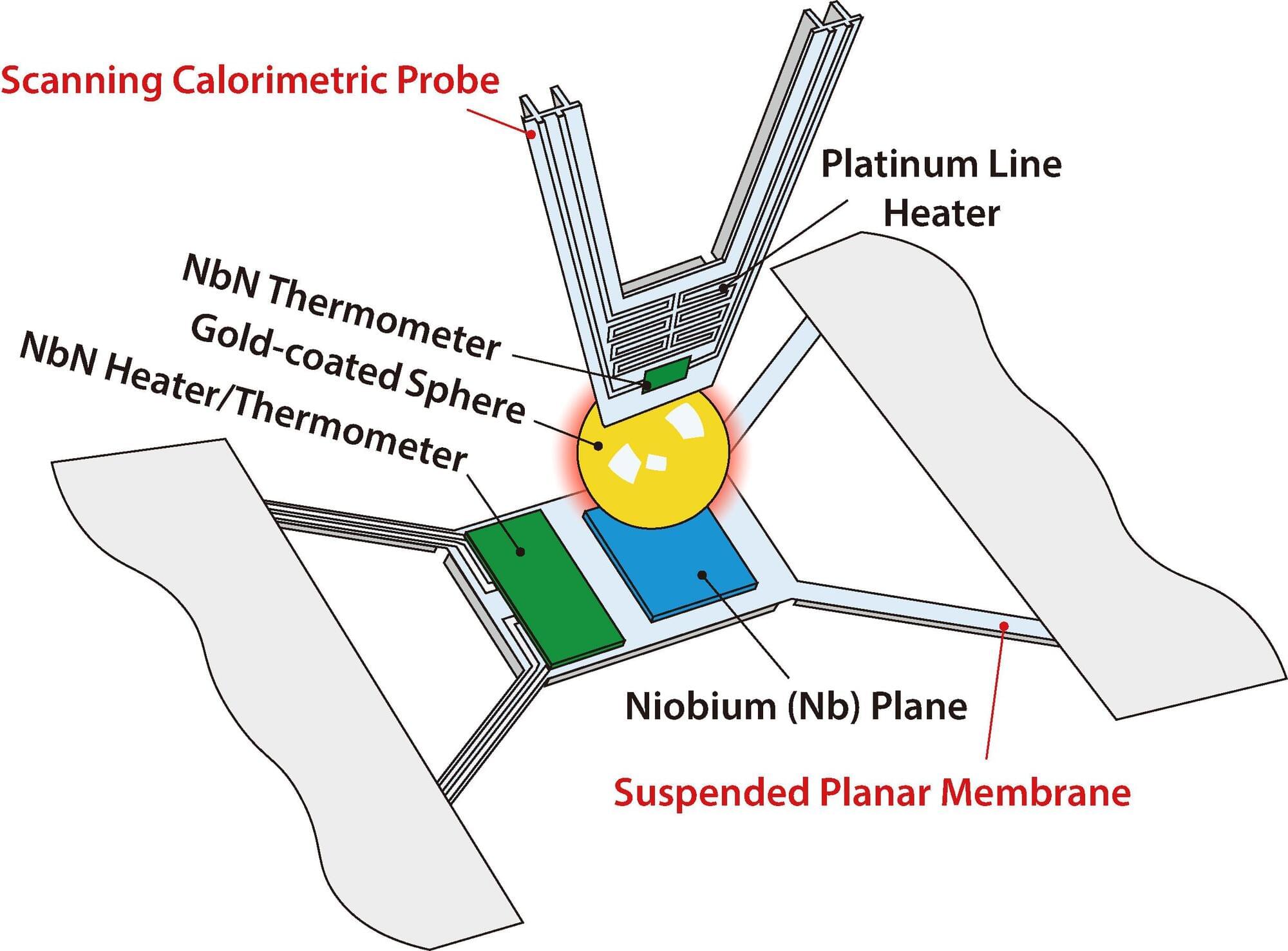
When cooled to its superconducting state, niobium blocks the radiative flow of heat 20 times better than when in its metallic state, according to a study led by a University of Michigan Engineering team. The experiment marks the first use of superconductivity—a quantum property characterized by zero electrical resistance—to control thermal radiation at the nanoscale.
Leveraging this effect, the researchers also experimentally demonstrated a cryogenic thermal diode that rectifies the flow of heat (i.e., the heat flow exhibits a directional preference) by as much as 70%.
“This work is exciting because it experimentally shows, for the very first time, how nanoscale heat transfer can be tuned by superconductors with potential applications for quantum computing,” said Pramod Sangi Reddy, a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and engineering at U-M and co-corresponding author of the study published in Nature Nanotechnology.