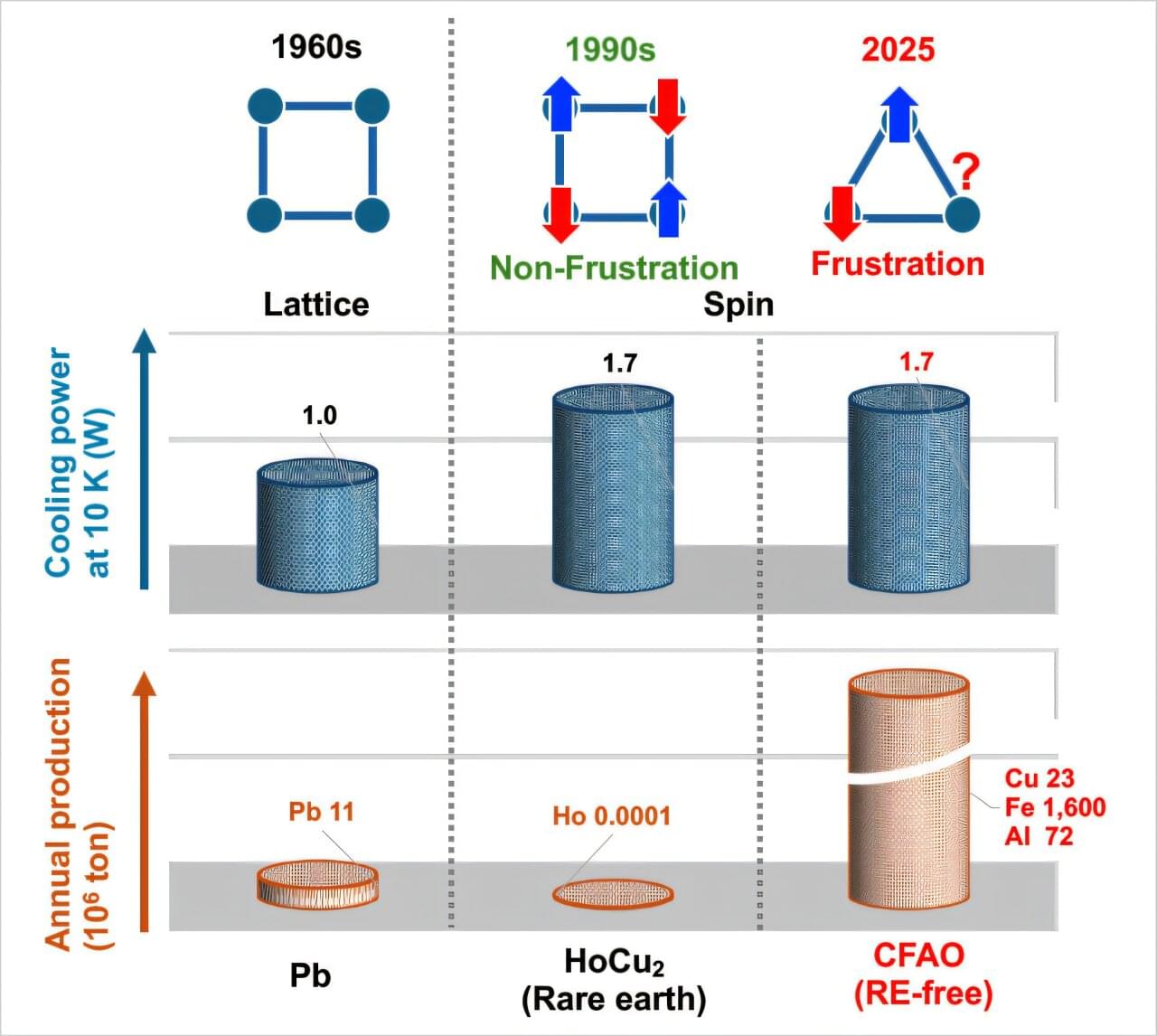
In collaboration with the National Institute of Technology (KOSEN), Oshima College, the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS) succeeded in developing a new regenerator material composed solely of abundant elements, such as copper, iron, and aluminum, that can achieve cryogenic temperatures (approx. 4K = −269°C or below) without using any rare-earth metals or liquid helium.
By utilizing a special property called “frustration” found in some magnetic materials, where the spins cannot simultaneously satisfy each other’s orientations in a triangular lattice, the team demonstrated a novel method that replaces the conventional rare-earth-dependent cryogenic cooling technology.
The developed material holds promise for responding to the lack of liquid helium as well as for stable cooling in medical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and quantum computers, which are expected to see further growth in demand. The results are published in Scientific Reports.