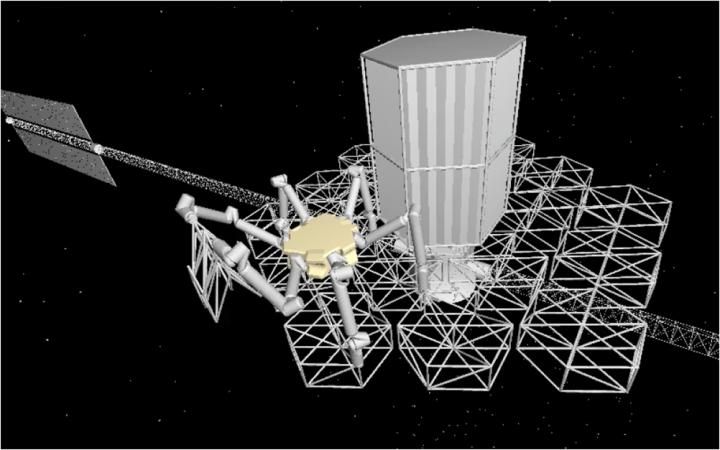
Enhancing astronomers’ ability to peer ever more deeply into the cosmos may hinge on developing larger space-based telescopes. A new concept in space telescope design makes use of a modular structure and an assembly robot to build an extremely large telescope in space, performing tasks in which astronaut fatigue would be a problem.
The robotically assembled modular space telescope (RAMST) design is described by Nicolas Lee and his colleagues at the California Institute of Technology and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in an article published this week by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics, in the Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems (JATIS).
Ground-based telescopes are limited by atmospheric effects and by their fixed location on the Earth.