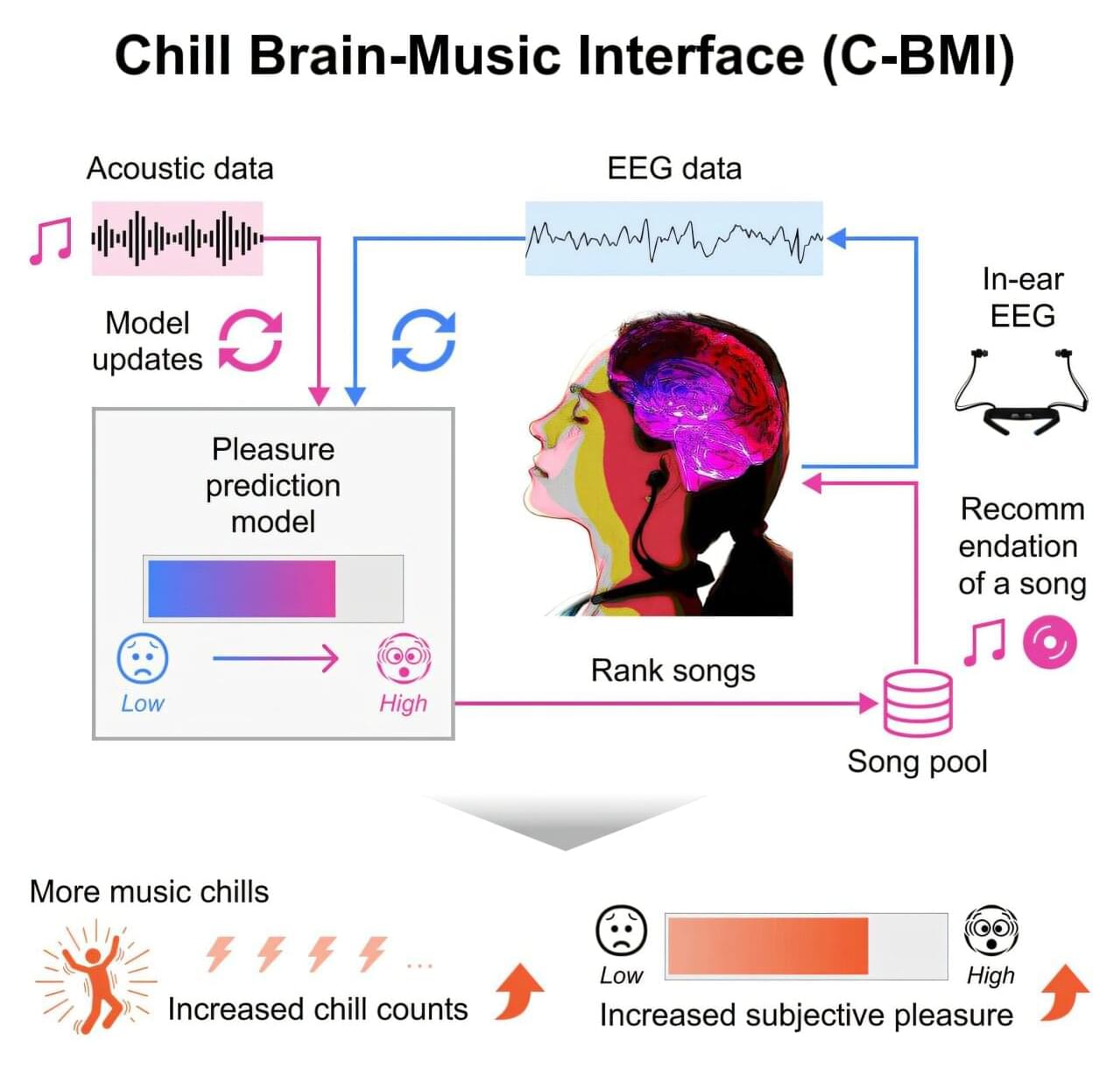
Musical chills are pleasurable shivers or goosebump sensations that people feel when they resonate with the music they’re listening to. They reduce stress and have beneficial side effects, but they are difficult to induce reliably. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a practical system that uses in-ear electroencephalography sensors to measure the brain’s response to music in real time and provide music suggestions that enhance chills.
Most people are familiar with “musical chills”—a sudden, involuntary shiver or goosebump sensation that occurs when a song resonates perfectly with one’s emotions. These chills are not just a surface-level feeling, but a profound neurological event. When we experience intense musical pleasure, parts of the brain’s reward system activate in a manner similar to how they would respond to life-affirming stimuli, such as beloved foods or positive social connections.
However, despite the universal nature of the experience, musical chills are difficult to trigger reliably. This limits our ability to harness their psychological and physiological benefits, even with today’s on-demand access to vast libraries of music.