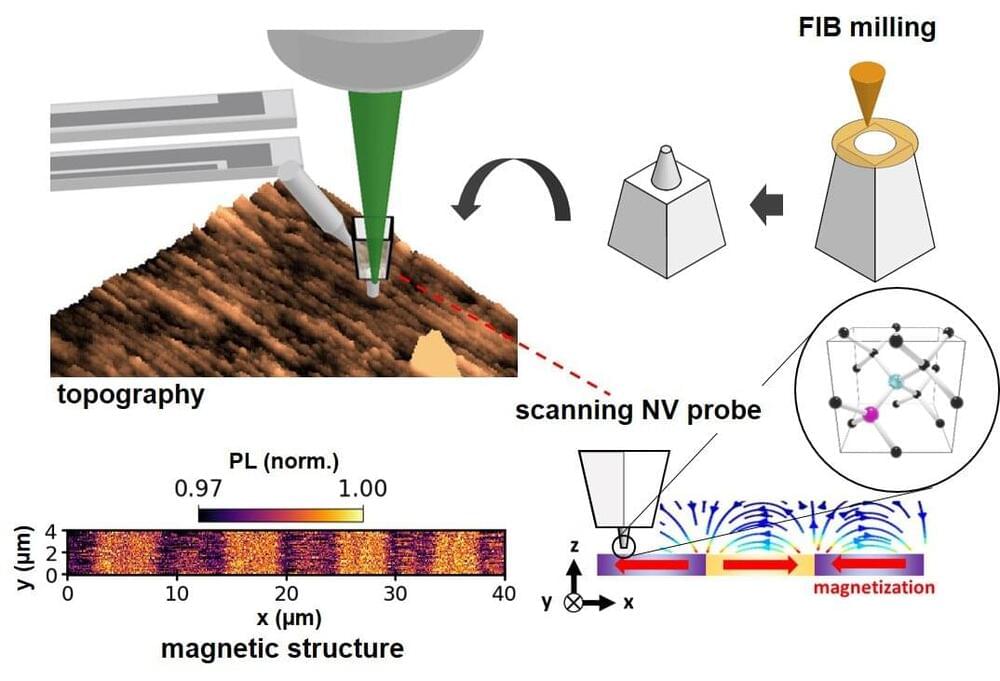
In this regard, nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamond (defects in diamond structure formed by nitrogen atoms adjacent to “vacancies” created by missing atoms) have gained significant interest. The NV pair, it turns out, can be combined with AFM to accomplish local magnetic imaging and can operate at room temperature and pressures. However, fabricating these probes involve complex techniques that do not allow for much control over the probe shape and size.