Roger McNamee, Elevation Partners co-founder, joins ‘Money Movers’ to discuss tech’s bull run and the ongoing AI race.




Recent advances suggest the technology is hitting its stride. The UC Davis team’s speech synthesis system represents a fundamental shift from previous approaches. Rather than translating brain signals into text and then synthesizing speech — a process that created significant delays — UC Davis’ system converts thoughts directly into sounds with near-instantaneous 10-millisecond latency.
H2]:text-3xl pb-8
Meanwhile, researchers at Carnegie Mellon achieved real-time control of individual robotic fingers using non-invasive EEG technology, wearing a cap that reads brain signals through the skull. This suggests that future brain interfaces might not require surgery at all for certain applications.
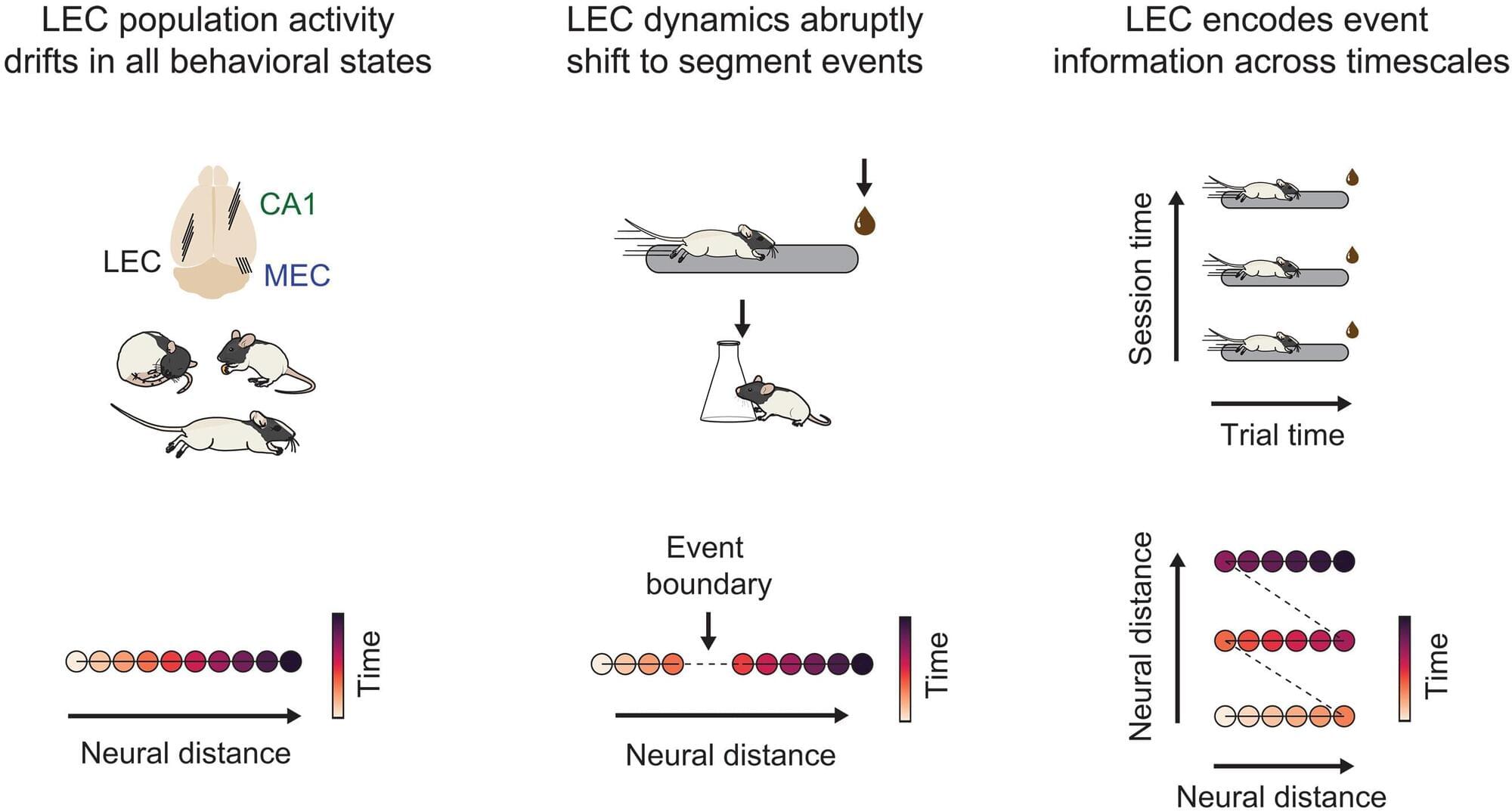
The brain doesn’t merely register time—it structures it, according to new research from the Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience published in Science.
The research team led by NTNU’s Nobel Laureates May-Britt and Edvard Moser, from the Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience, is already known for their discovery of the brain’s sense of place.
Now they have shown that the brain also weaves a tapestry of time: The brain segments and organizes events into experiences, placing unique bookmarks on them so that our lives don’t become a blurry stream, but rather a series of meaningful moments and memories we can revisit and learn from.
Tokyo researchers create 6-DoF hand-control system using gestures and motion tracking for precise drone operation in complex spaces.

A research team led by Prof. Li Hai from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel deep learning framework that significantly improves the accuracy and interpretability of detecting neurological disorders through speech. The findings were recently published in Neurocomputing.
“A slight change in the way we speak might be more than just a slip of the tongue—it could be a warning sign from the brain,” said Prof. Hai, who led the team. “Our new model can detect early symptoms of neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Wilson disease, by analyzing voice recordings.”
Dysarthria is a common early symptom of various neurological disorders. Since speech abnormalities often reflect underlying neurodegenerative processes, voice signals have emerged as promising noninvasive biomarkers for the early screening and continuous monitoring of such conditions.
By Heidi Hausse & Peden Jones/The ConversationTo think about an artificial limb is to think about a person.


What if a city’s mood could be mapped like weather? Researchers at the University of Missouri are using AI to do exactly that—by analyzing geotagged Instagram posts and pairing them with Google Street View images, they’re building emotional maps of urban spaces.
These “sentiment maps” reveal how people feel in specific locations, helping city planners design areas that not only function better but also feel better. With potential applications ranging from safety to disaster response, this human-centered tech could soon become part of the city’s real-time dashboard.
Human-Centric City Vision