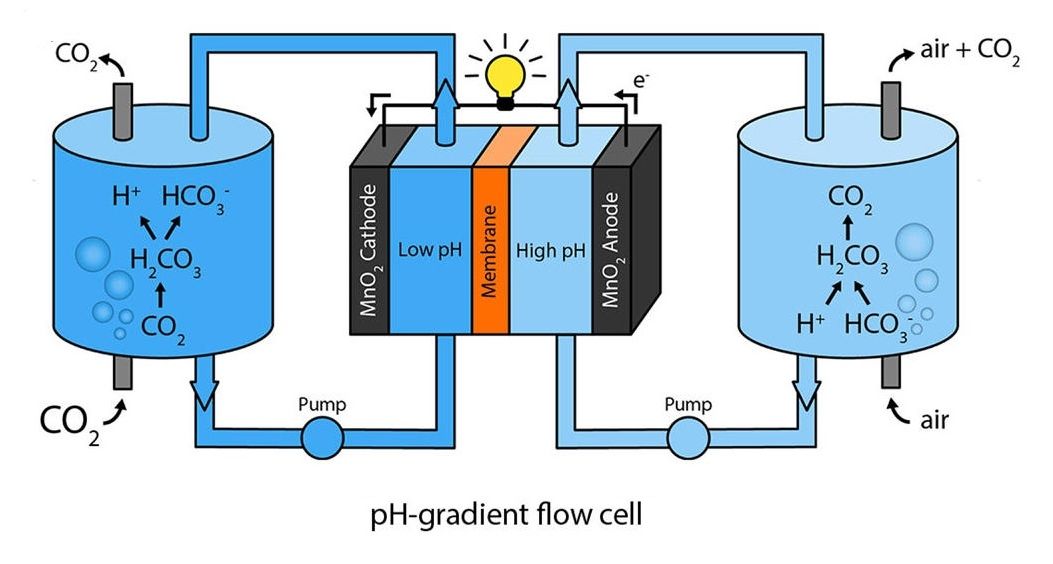
(Phys.org)—Researchers have developed a type of rechargeable battery called a flow cell that can be recharged with a water-based solution containing dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2) emitted from fossil fuel power plants. The device works by taking advantage of the CO2 concentration difference between CO2 emissions and ambient air, which can ultimately be used to generate electricity.
The new flow cell produces an average power density of 0.82 W/m, which is almost 200 times higher than values obtained using previous similar methods. Although it is not yet clear whether the process could be economically viable on a large scale, the early results appear promising and could be further improved with future research.
The scientists, Taeyong Kim, Bruce E. Logan, and Christopher A. Gorski at The Pennsylvania State University, have published a paper on the new method of CO2-to-electricity conversion in a recent issue of Environmental Science & Technology Letters.